Multi-layered film window system
a film window system and multi-layer technology, applied in the field of energy-efficient windows, can solve the problems of preventing the application of curtain-wall covers, difficult to construct such covers to be weather-tight, reliable, movable, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing solar gain and promoting solar heating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
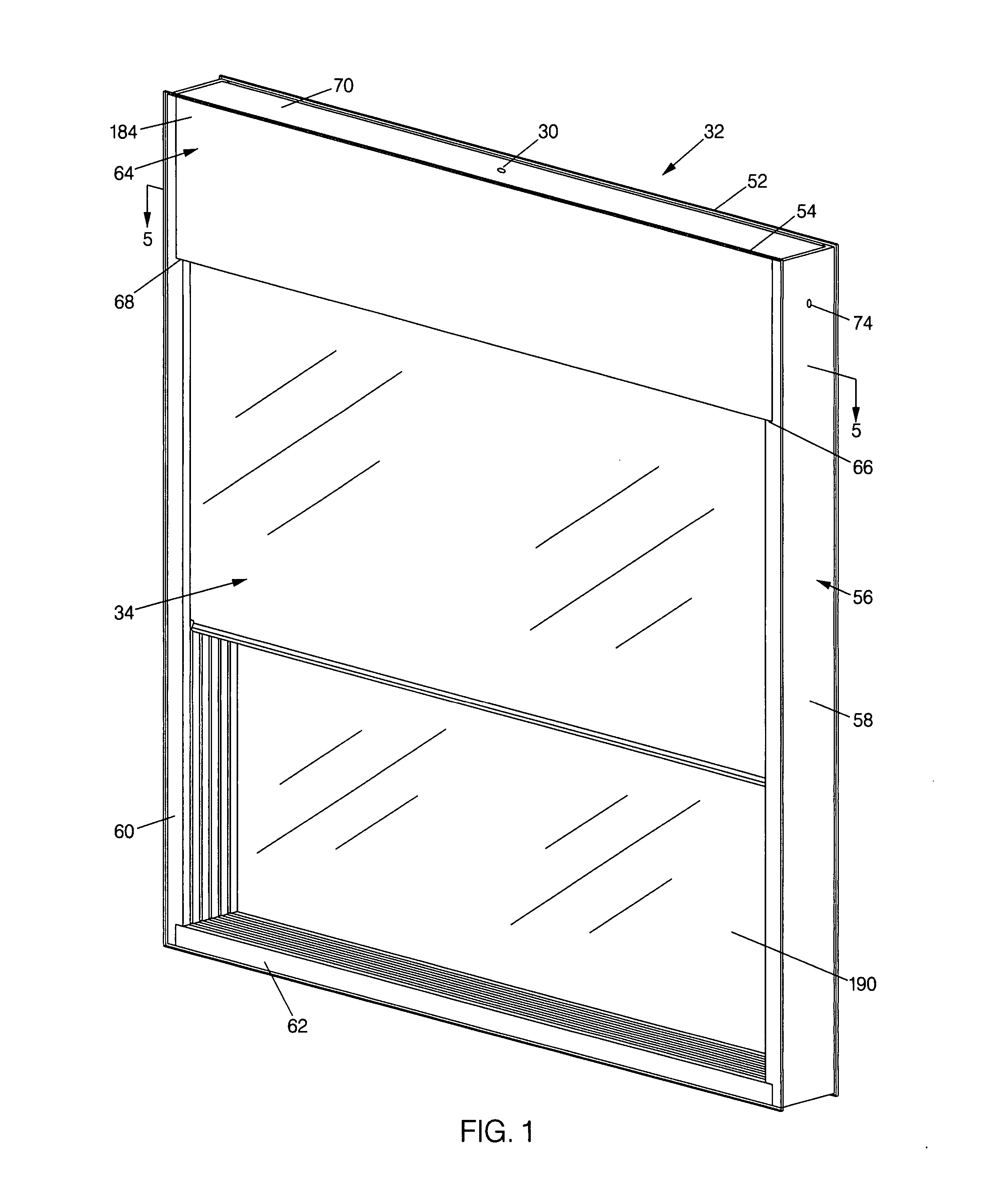
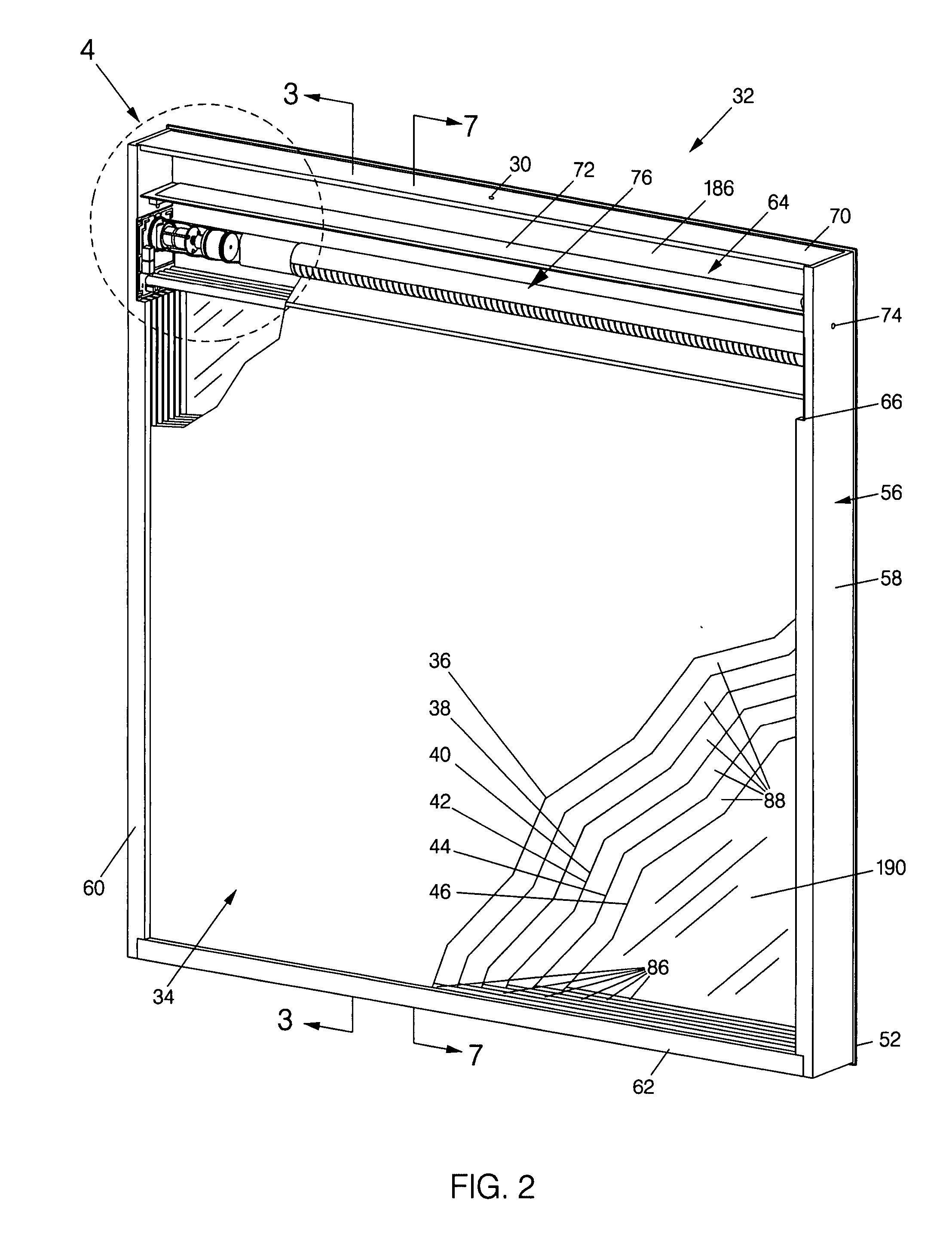
[0059] As generally noted above, the invention seeks to provide a sealed, glazed window assembly 32 having two layers of glass 52 and 54 or other suitably transparent material separated by several intermediate film layers 36-46. The assembly 32 is designed to demonstrate an insulation R-value on the order of a frame wall (e.g. R18 to R20). In contrast, a typical frame wall R-value of 19 is achieved with fiberglass bats fitted in a 6″ solid, opaque framed wall.
[0060] The significance of the capabilities of the assembly 32 can be appreciated upon consideration of the applicable physics relating to multi-layered glazed assemblies and available multi-layered windows. The physics of the assembly 32 derives from basic considerations that glass is transparent in the visible spectrum and a layer of glazing transmits approximately 95% of incident sunlight. A single layer of glass, which has a through-glass resistance of about 0.02 hrft2F / BTU has a measured R-value of about 1.0 hrft2F / BTU. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com