Devices and methods for controlling expandable prostheses during deployment
a technology of expandable prostheses and devices, applied in the field of devices and methods for controlling expandable prostheses during deployment, can solve the problems of stents facing, large vessel size, and very long stents, and achieve the effect of preventing excessive spacing or overlap and facilitating the delivery of stents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
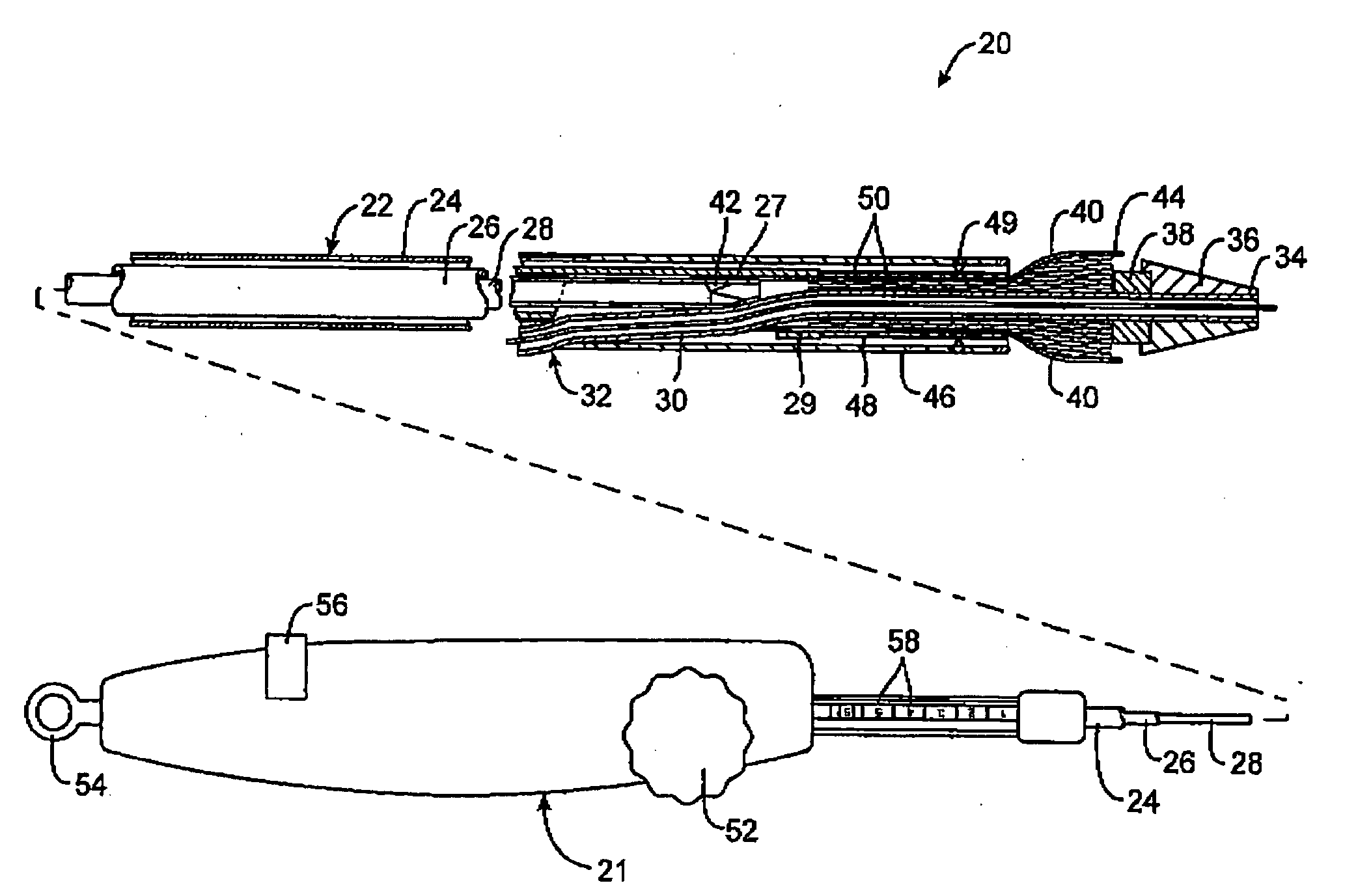
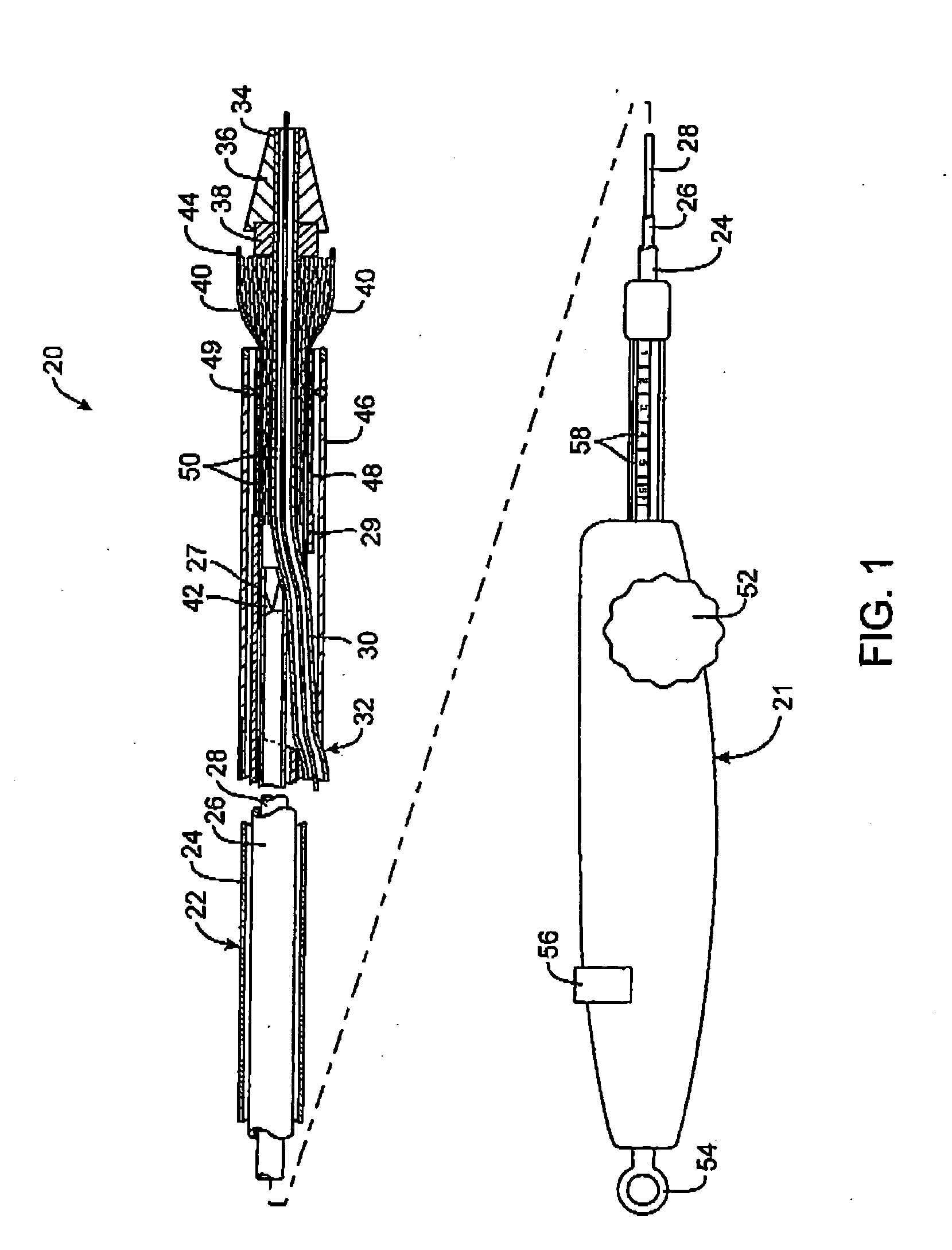
[0039] Referring to FIG. 1, a first embodiment of a prosthesis delivery catheter according to the invention is illustrated. Delivery catheter 20 may have any of various constructions, including that described in co-pending application Ser. No. 10 / 637,713, filed Aug. 8, 2003 (Attorney Docket No. 21629-000340), which is incorporated herein by reference. Delivery catheter 20 has a handle assembly 21 and an elongated catheter body 22 that includes three concentric tubular shafts all axially slidable relative to one another: an outer shaft 24, a pusher 26, and an inner shaft 28. Pusher 26 has a distal extension 27 to which a pusher ring 29 is fixed. In a distal region of the catheter body 22, a guidewire tube 30 extends slidably through a port 32 in outer shaft 24 and through pusher ring 29 and has a distal end 34, to which is mounted a nosecone 36 and a stop member 38.
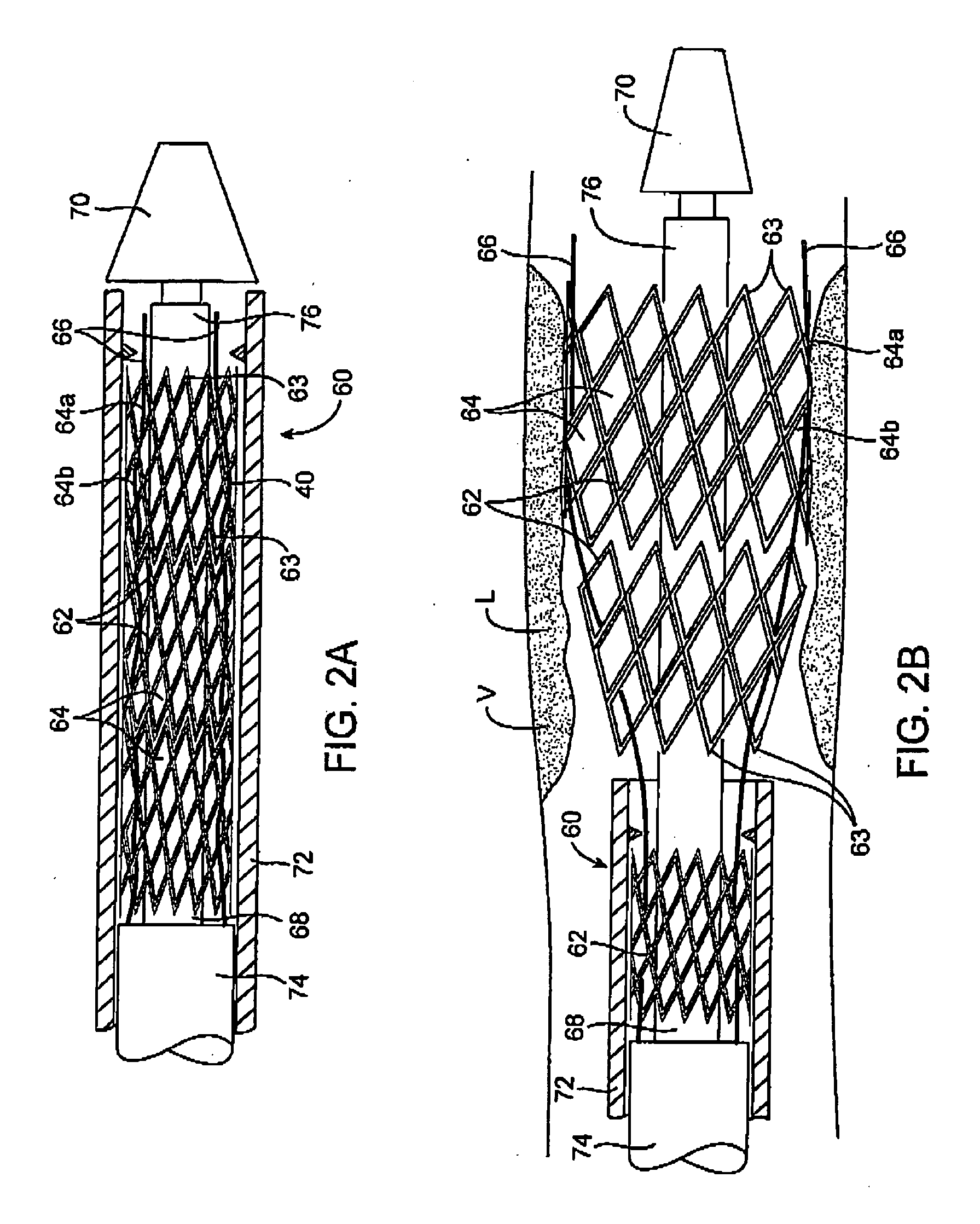
[0040] Delivery catheter 20 further includes one or more stent expansion control members, which in the illustrated embo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com