Method and system of determining the absolute velocity of a vehicle
a technology of absolute velocity and vehicle, applied in the direction of time traversed devices, tyre measurements, devices using electric/magnetic means, etc., can solve the problems of inability to precisely determine the wheel radius, no standard sensors in commercial cars that can measure absolute velocity, and up to 10% error in velocity measuremen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
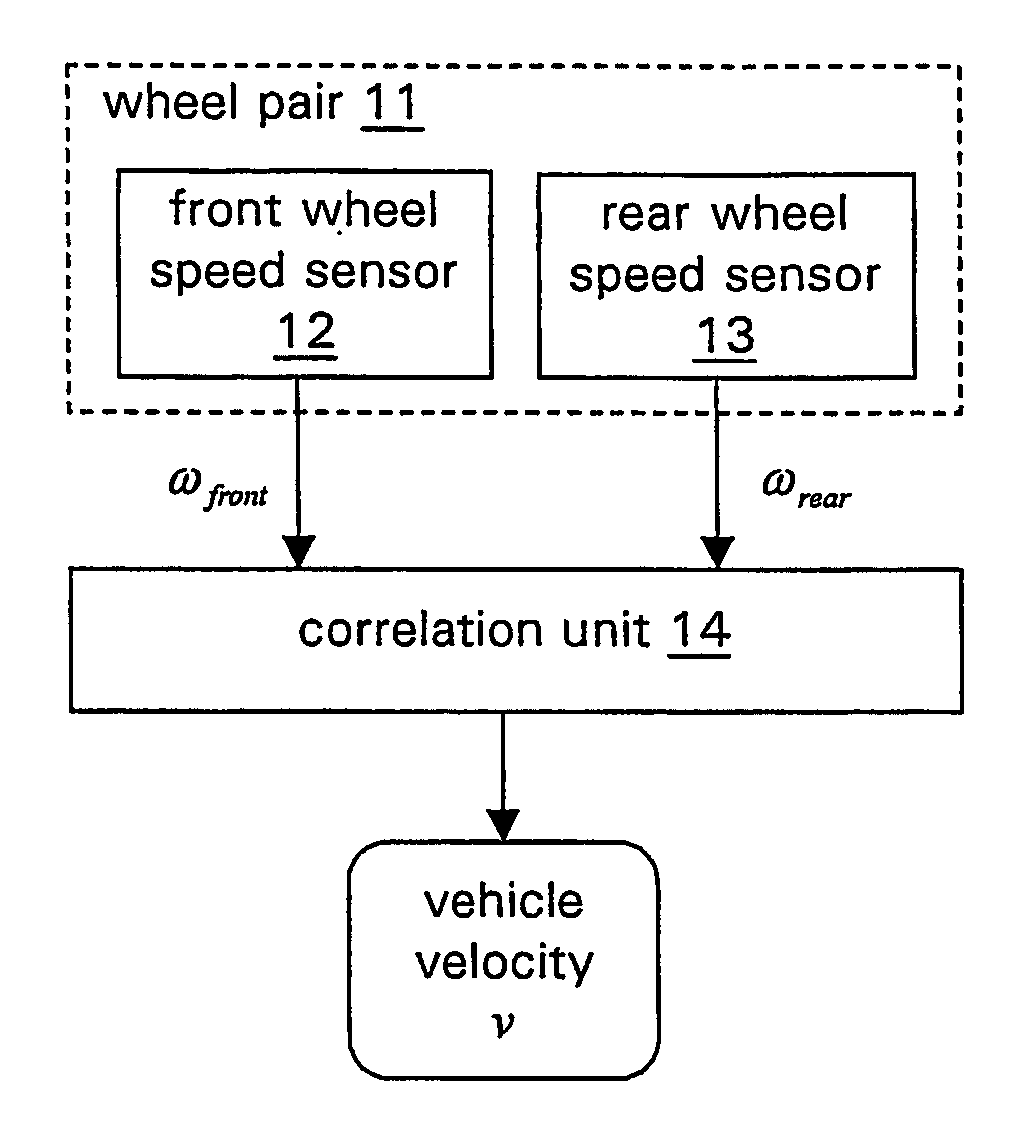
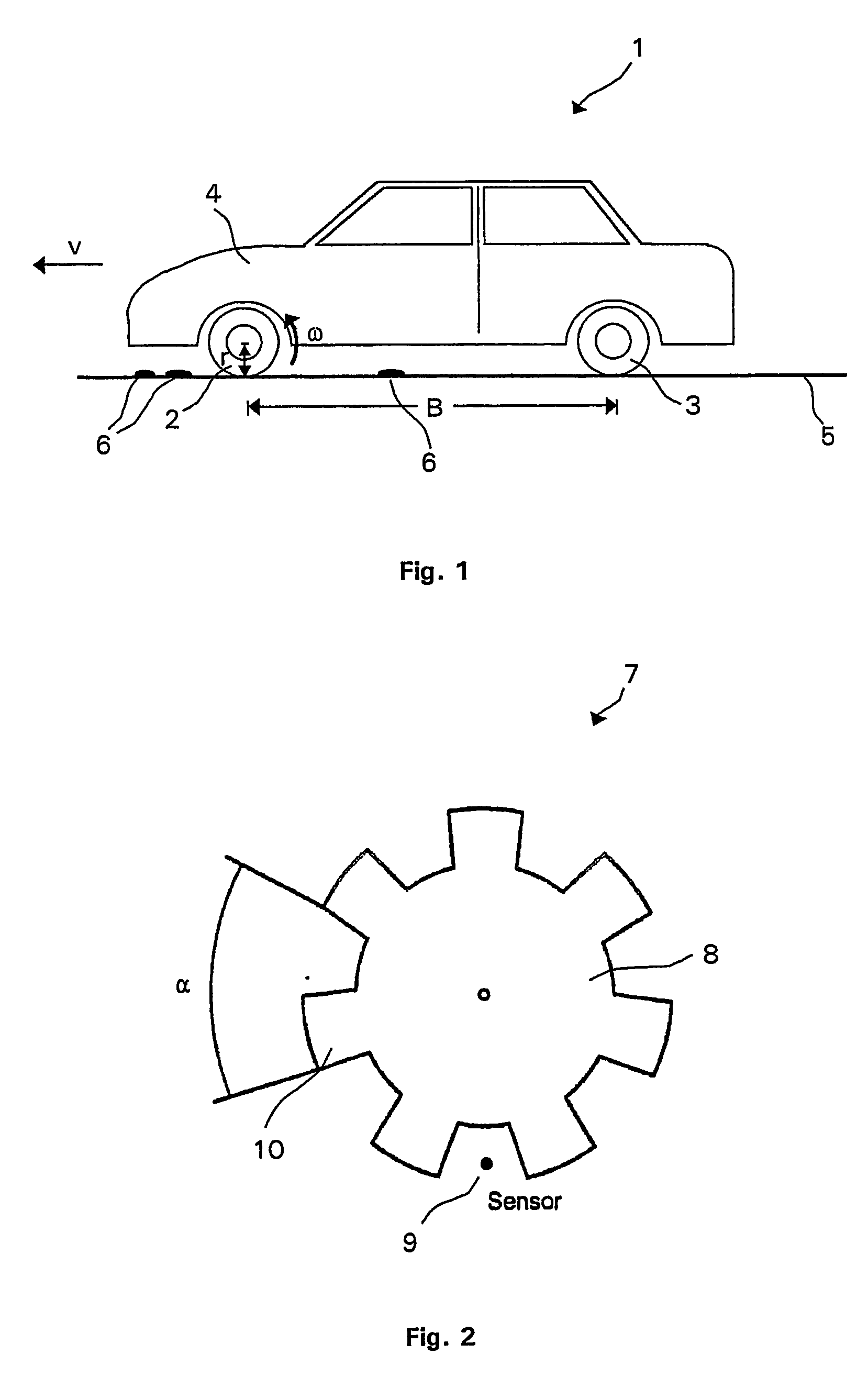
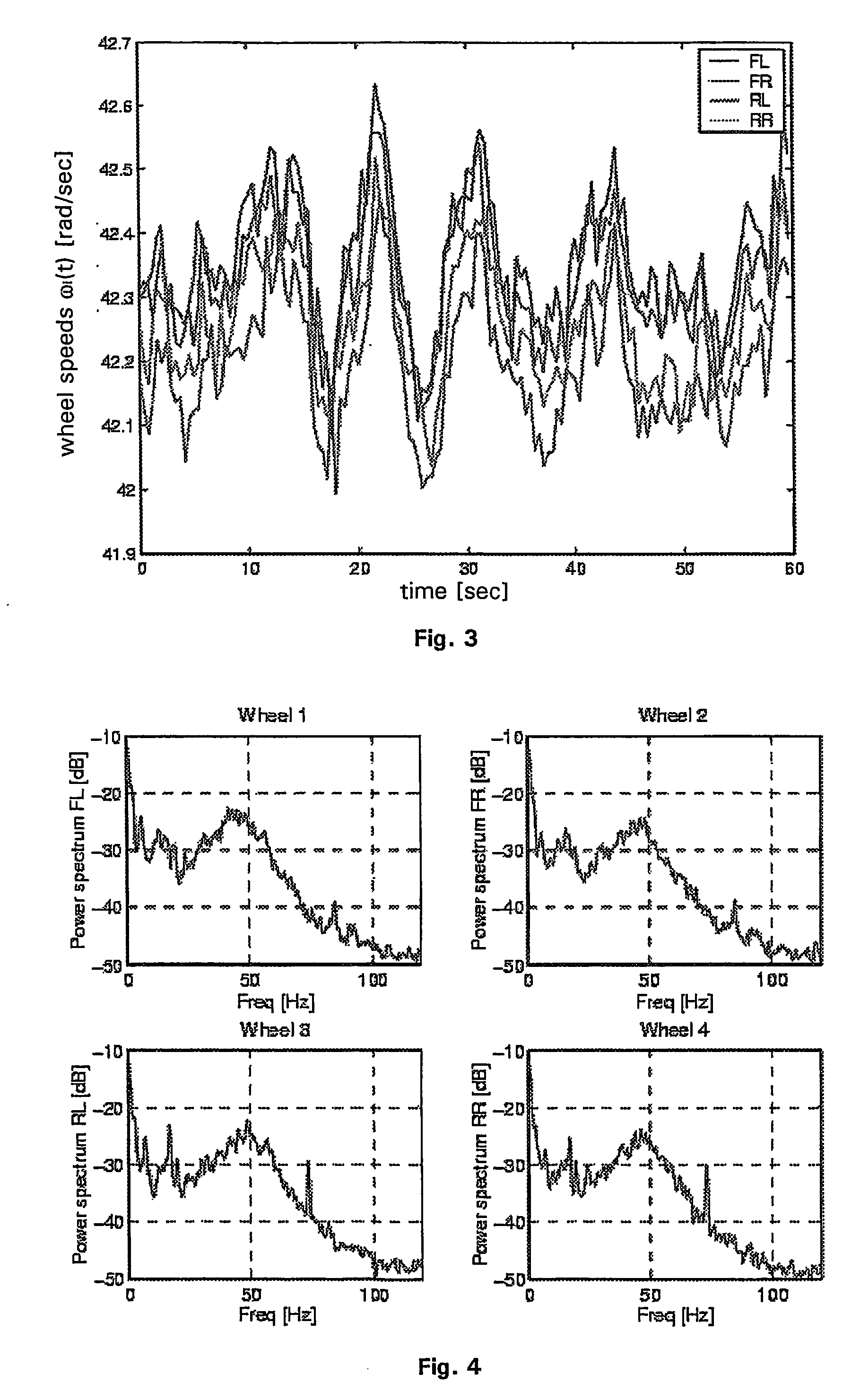
[0036] In general the presented method and system for determining the velocity of a vehicle is based on a correlation analysis of the time dependent behavior of wheel speed signals of a vehicle's front and rear wheels which varies with road bumpiness or unevenness. The cause for such variations may be any small or large road feature like asphalt texture, split, small stones, bumps, etc. These features induce these variations via the tire-road contact. The variations which are induced at a particular wheel result in a specific time dependent behavior of the respective wheel speed signal. The wheel speed signals are measured in a pair of a front and a rear wheel which are running in a lane so that they feel the same road features in a time delayed manner. Wheel speed sensors measure the front and rear wheel speed signals. The instantaneous wheel speed signals are influenced by the road features which were instantaneously passed by an individual wheel. A correlation analysis of the fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com