Replicated multi-channel sensors for decucing ink thicknesses in color printing devices
a color printing device and multi-channel sensor technology, applied in the field of color printing, can solve the problems of not always providing a correct mapping between sensor input variables and ink dot size output variables, and the control of ink aperture is not precisely adapted to the current operating conditions of the press, and achieves the effect of high color accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
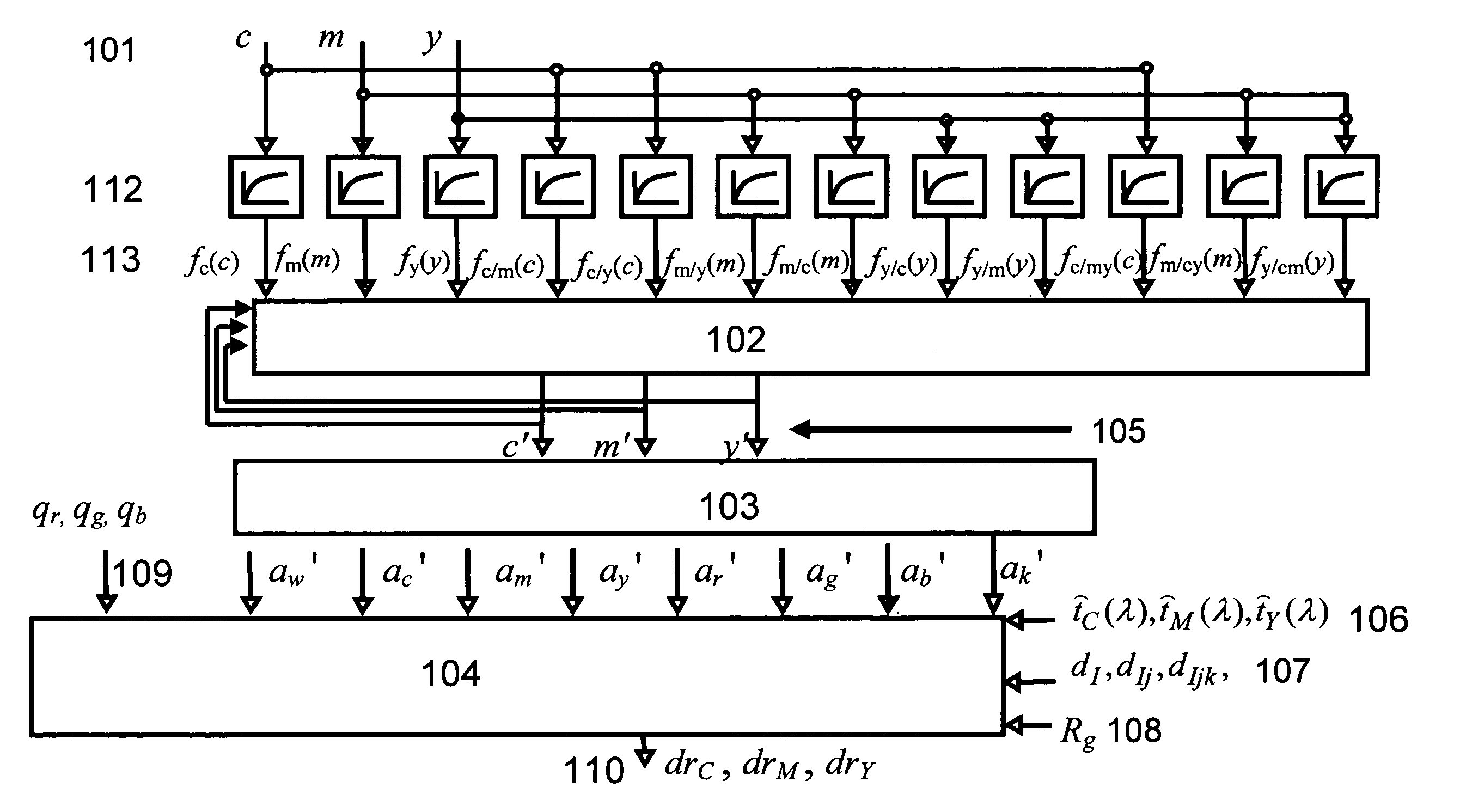
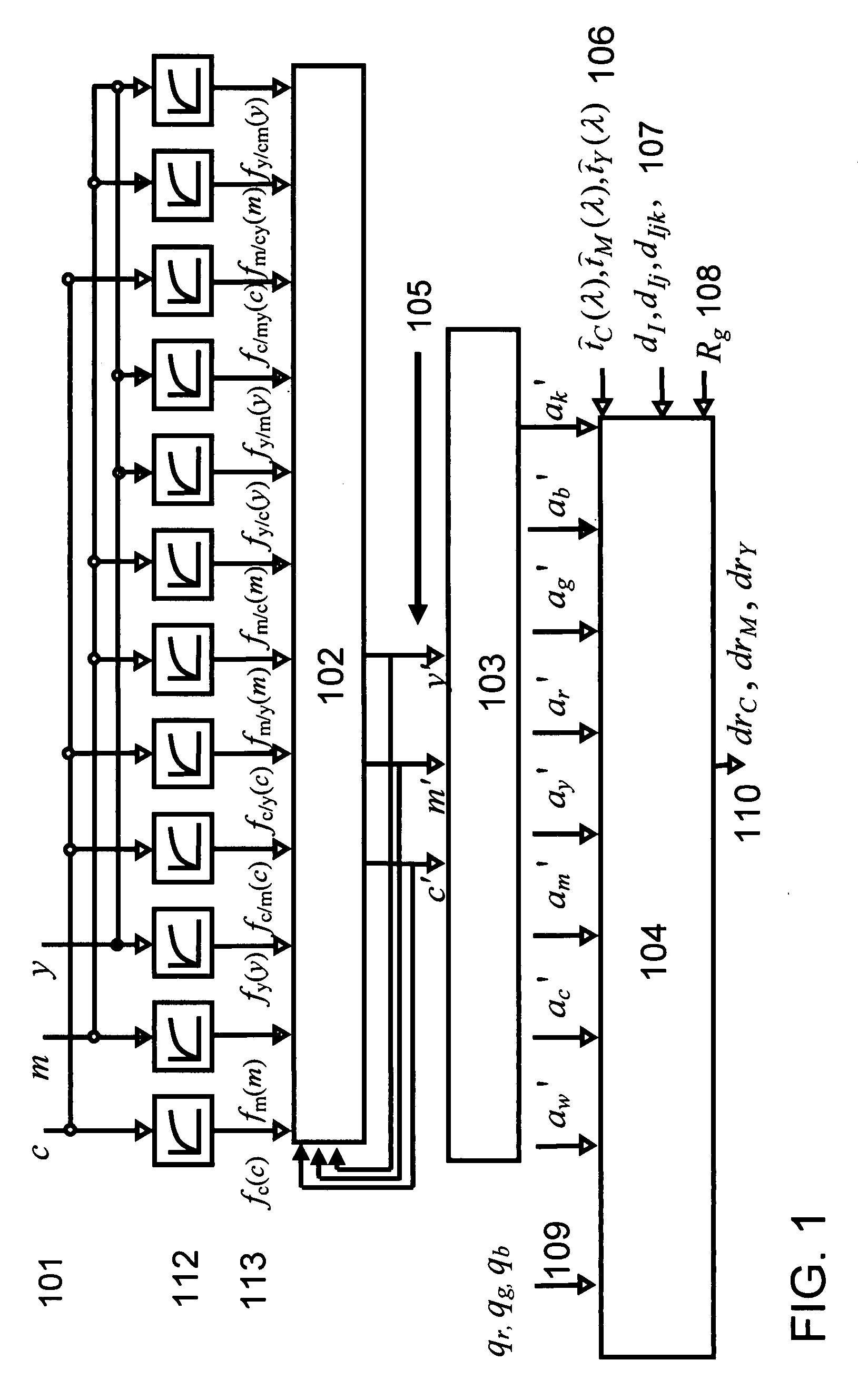
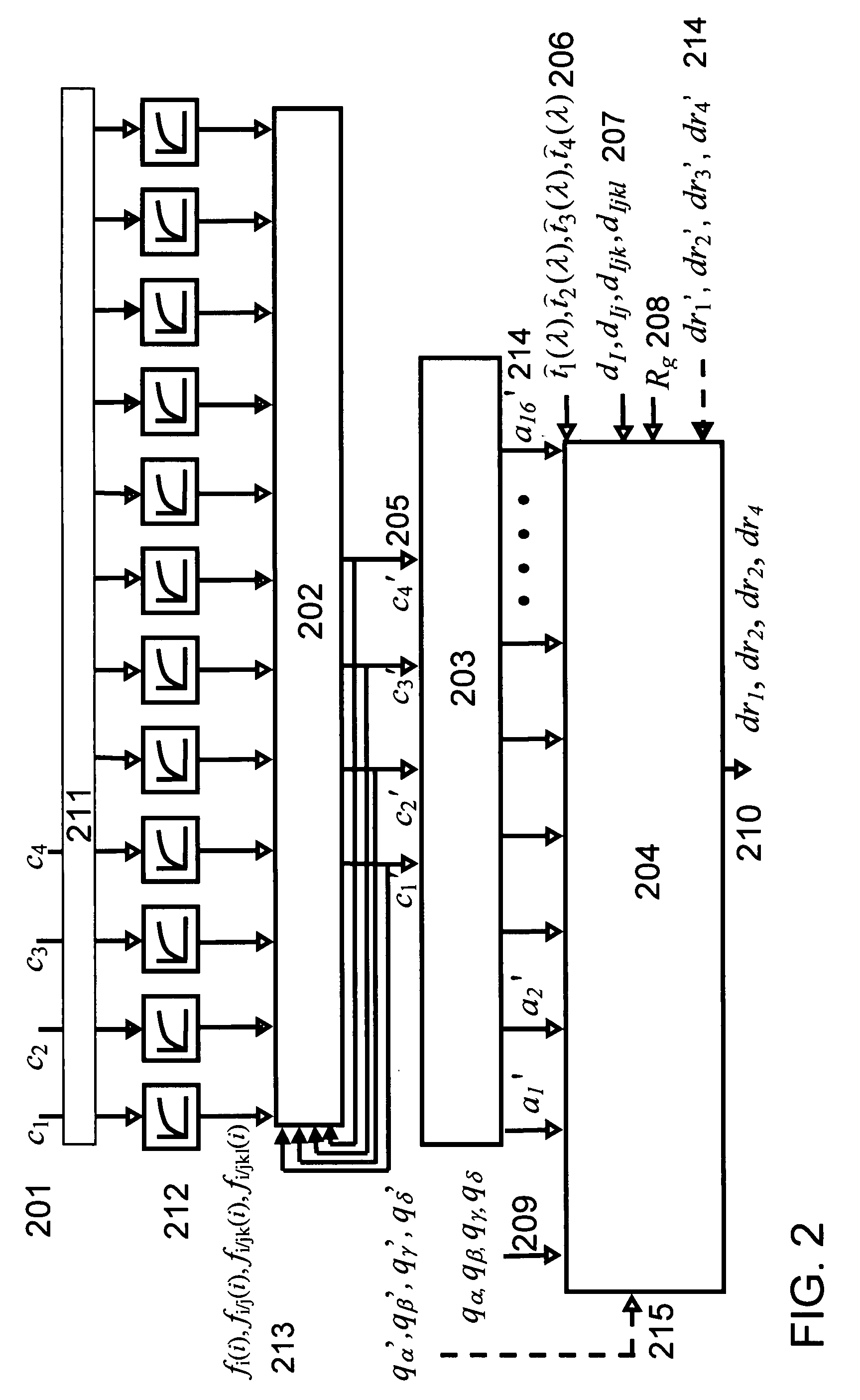
[0039] The present invention proposes models, a computing system as well as methods for deducing ink thickness variations from sensor responses obtained on a printer or printing press, online and in real-time. The computed ink thickness variations enable controlling the ink deposition and therefore the color accuracy, in the case of high-speed printing presses, of network printers and desktop printers. The ink thickness variations can be directly used for the real-time control of the print actuation parameters which influence the ink deposition, such as the ink feed in the case of an offset press.
[0040] The proposed method and computing system rely on a spectral prediction model incorporating as input parameters the responses from multi-channel sensors, as internal parameters the ink thicknesses and as output parameters ink thickness variation factors. Hereinafter, such a model is called “thickness variation and sensor response enhanced spectral prediction model”. Ink thickness var...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com