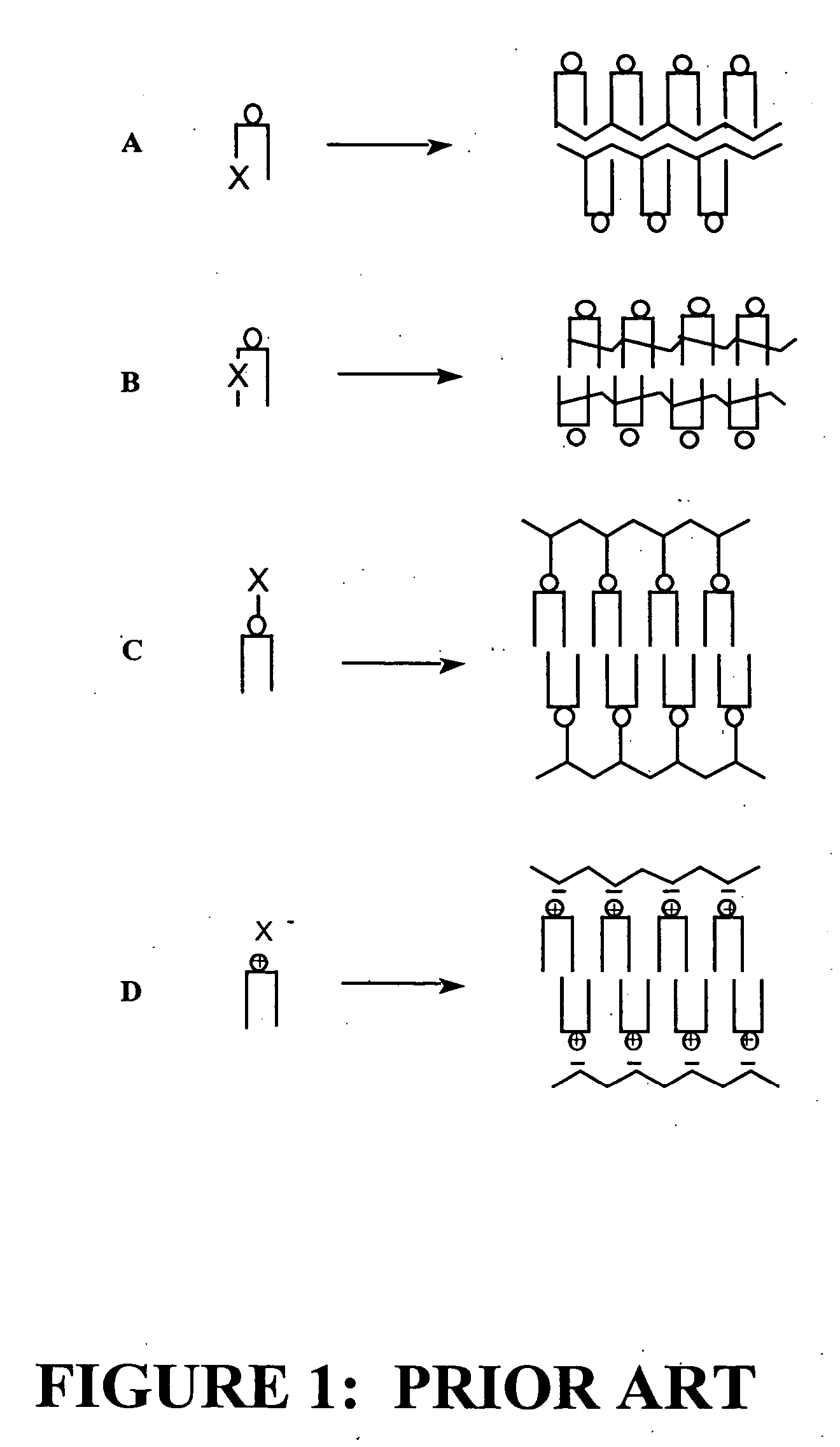
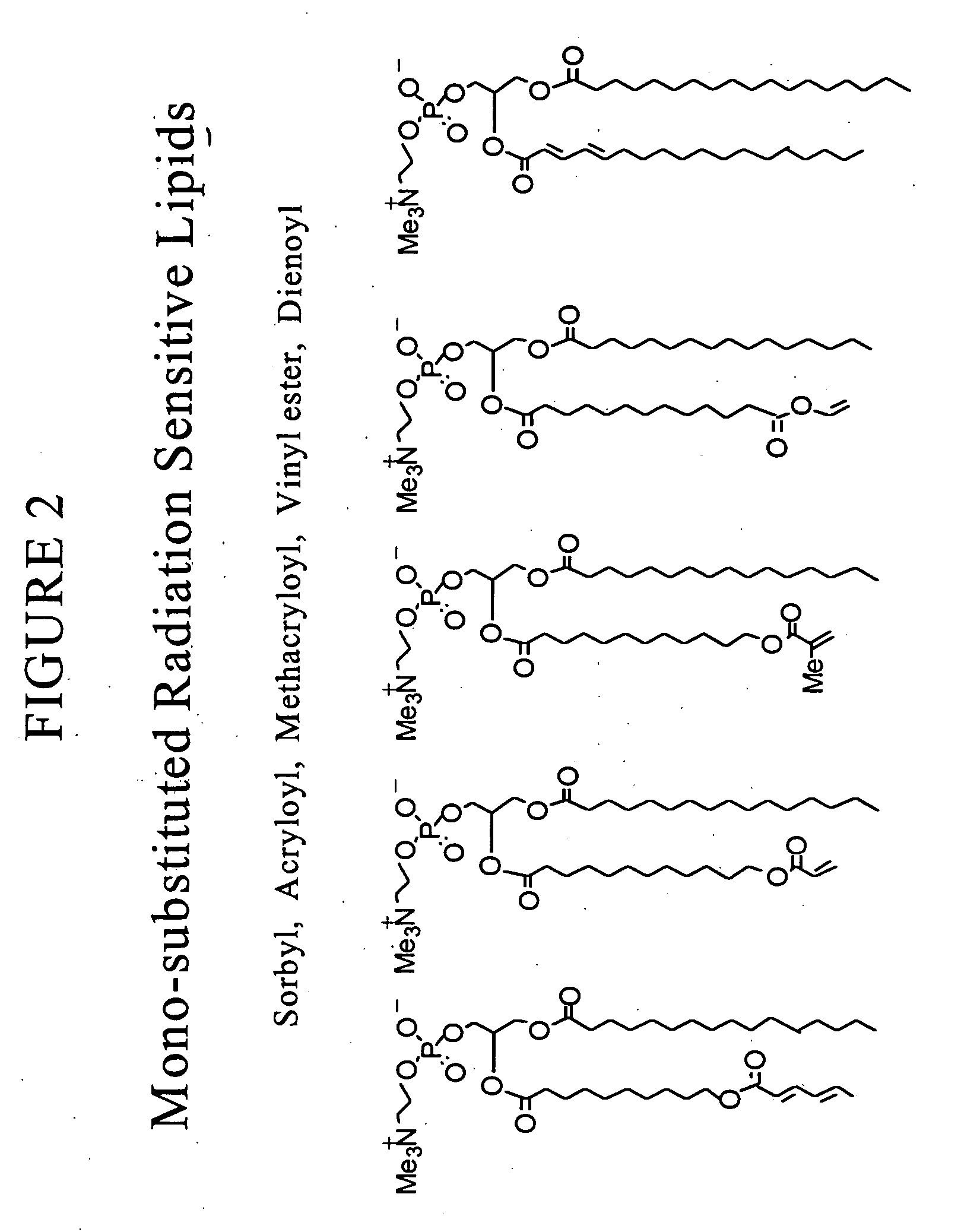
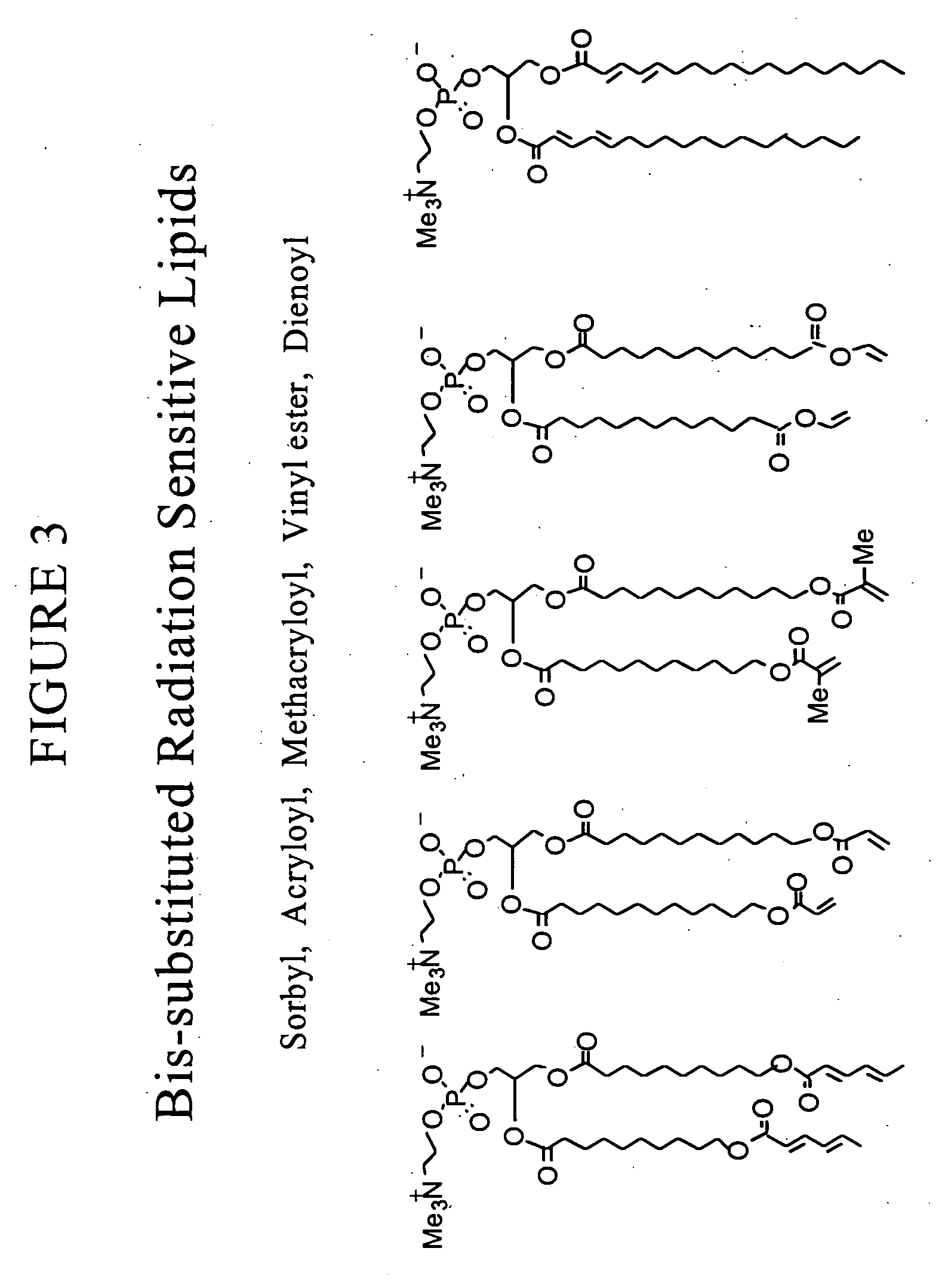
Radiation sensitive liposomes
a liposome and liposome technology, applied in the field of radiation sensitive liposomes, can solve the problems of slow passive leakage of encapsulated chemotherapeutics, can significantly affect the cells at the site, and can localize the destruction of target cells, and achieve the effect of enhancing the release of encapsulated water soluble molecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] a) Definitions and General Parameters
[0038] The following definitions are set forth to illustrate and define the meaning and scope of the various terms used to describe the invention herein.
[0039] The term “liposome” refers to a microscopic vesicle comprising lipid bilayer(s). Structurally, liposomes range in size and shape from long tubes to spheres and are normally 100±10 nm in diameter, but can be as small as 25 nm and as large as 500 nm in diameter. Liposomes may contain one or more bilayer(s). Agents or molecules can be incorporated into the liposome. For example, molecules may be encapsulated in or associated with the liposome. A liposome with such encapsulated or associated agents (e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents) may be targeted to specific site(s) (e.g., tissue of interest such as a tumor tissue) and its contents released when appropriate. Liposomes may also be targeted to specific site(s) in vitro or in vivo through attached targeting sequences such as pept...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com