Ejector cycle device
a cycle device and ejector technology, applied in the direction of defrosting, heating apparatus, domestic cooling apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of deteriorating the life of the compressor, flowing noise, and affecting the efficiency of the compressor, so as to prevent the noise of refrigerant flowing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
1st embodiment
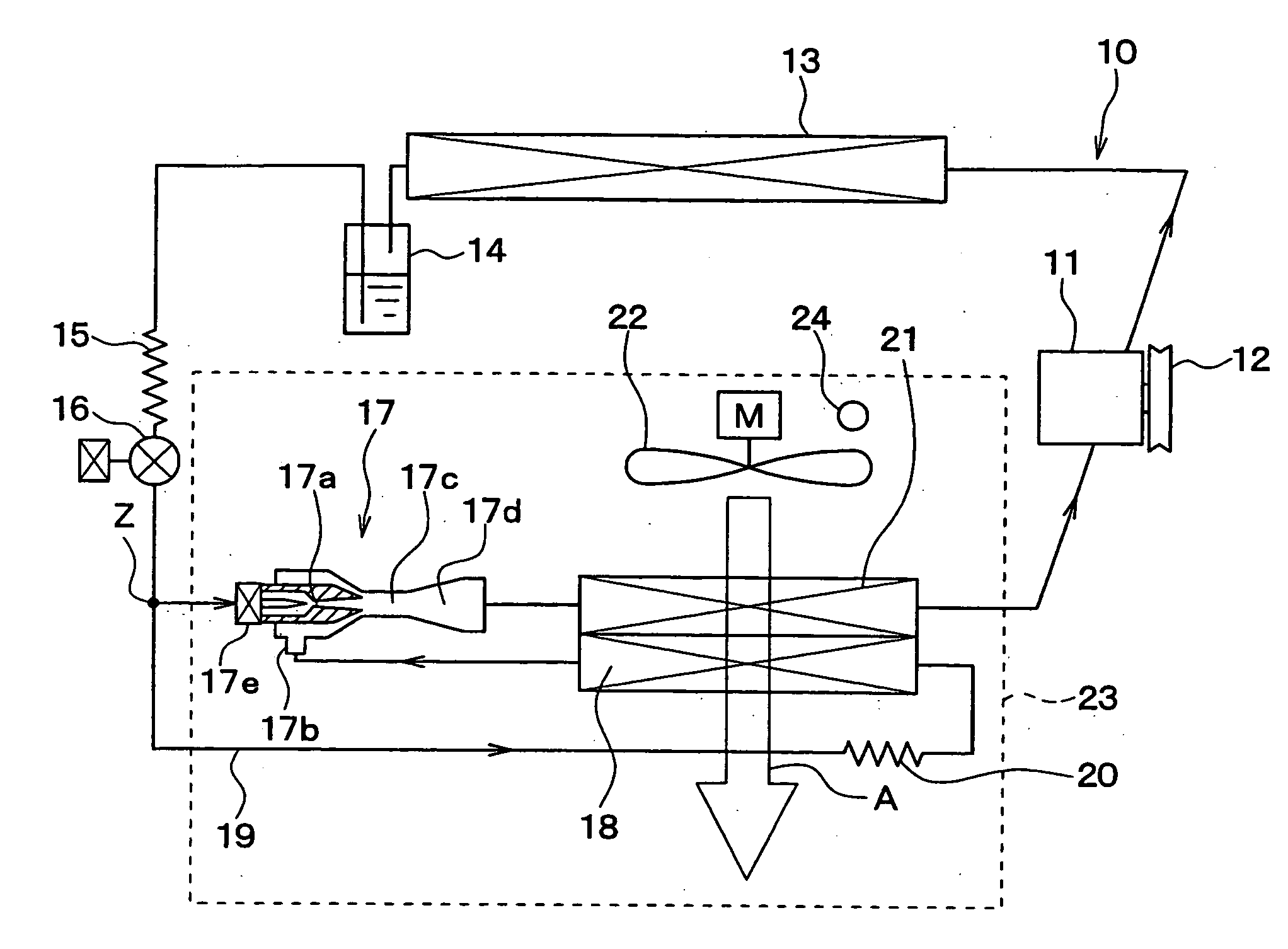
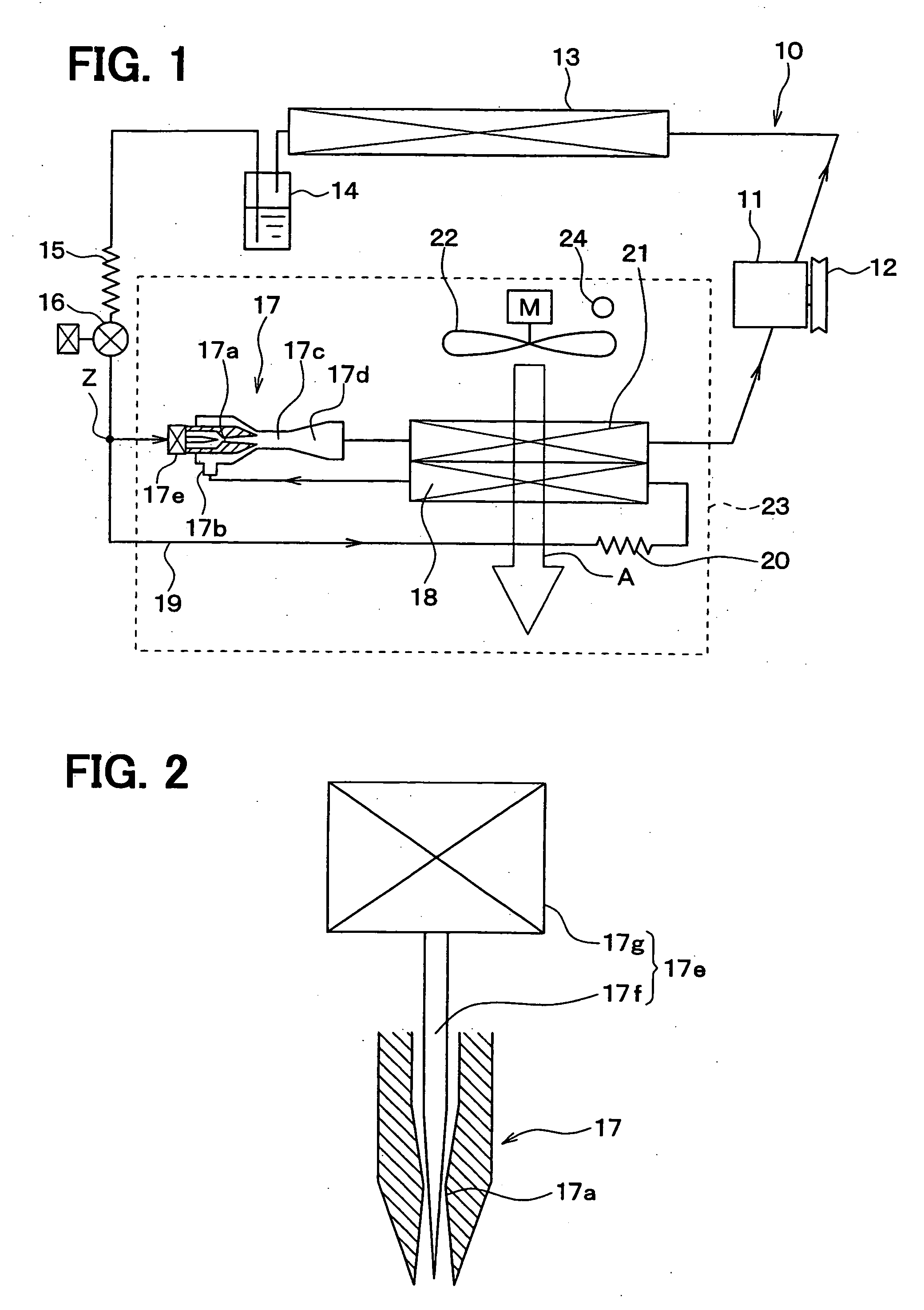
[0090]FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 show the 1st embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 1 shows an example to which an ejector cycle device 10 in accordance with the 1st embodiment is used for a refrigerating device for a vehicle. Here, the refrigerating device for a vehicle of this embodiment cools the inside of a compartment (space) to an extremely low temperature of, for example, approximately −20° C.
[0091] In the ejector cycle device 10 of this embodiment, a compressor 11 for sucking and compressing refrigerant is rotated and driven by a vehicle driving engine (not shown) via an electromagnetic clutch 12, a belt, and the like. This compressor 11 is connected to and disconnected from the vehicle driving engine by intermittently passing current through the electromagnetic clutch 12, thereby being intermittently operated. That is, the refrigerant discharge capacity of the compressor 11 is controlled by changing the rate of intermittent operation of the compressor 11 by intermittently opera...
2nd embodiment
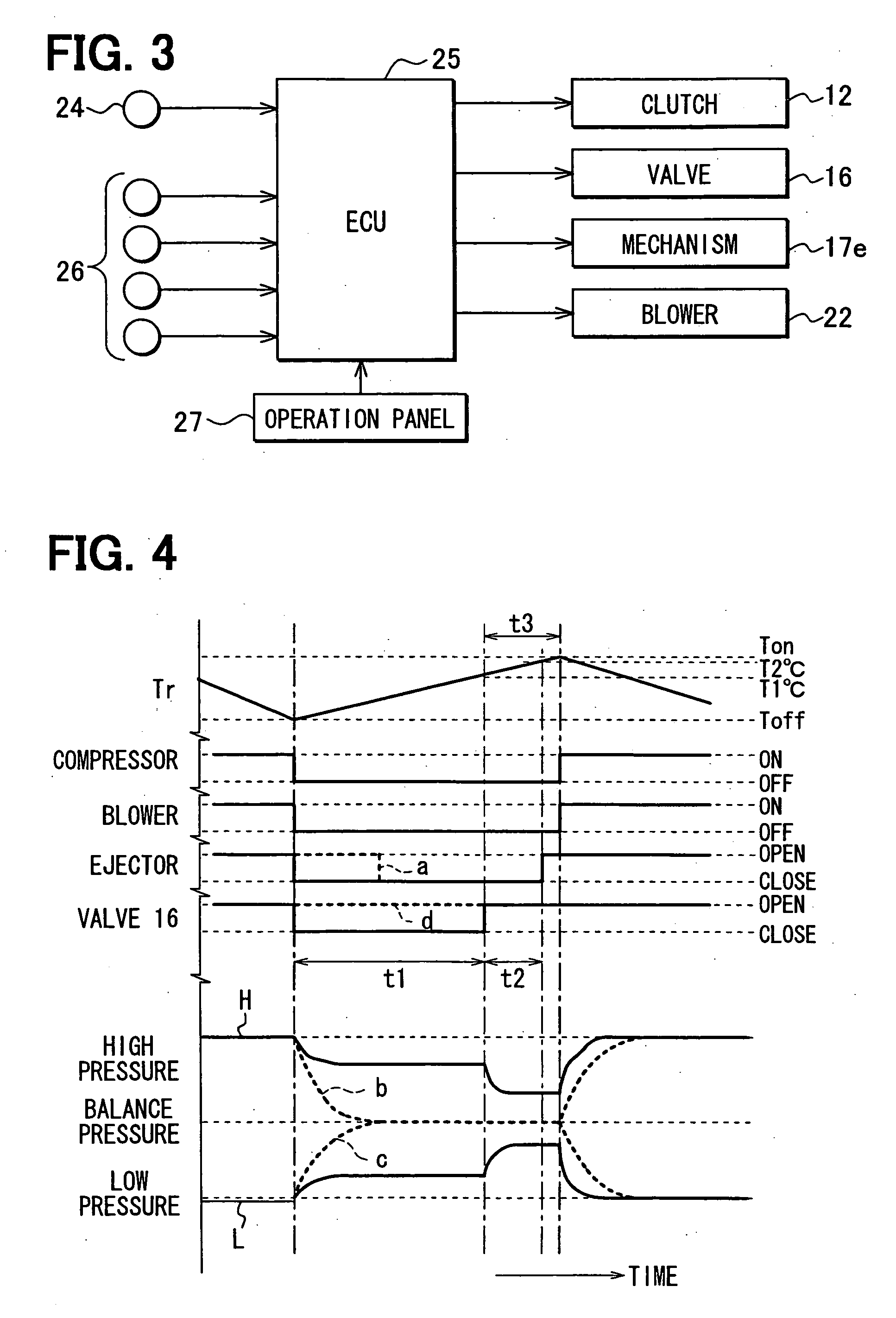
[0163] In the 1st embodiment, the opening / closing valve 16 is closed in operative connection with the operation of stopping the compressor 11. However, in the 2nd embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, when the inside temperature Tr of the space to be cooled decreases to the lower limit set temperature Toff, first, the opening / closing valve 16 is closed before the compressor 11 is stopped. With this, the compressor 11 is continuously operated for a specified time t4 with the upstream passage of the branch point Z held shut and then is stopped after this specified time t4 passes.
[0164] Here, the specified time t4 is a period of a pump-down operation in which the compressor 11 draws refrigerant on the low pressure side of the cycle and moves the refrigerant to high pressure side and holds the refrigerant on the high pressure side. By performing this pump-down operation, the amount of refrigerant collected in the first and second evaporators 18, 21 when the compressor 11 is stopped can be fu...
3rd embodiment
[0167] In the 1st embodiment, the throttle mechanism 15 and the opening / closing valve 16 are arranged on the upstream side of the branch point Z on the upstream side of the ejector 17. However, in the 3rd embodiment, as shown in FIG. 8, the throttle mechanism 15 and the opening / closing valve 16 arranged on the upstream side of the ejector 17 in the above-described first embodiment are not arranged, but the opening / closing valve 16 is interposed between the downstream side of the throttle mechanism 20 of the refrigerant branch passage 19 and the upstream side of the first evaporator 18.
[0168] Hence, according to the 3rd embodiment, the opening / closing valve 16 shuts only the passage of the refrigerant branch passage 19. Hence, in the 3rd embodiment, both of the opening / closing valve 16 and the passage opening / closing mechanism 17e of the ejector 17 are brought into a closing state at the same time in operative connection with the operation of stopping the compressor 11. With this, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com