Encoding video information using block based adaptive scan order
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
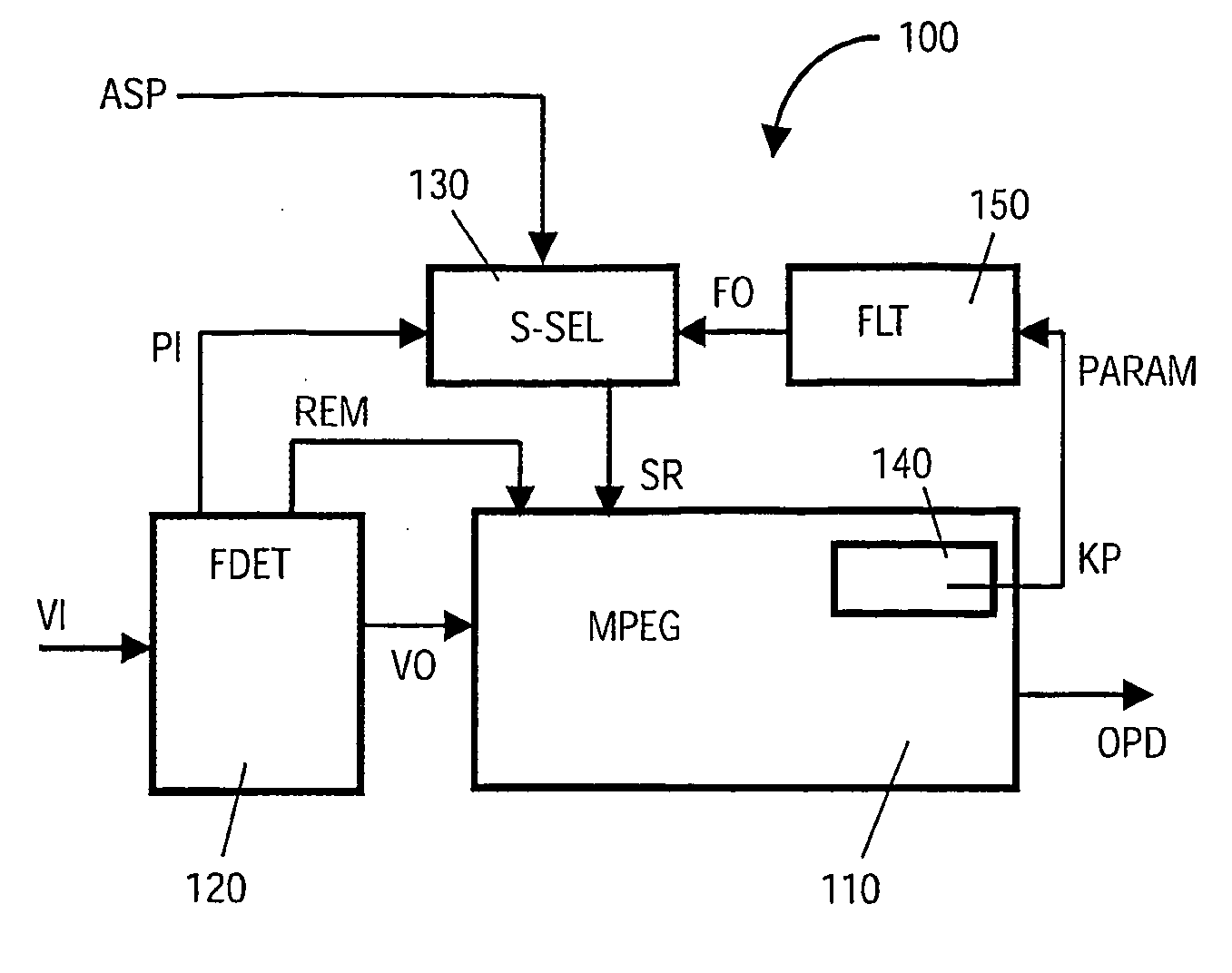
[0043] In order to describe the present invention in context, a brief description of contemporary MPEG video information encoding will firstly herewith be provided.
[0044] Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown processing steps implemented by a contemporary MWEG encoder when encoding image information; the steps are indicated generally by 10. In overview, the encoder receives a series of video image frames (FRM) in a temporal sequence t and processes them to provide corresponding MPEO encoded output data (OPD) denoted by 15.
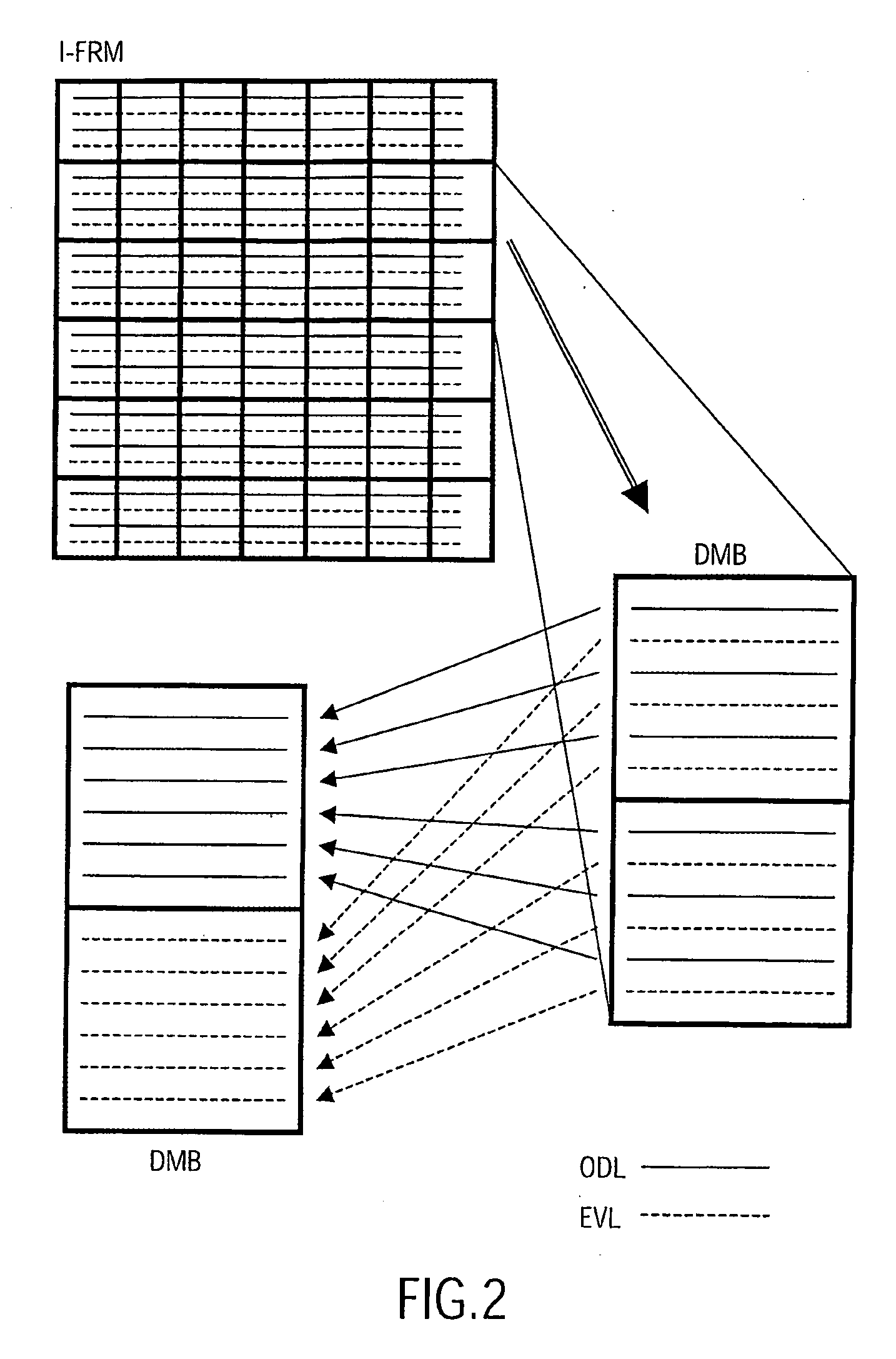
[0045] Each received video frame FRM comprises a two-dimensional field of pixels which is subdivided within the encoder into data macro blocks DMB; conveniently, each macro block DMB comprises a two-dimensional 16×16 pixel field, although other field sizes are also feasible. For example, an image frame designated by 20 presently being processed within the encoder is subdivided into corresponding macro blocks DMB designated by 30.
[0046] The encoder further processe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com