Nonwoven fabric
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
1. FIRST EMBODIMENT
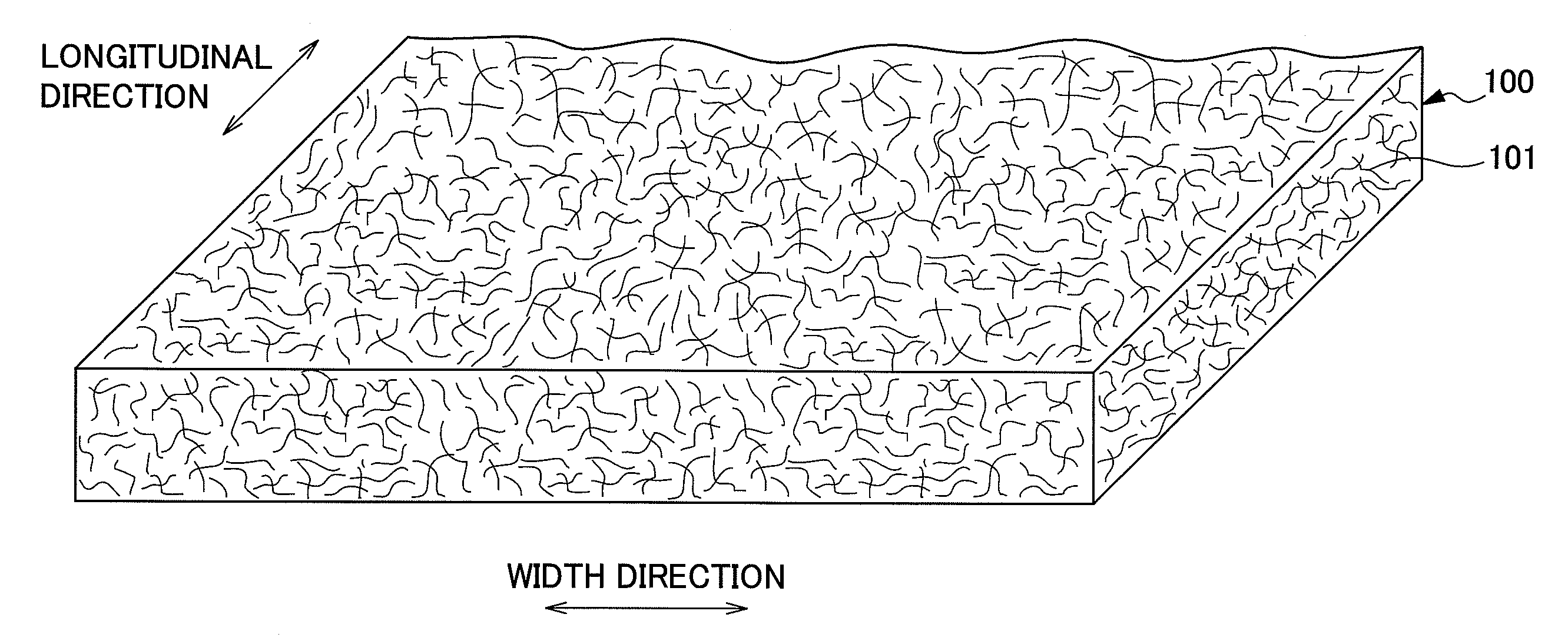
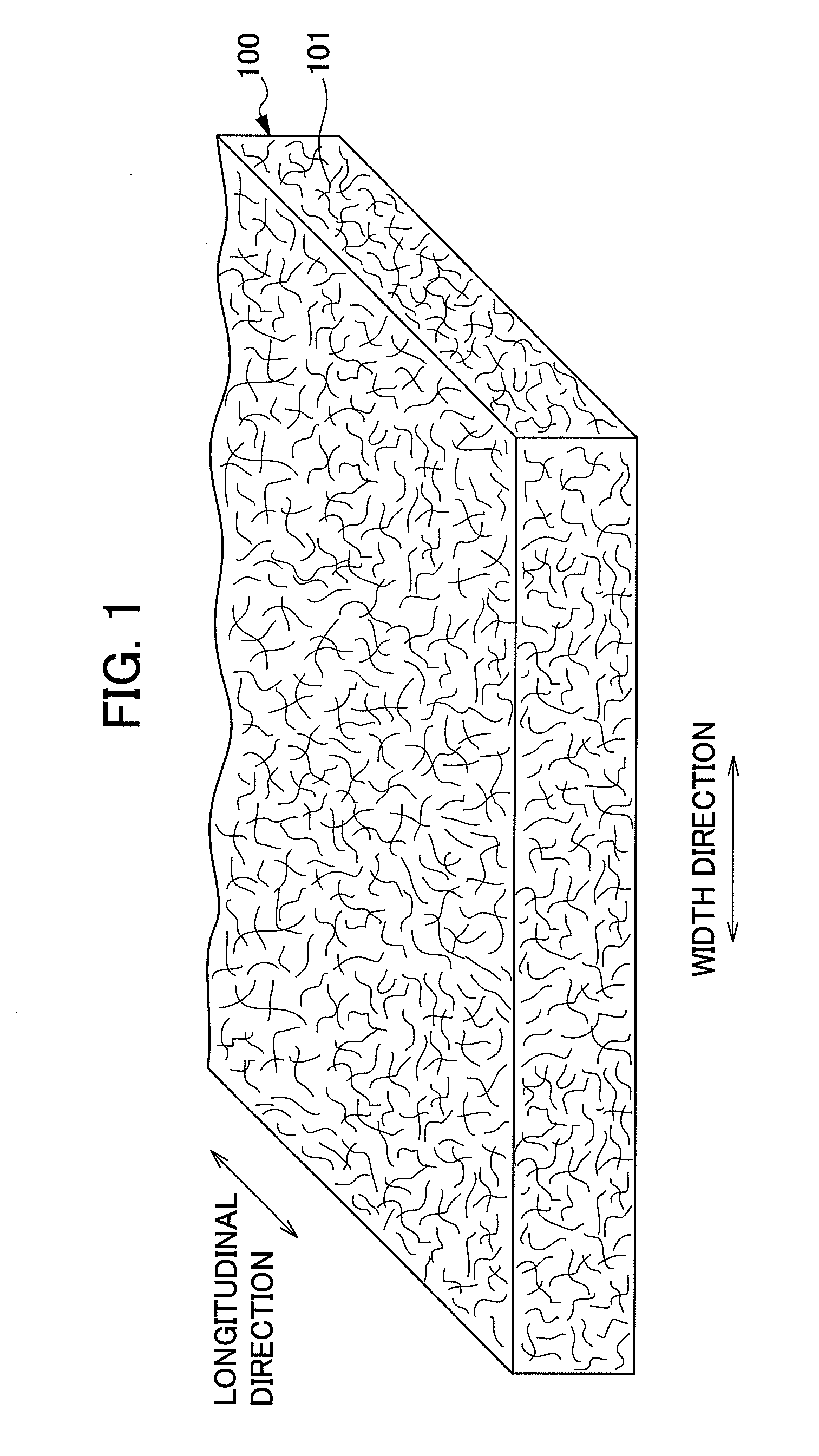
[0061]The nonwoven fabric of the present invention according to the first embodiment will be explained while referring to FIGS. 2 to 5.
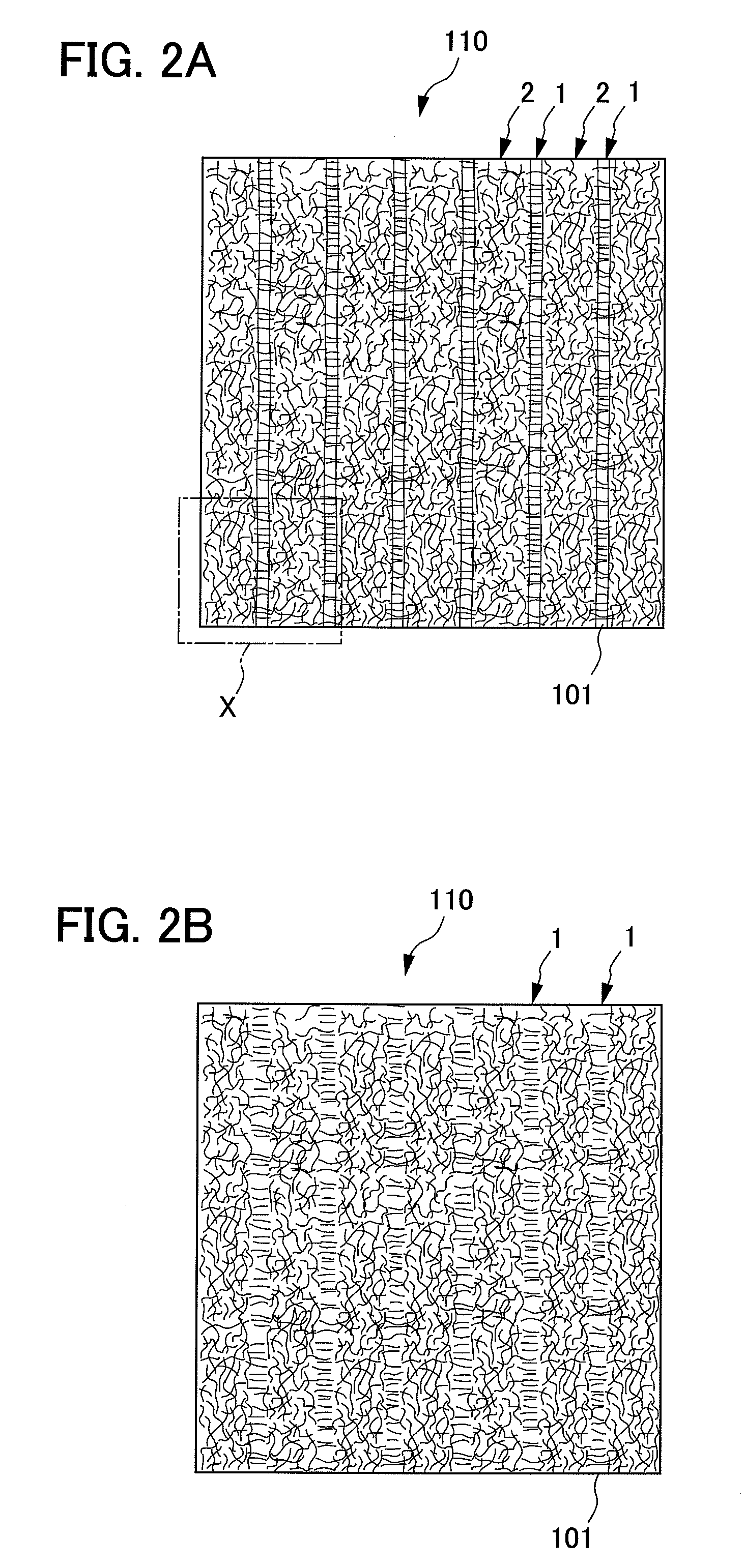
[0062]The nonwoven fabric 110 according to the first embodiment is a nonwoven fabric formed by jetting a fluid, consisting mainly of gaseous matter, into a fiber aggregate. A groove portion 1, which is an injected area to which the fluid, consisting mainly of gaseous matter, is jetted, and a convex portion 2, which is a nonjetted area to which the fluid, consisting mainly of gaseous matter, is not jetted, are formed. Furthermore, the nonwoven fabric 110 is a nonwoven fabric which has been adjusted so as the fiber density of the groove portion 1 to less than the fiber density of the convex portion 2.
1.1. Shape
[0063]In the nonwoven fabric 110 according to the first embodiment, a number of groove portions 1 are formed in parallel with each other at approximately regular intervals on one side of the nonwoven fabric 110 as shown in FIGS...
second embodiment
2.1. Second Embodiment
[0136]The nonwoven fabric of the present invention according to the second embodiment will be explained referring to FIG. 10.
2.1.1. Shape
[0137]The nonwoven fabric 114 according to the second embodiment is a nonwoven fabric having substantially flat surfaces on both sides as shown in FIG. 10. And areas of different fiber orientation are formed in predefined areas in the nonwoven fabric. The explanation below will focus on points which differ from the first embodiment.
2.1.2. Fiber Orientation
[0138]A number of areas which differ in the content of longitudinally oriented fibers are formed in the nonwoven fabric 114 as shown in FIG. 10. Examples of the areas which differ in the content of longitudinally oriented fibers include longitudinally oriented portions 13 where the content of the longitudinally oriented fibers is the greatest in the nonwoven fabric 114, center portions 12 where the content of the longitudinally oriented fibers is less than that of the longitu...
third embodiment
2.2. Third Embodiment
[0151]The nonwoven fabric of the present invention according to the third embodiment will be explained referring to FIGS. 11 and 12.
2.2.1. Nonwoven Fabric
[0152]The nonwoven fabric 116 according to the third embodiment differs from the nonwoven fabric as described in the first embodiment in having alternate roughness so that the entire nonwoven fabric 116 is crossed in the longitudinal direction. The nonwoven fabric 116 according to the third embodiment will be explained focusing on the points differing from the first embodiment.
[0153]The nonwoven fabric 116 according to the third embodiment is formed so as for the entire nonwoven fabric 116 to be corrugated in the longitudinal direction as machine direction.
2.2.2. Manufacturing Method
[0154]The method for manufacturing the nonwoven fabric 116 according to the third embodiment is similar to the method described in the first embodiment except for the embodiment of the net-like support member 260 as a breathable sup...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com