Nucleic acid amplification and detection method
a nucleic acid and detection method technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid chemistry, can solve the problems of limiting the sensitivity of this latter, affecting the cost-effectiveness of industrial-scale production, and affecting the development of microarrays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Efficient Introduction of Nucleophiles onto Glass Surfaces
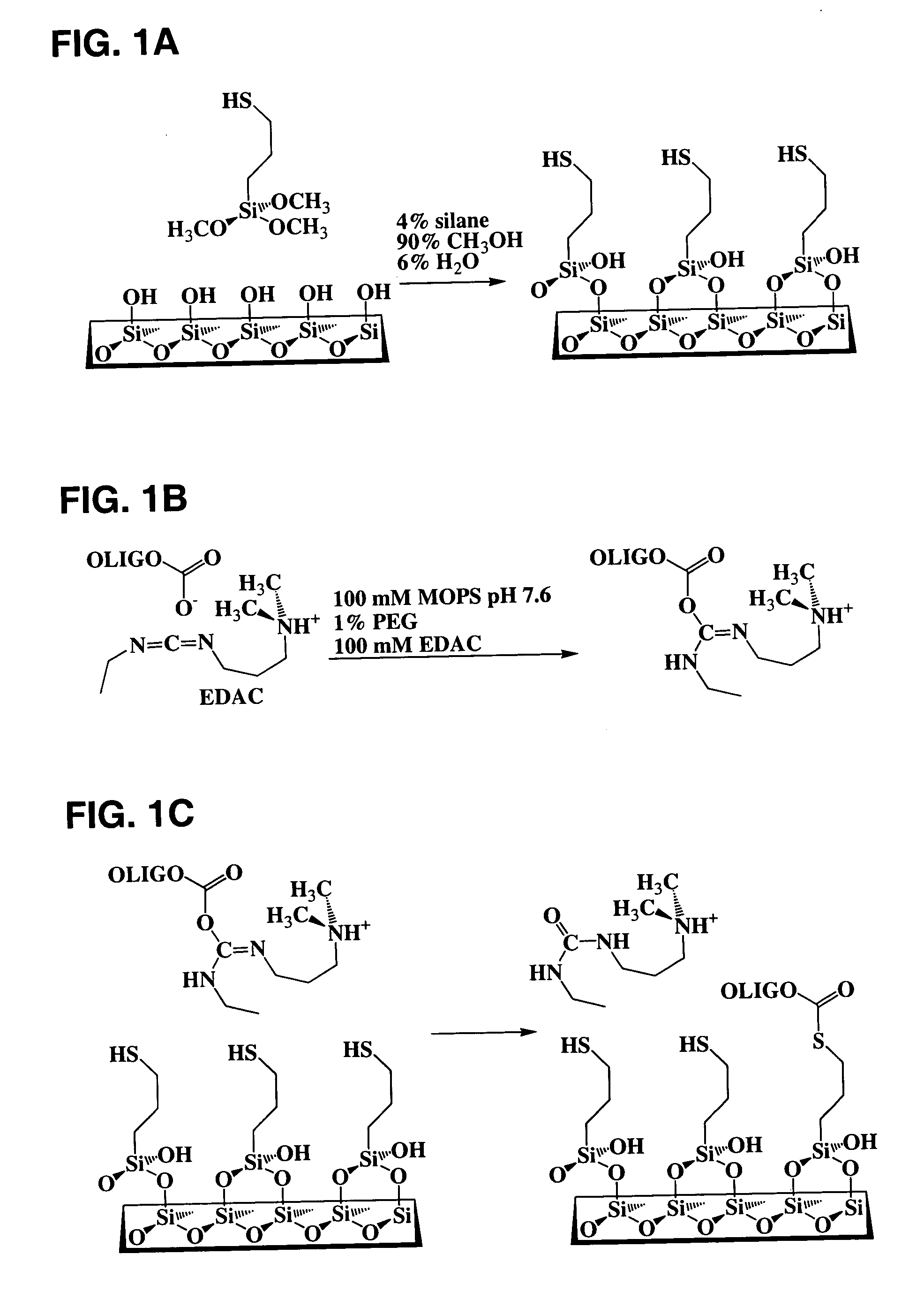
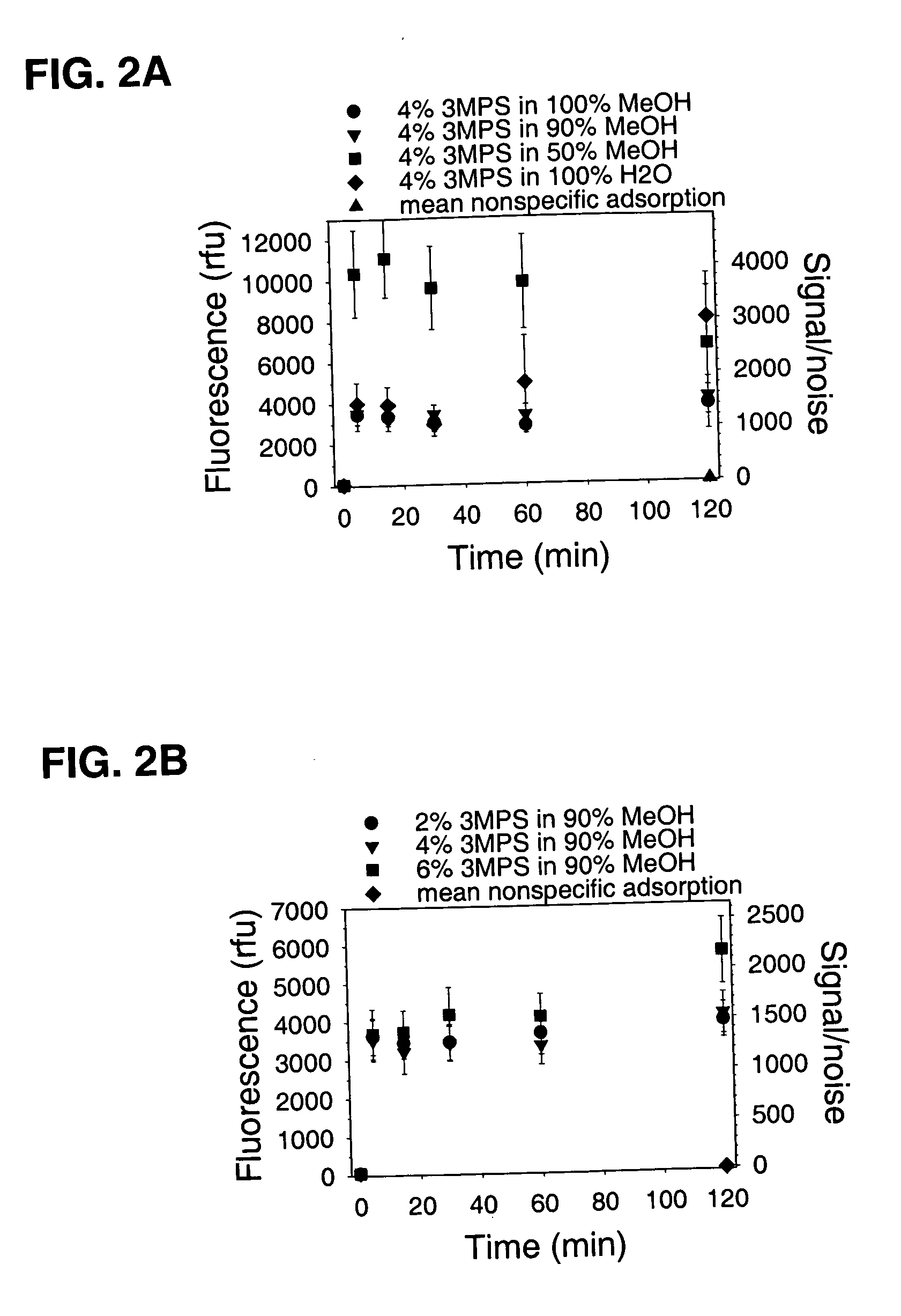
[0073] Glass-bottomed polystyrene 96-well plates (Whatman Polyfiltronics; Rockland, Mass.) were cleaned by soaking in a solution of 10% H2O / 50% MeOH in water for 30 minutes at room temperature, washed with water three times using an automated plate washer, and then dried in a vacuum desiccator for at least 2 hours. Cleaned and dried plates were contacted with 100 μl per well of different concentrations of 3-(mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (3 MPS) in various solvent mixtures for different times at room temperature (about 23° C.), washed manually three times with 100 μl of 90% MeOH, washed three times with 100 μl water using the automated plate washer, and then vacuum desiccated overnight. Wells (n=12) from the 120 minute time point were used subsequently for studying nonspecific binding. Coupling reactions were carried out by contacting the silanized surfaces for 60 minutes at room temperature with 25 pmol of a synthetic oli...
example 2
Coupling Oligonucleotides to Glass or Plastic Microparticles
[0077] Batches of magnetic porous glass (MPG) 5 μm microparticles obtained from CPG, Inc., (Lincoln Park, N.J.) were allowed to react with 3 MPS or γ-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (GAPS) and subsequently coupled with a fluorescent oligonucleotide. In this procedure GAPS was used for introducing functional amine groups instead of sulfhydryl groups onto different surfaces. Uncoated 5 μm Magnetic Porous Glass microparticles had nominal surface areas of 314 μm2 per particle. Sulfhydryl derivatized 1.46 μm ESTAPOR polystyrene magnetic microparticles from Merck Eurolab S.A., (France) had nominal surface areas of 6.70 μm2 per particle. Using either 3.60×106 glass or 1.69×108 polystyrene microparticles per ml, samples were washed 3 times using 1 ml volumes of 90% MeOH, and placed in vacuum desiccator to dry. Separate aliquots of glass microparticles were suspended in 4% 3 MPS or GAPS dissolved in 90% MeOH, incubated for 2 hours with...
example 3
Effect of pH Range and Buffer Type on Oligonucleotide Coupling
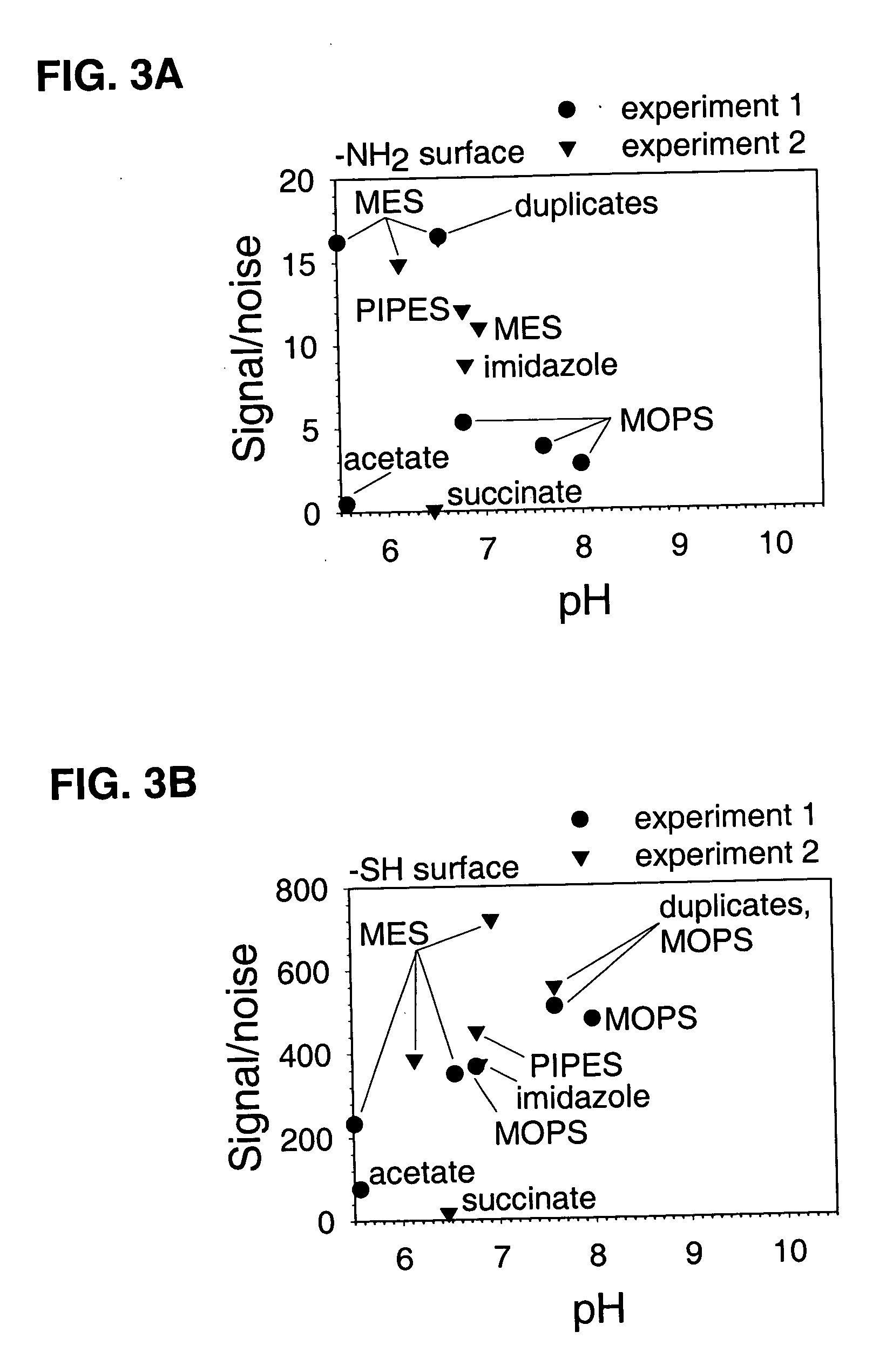
[0080] A glass-bottomed polystyrene 96 well plate was cleaned and then dried overnight as described under Example 1. Wells of the cleaned plate were contacted with 100 μl per well of 4% 3 MPS or 4% GAPS dissolved in 90% MeOH at room temperature for 120 minutes, then washed manually three times with 90% MeOH, washed with an automated plate washer three times with water, and vacuum desiccated overnight. Wells from the 120 minute timepoint (n=12) were subsequently used for studying nonspecific binding of oligonucleotides. Coupling reactions were performed using 25 pmol of the carboxylated and fluoroscein-labeled oligonucleotide from Example 1 in 100 μl volumes of a solution made 0.1 M of the indicated buffer, 1% PEG, and 0.1 M EDAC for 60 minutes at room temperature. EDAC was omitted from control trials that monitored nonspecific reactions. Wells were soaked in 1× TENT buffer (for 3 MPS-treated surfaces) or in a solution of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com