Refrigerant cycle device with ejector
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
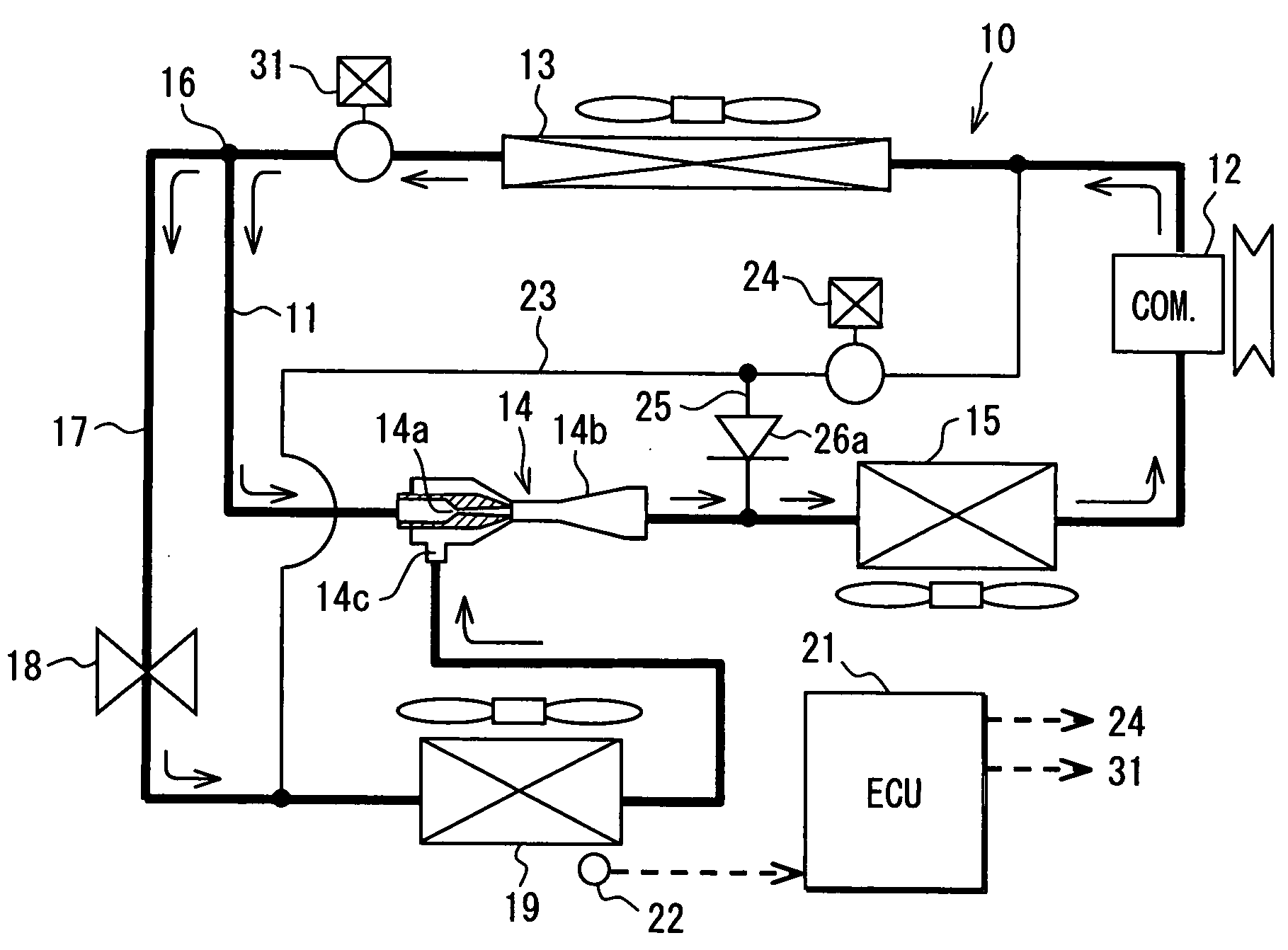
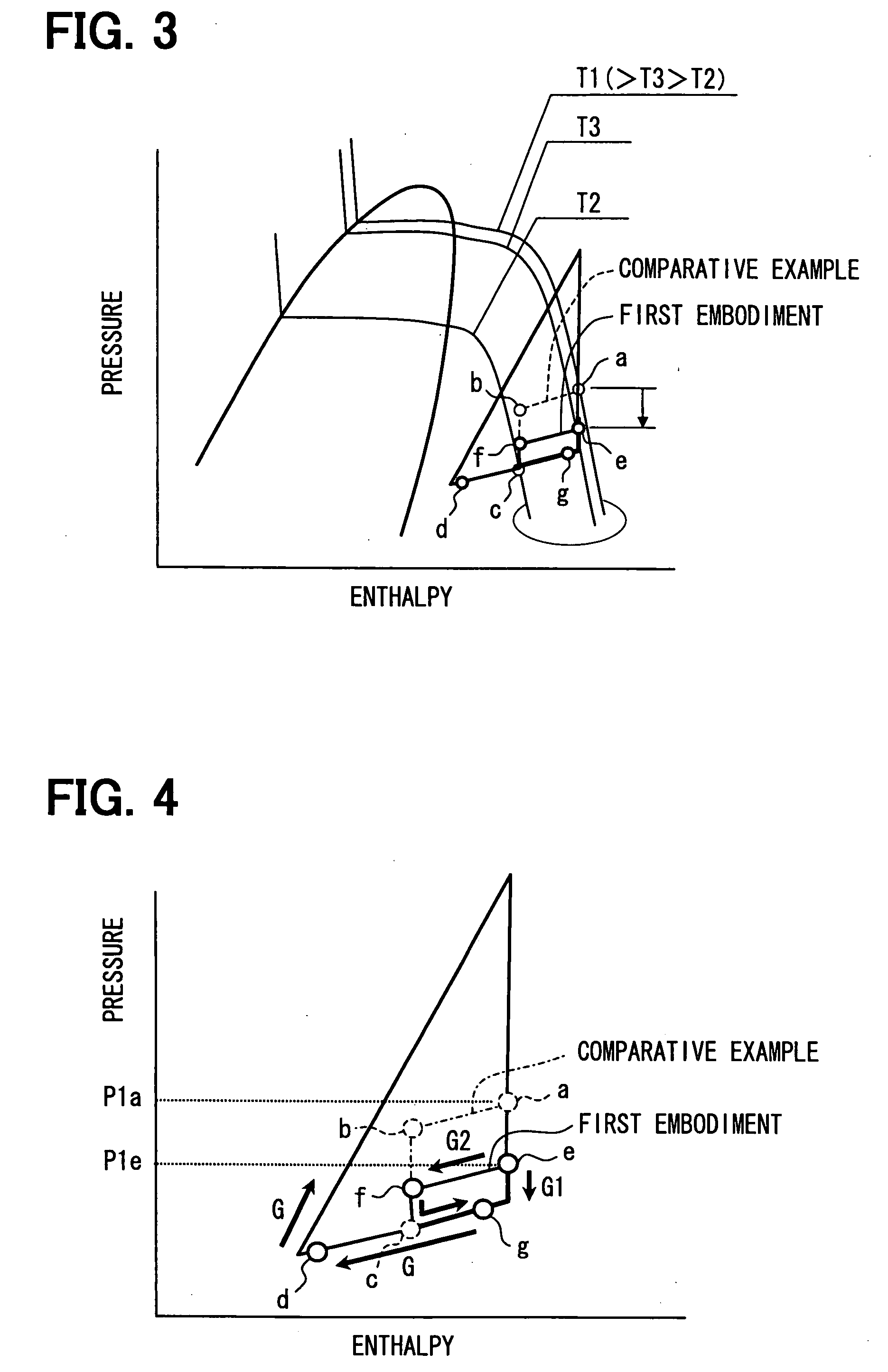
[0042]A first embodiment of the present invention will be now described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 5.
[0043]FIG. 1 illustrates an example in which a vapor-compression refrigerant cycle device 10 of the first embodiment is typically used for a refrigeration cycle of an air conditioner for vehicles. The refrigerant cycle device 10 is provided with a refrigerant circulation passage 11, and a compressor 12 that sucks in and compresses refrigerant is located in the refrigerant circulation passage 11.
[0044]The compressor 12 is rotationally driven by a vehicle running engine, not shown, through a belt or the like. For the compressor 12, a variable displacement compressor whose refrigerant discharging capacity can be adjusted by change in a discharge capacity may be used. A discharge capacity of refrigerant discharged from the compressor 12 is equivalent to a refrigerant discharge quantity per rotation. The discharge capacity can be changed by changing a capacity for sucking in refrigerant...
second embodiment
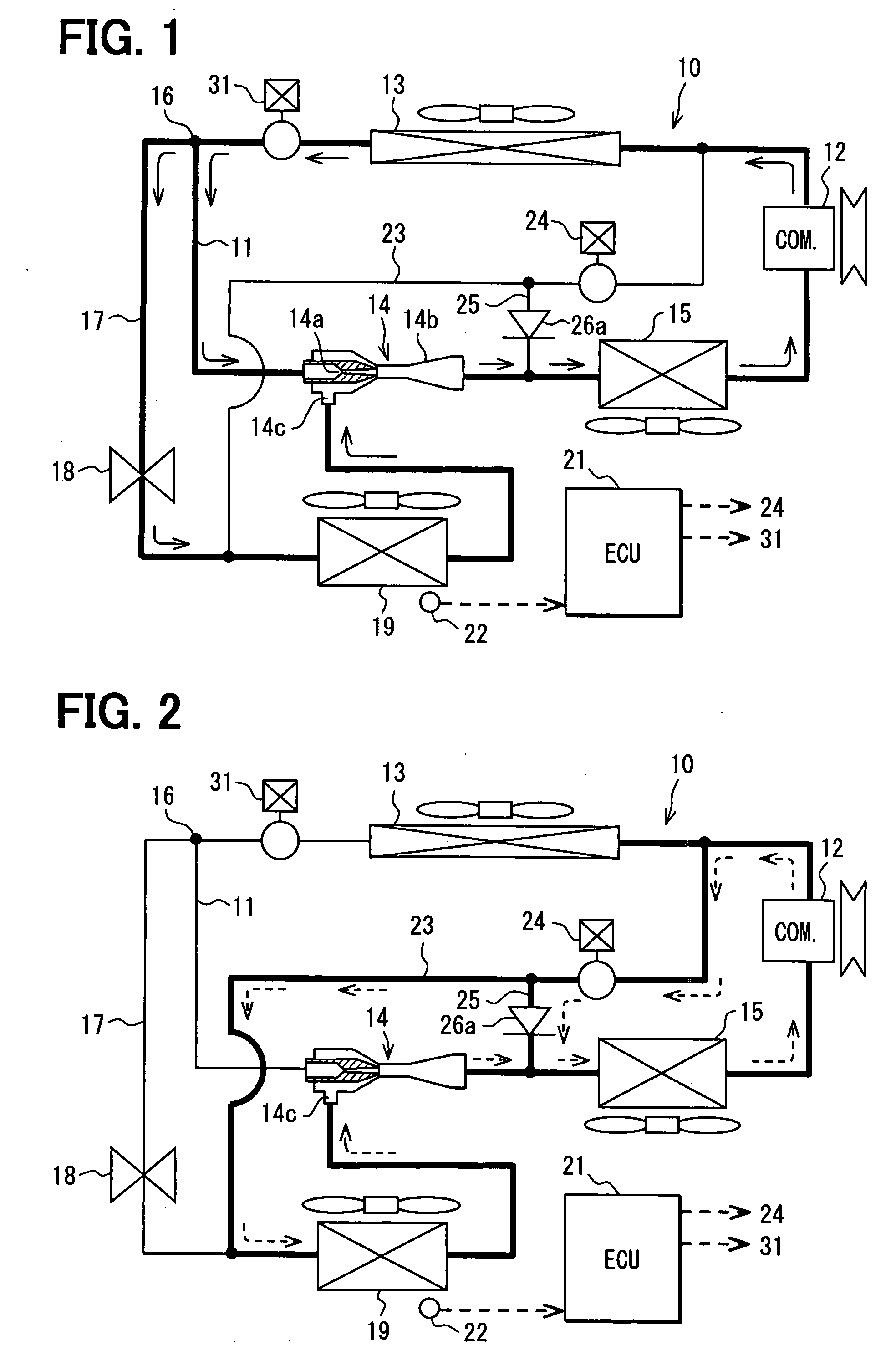
[0080]FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 illustrate a second embodiment of the invention. The second embodiment is implemented by replacing the check valve 26a in the first embodiment with an on-off switching valve 26b (flow control unit, backward flow preventing means).
[0081]The on-off switching valve 26b is a valve installed in the branch passage 25, the opening / closing of which is controlled by the electrical control unit 21. For example, the on-off switching valve 26b is so constructed that: it is closed when the opening and closing device 24 in the bypass passage 23 is closed in the cooling mode; and it is opened when the opening and closing device 24 is opened in the defrosting mode.
[0082]In the second embodiment, the other parts of the refrigerant cycle device 10 can be made similar to those of the above described first embodiment.
[0083]Thus, the flow of refrigerant (solid line arrows) illustrated in FIG. 6 can be formed in the cooling mode; and the flow of refrigerant (broken line arrows) il...
third embodiment
[0084]FIG. 8 to FIG. 10 illustrate a third embodiment of the invention. In the third embodiment, a flow adjusting valve 26c (flow control unit, backward flow preventing means) is used instead of the check valve 26a of the first embodiment; a temperature detector 27 for directly or indirectly detecting the refrigerant temperature on the refrigerant inlet side of the first evaporator 15 is provided; and a temperature detector 28 for directly or indirectly detecting the refrigerant temperature on the outlet side of the second evaporator 19 is provided. The flow adjusting valve 26c is located to adjust a flow amount of refrigerant flowing through the branch passage 25. An open degree of the flow adjusting valve 26c is set zero in the cooling mode. The temperature detector 27 is located to detect the refrigerant temperature flowing into the first evaporator 15. The temperature detector 28 is located to detect the refrigerant temperature flowing out of the second evaporator 19.
[0085]The f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com