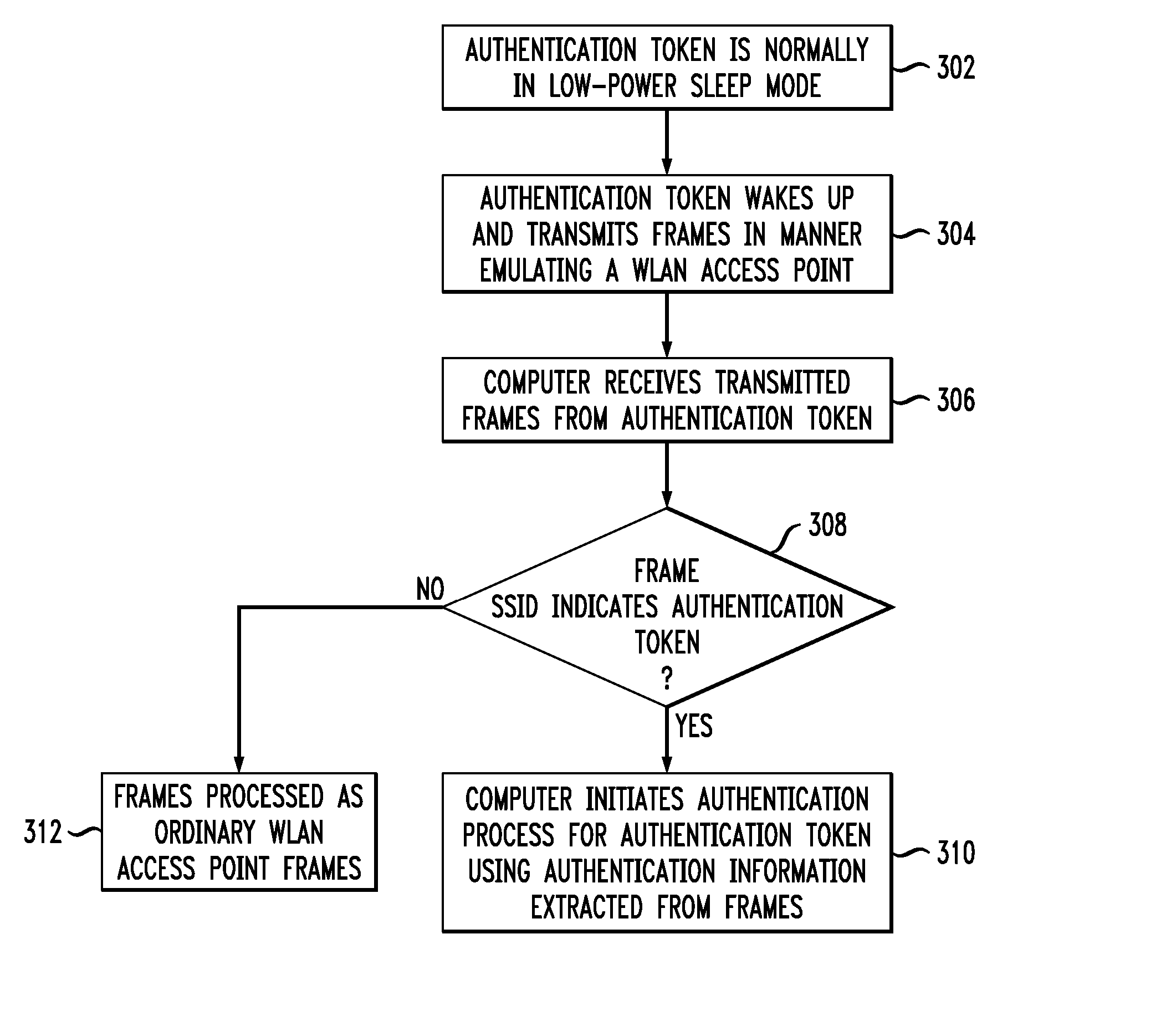
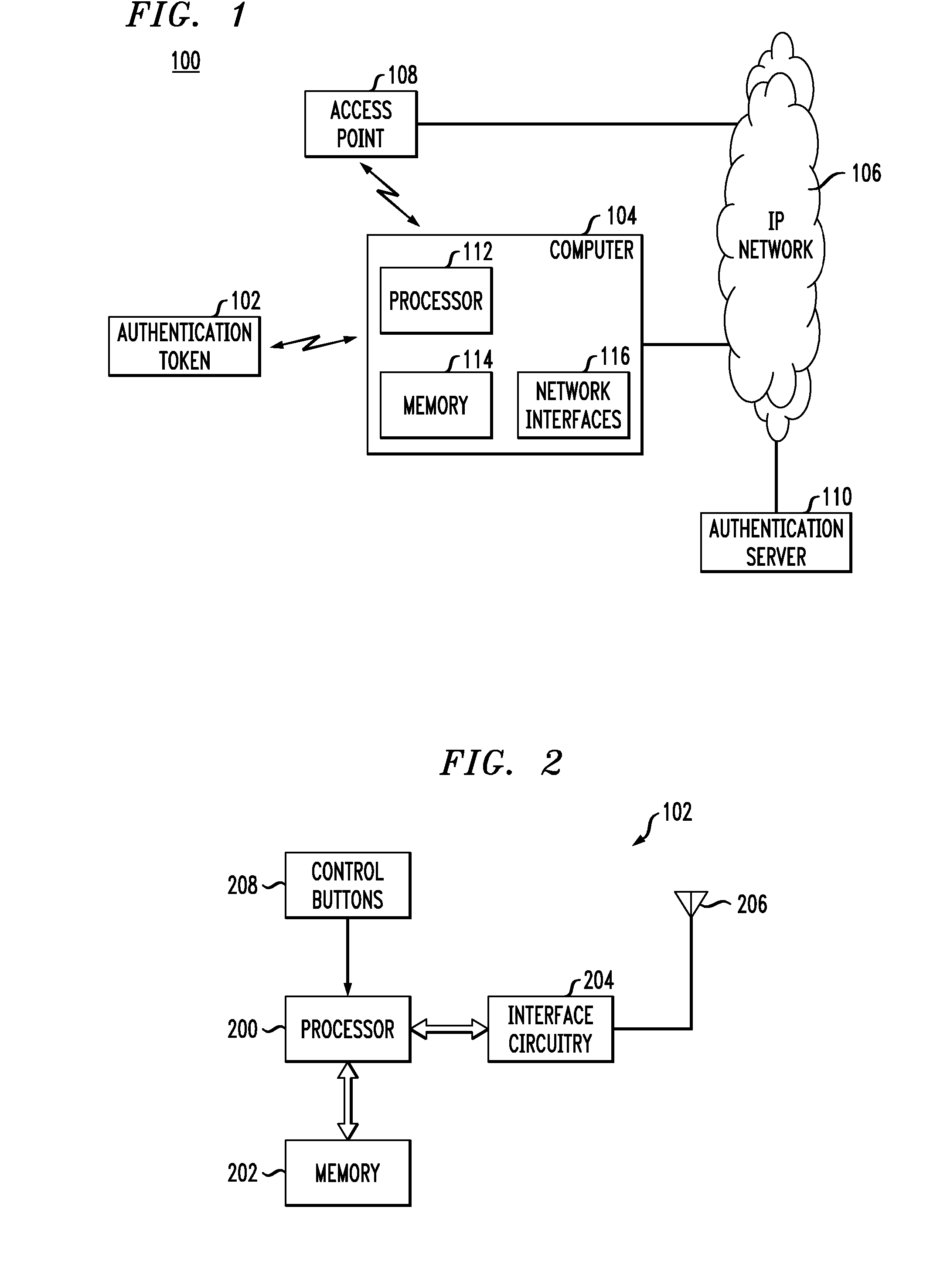
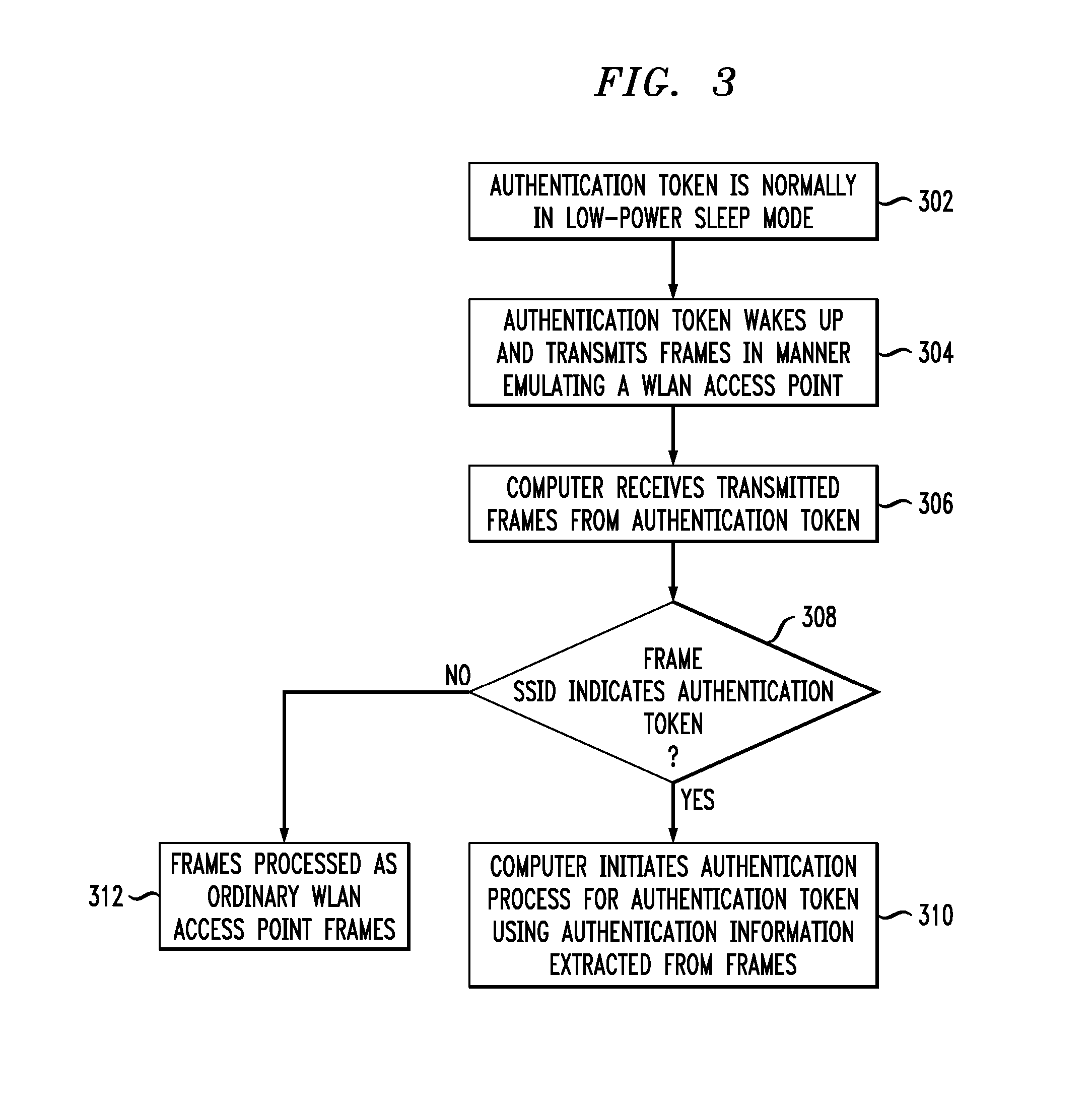
Wireless Authentication Methods and Apparatus
a technology of authentication tokens and authentication methods, applied in the field of wireless communication systems, can solve the problems of easy guessing, inability to accept input in authentication protocols, and inability to detect and detect the identity of users, etc., and achieve the effect of improving security and being suitable for low-power operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0181] To meet tight bandwidth constraints, a token might perform windowing by emitting two keys, k and {circumflex over (k)}. The token refreshes the first key at time steps d, 3d, 5d, . . . and the second key at time steps 2d, 4d, 6d, . . . . In other words, we employ two, gradually rotating keys with overlapping intervals. This compact scheme creates a synchronization window of size at least d, and provides a good degree of time insulation, as keys change on a regular basis. It fails, however, to achieve strong encryption. An adversary can potentially intercept a token output first and then compromise the mobile.
[0182] Formally, an encryption system in this model comprises a set of functions ES={KeyGen, Enc, Dec, Token}, defined as follows:
[0183] KeyGen(l)→(Kt(0), Km(0)): The key-generation function takes as input a security parameter l. It outputs initialization keys for the token and mobile devices respectively.
[0184] Enc(M, Km(i), k)→(C; {tilde over (K)}m(i+1)): The encrypt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com