Hydroxide-releasing agents as skin permeation enhancers
a technology of hydroxide-releasing agents and skin permeation enhancers, which is applied in the direction of inorganic non-active ingredients, peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing the rate of an active agen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
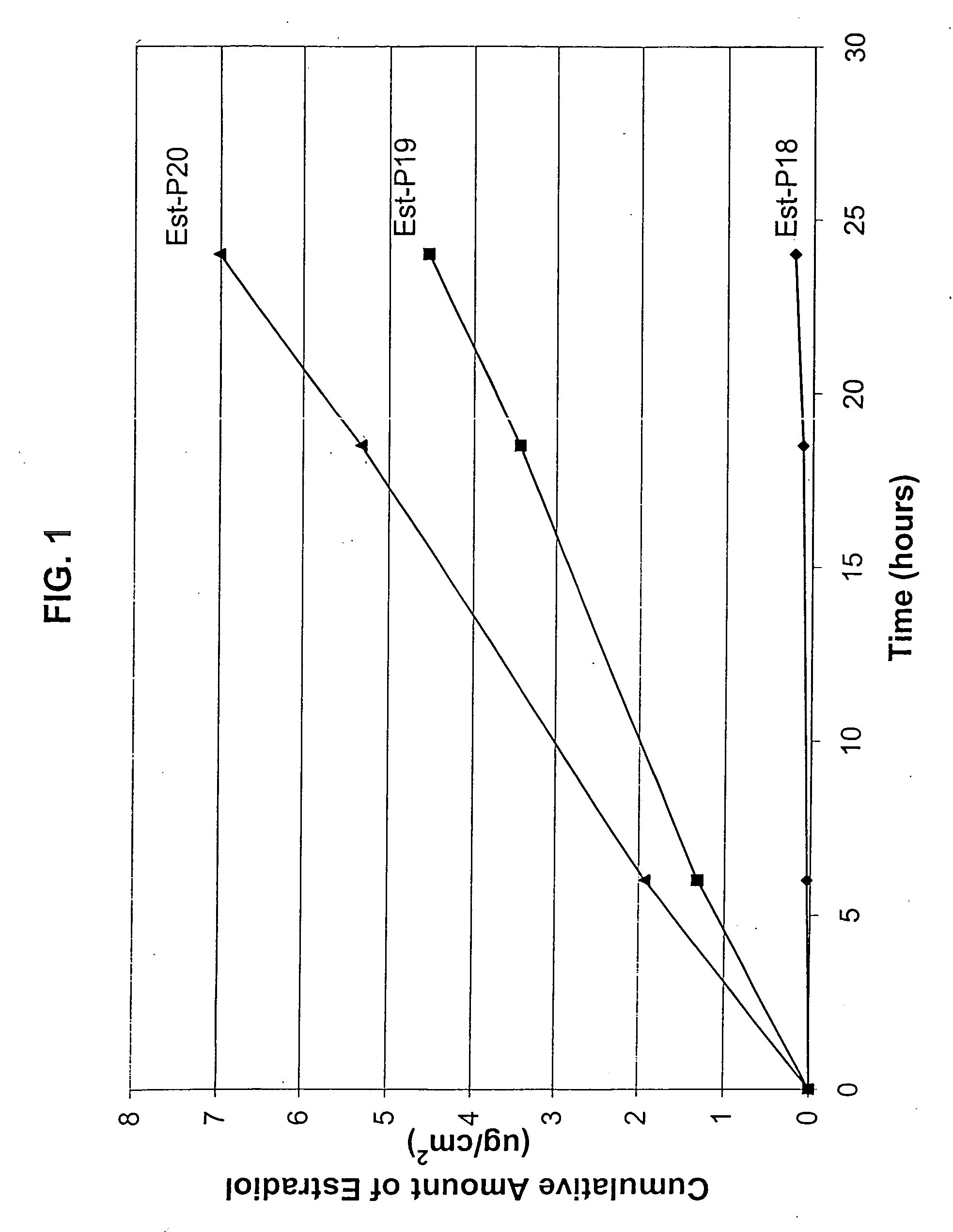
[0153] An in vitro skin permeation study was conducted using three estradiol transdermal systems. The formulations used to prepare these systems are listed in Table 1, which includes weight and weight percent of each component of the formulations. The weight of sodium hydroxide was 0 g, 0.0155 g, and 0.025 g for formulation #Est-P18, #Est-P19 and #Est-P20 respectively. Each formulation was coated onto a release liner and dried in an oven at 55° C. for two hours to remove water and other solvents. The dried drug-in-adhesive / release liner film was laminated to a backing film. The backing / drug-in-adhesive / release liner laminate was then cut into discs with a diameter of 11 / 16 inch. The theoretical percent weight for each ingredient after drying (calculated assuming all volatile ingredients were completely removed during drying) is set forth in Table 2.
[0154] The in vitro permeation of estradiol through human cadaver skin from these discs was performed using Franz-type diffusion cells ...
example 2
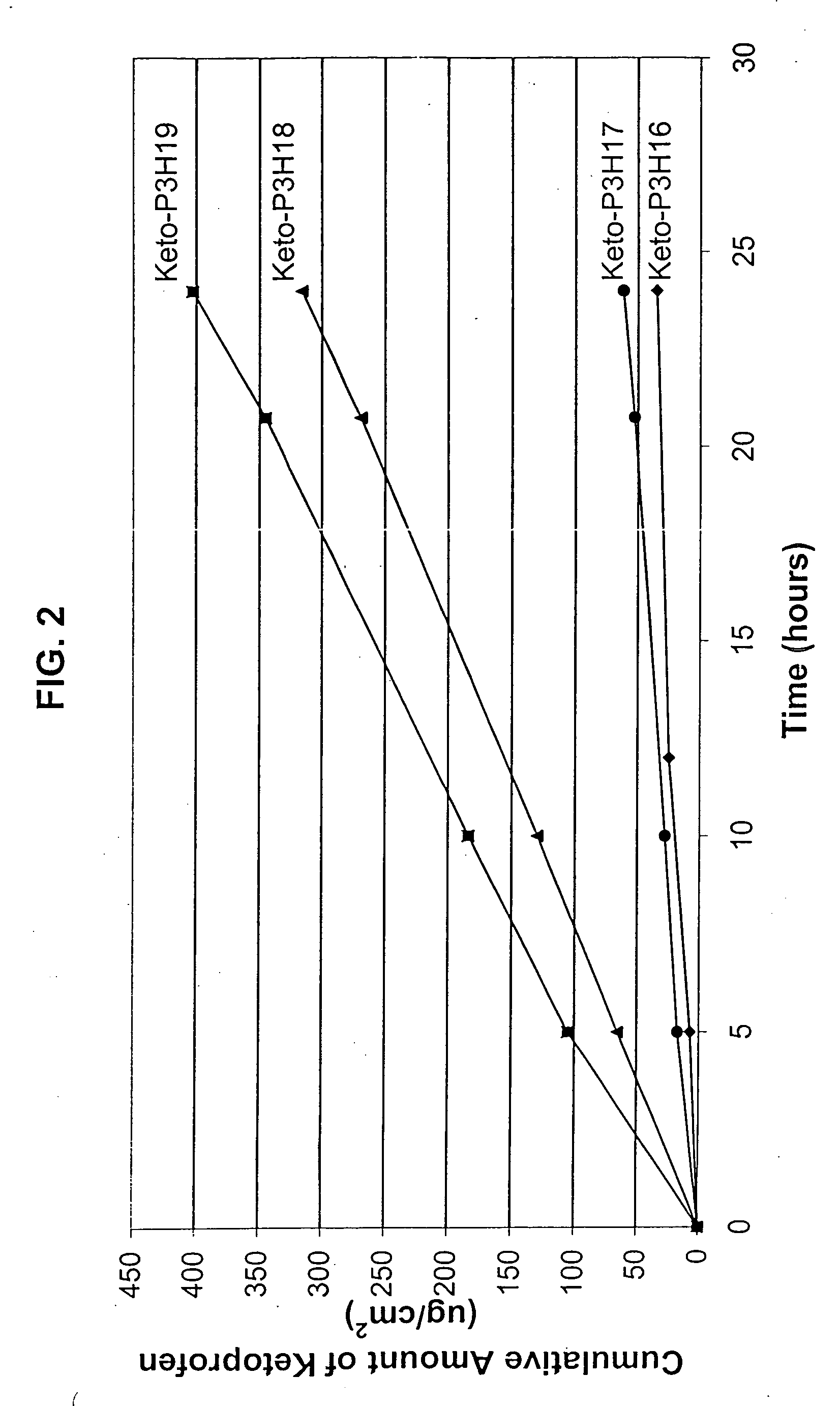
[0159] An in vitro skin permeation study was conducted using four ketoprofen transdermal systems. The formulations used to prepare these systems are listed in Table 4, which includes weight and weight percent of each component of the formulations. The weight of sodium hydroxide was 0 g, 0.19 g, 0.215 g, and 0.225 g for formulation #Keto-P3H16, -P3H17, P3H18, and -P3H19, respectively. Each formulation was coated on a release liner and dried in an oven at 55° C. for two hours to remove water and other solvents. The dried drug-in-adhesive / release liner film was laminated to a backing film. The backing / drug-in-adhesive / release liner laminate was then cut into discs with a diameter of 11 / 16 inch. The theoretical percent weight for each ingredient after drying (calculated assuming all volatile ingredients were completely removed during drying) is set forth in Table 5.
[0160] The in vitro permeation of ketoprofen through human cadaver skin from these discs was performed using Franz diffusi...
example 3
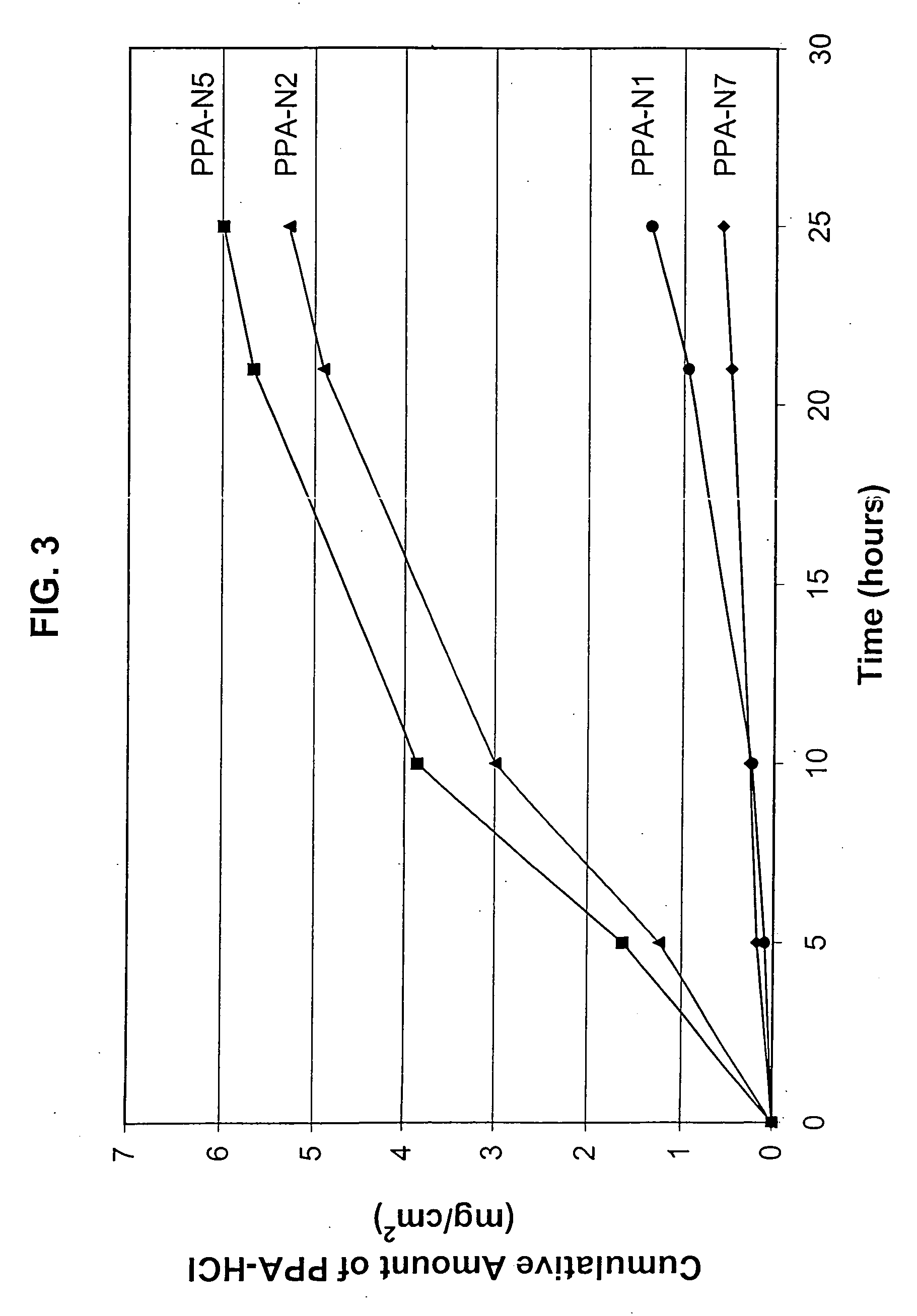
[0167] An in vitro skin permeation study was conducted using four phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride (PPA-HCl) transdermal systems. The formulations used to prepare these systems are listed in Table 7, which includes weight and weight percent of each component in the formulations. The weight of sodium hydroxide was 0 g, 0.165 g, 0.195 g, and 0.23 g for formulation #PPA-N7, -N1, -N2, -and -N5, respectively. Each formulation was coated onto a release liner and dried in an oven at 55° C. for two hours to remove water and other solvents. The dried drug-in-adhesive / release liner film was laminated to a backing film. The backing / drug-in-adhesive / release liner laminate was then cut into round discs with a diameter of 11 / 16 inch. The theoretical percent weight for each component after drying (calculated assuming all the volatile ingredients were completely removed during drying) is listed in Table 8.
[0168] The in vitro permeation of PPA-HCl through human cadaver skin from these discs was pe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thick | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com