Delta 4, 5 glycuronidase and uses thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Molecular Cloning of Δ4, 5 Glycuronidase Gene from F. heparinum Genome
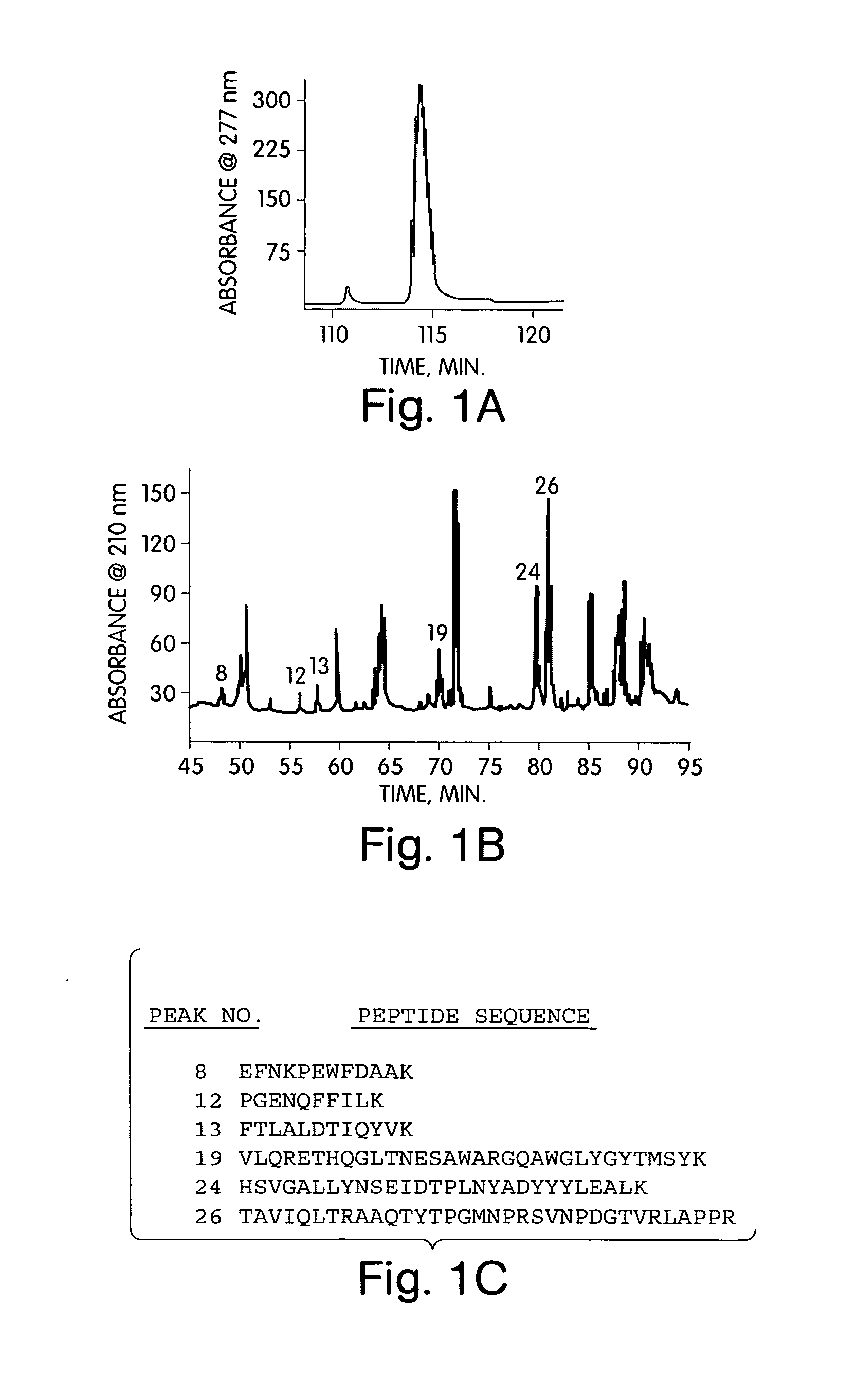
[0162] To clone the Δ4, 5 glycuronidase gene, we isolated a series of Δ4, 5 glycuronidase-derived peptides after protease treatment of the purified enzyme. The native enzyme was directly purified from fermentation cultures of F. heparinum using a 5-step chromatography scheme as previously described [McLean, M. W., Bruce, J. S., Long, W. F., and Williamson, F. B., 1984, Eur J Biochem 145, 607-15]. The extent of purity was ultimately characterized by reverse phase chromatography, which indicated a single major peak (FIG. 1A). We were able to generate a number of peptides by a limited trypsin digestion of the purified enzyme. 26 peptide fragments were resolved by reverse phase chromatography (FIG. 1B). From these 26, at least eight peptides (corresponding to major peaks 8, 12, 13, 19, 24, and 26) were of sufficient yield and purity and were selected for protein sequence determination (FIG. 1C).
[0163] Based on this ...
example 2
Recombinant Expression and Purification of the Δ4, 5 Glycuronidase
[0167] Using PCR, we cloned from the F. heparinum genome both the full-length enzyme and the “mature” enzyme lacking the N-terminal 20 amino acid signal sequence (Δ4,5Δ20) into a T7-based expression plasmid. Cloning into pET28a permitted the expression of the glycuronidase as an N-terminal 6×His-tag fusion protein. Pilot expression studies focused on the full-length enzyme. In these initial experiments, we examined several different induction conditions such as temperature, time and length of induction, and even IPTG concentrations. In every case, the full-length enzyme was present nearly exclusively as an insoluble fraction. Attempts to purify the enzyme directly from inclusion bodies and then refold the apparently mis-folded protein were initially not successful; while solubility was partially achieved by a combined use of detergents (e.g., CHAPS), increasing salt concentrations, and the presence of glycerol, the p...
example 3
Biochemical Conditions for Optimal Enzyme Activity
[0171] To determine the optimal reaction conditions for Δ4, 5 glycuronidase activity, we analyzed initial reaction rates as a function of buffer, pH, temperature, and ionic strength (FIG. 6). For these experiments, we used the disulfated heparin disaccharide substrate ΔUHNS,6S. Based on what is known about the degradation of heparin / heparan sulfate-like glycosaminoglycans byflavobacteria as well as initial biochemical characterization of this and related enzymes [Warnick, C. T. and Linker, A., 1972, Biochemisiry 11, 568-72], we hypothesized that a heparin disaccharide would be an optimal substrate for the Δ4, 5 glycuronidase. Enzyme activity was routinely monitored by a loss of absorbance at 232 nm, corresponding indirectly to the hydrolysis of the uronic acid from the non-reducing end.
Results
[0172] Under these conditions, we observed a NaCl concentration-activity dependence that was optimal between 50 and 100 mM. NaCl concentrat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Substance count | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com