Semiconductor device with multi-bank DRAM and cache memory
a multi-bank, cache memory technology, applied in the direction of memory adressing/allocation/relocation, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of mounting space, no refresh operation, and complicated and troublesome control of the dram
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
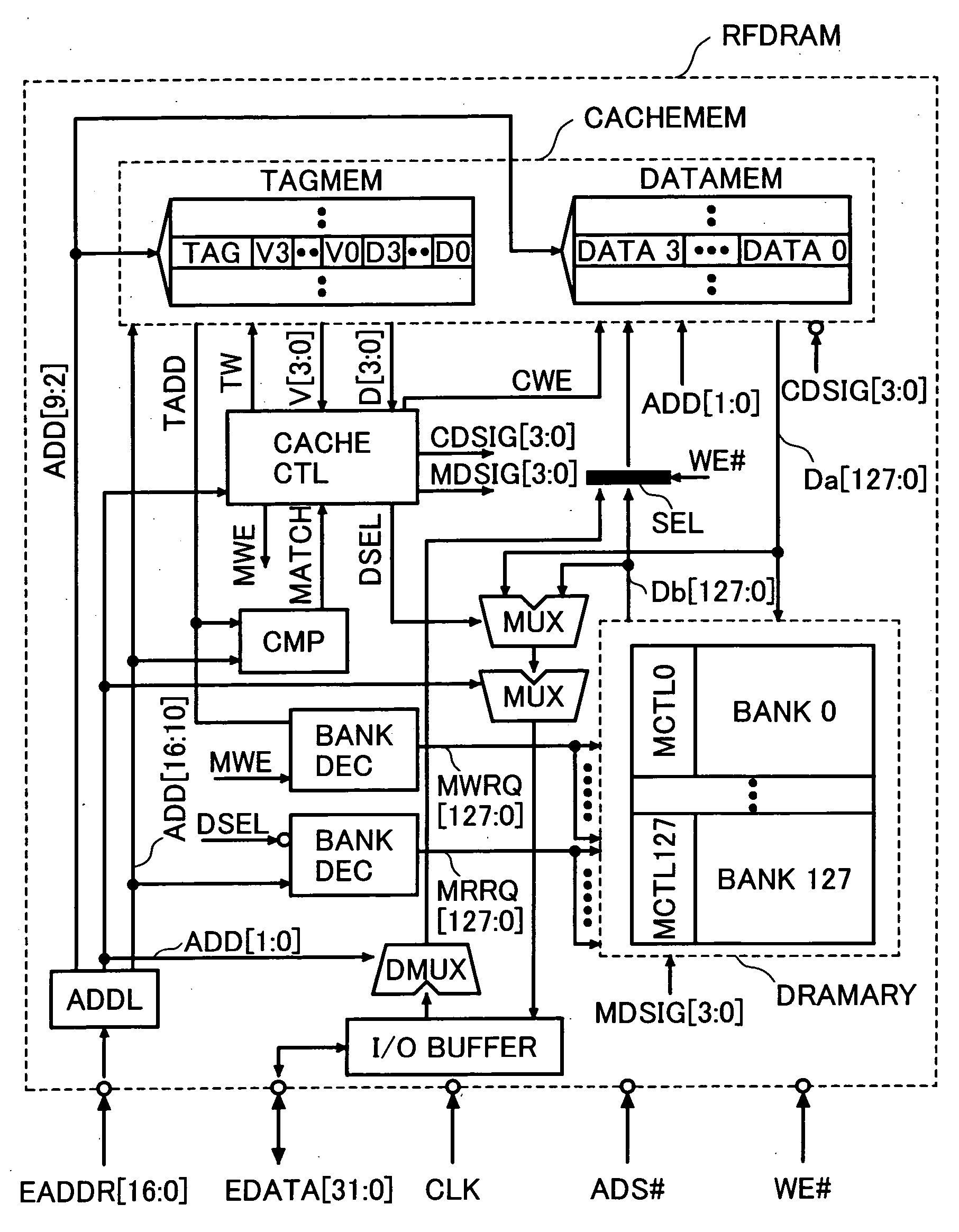
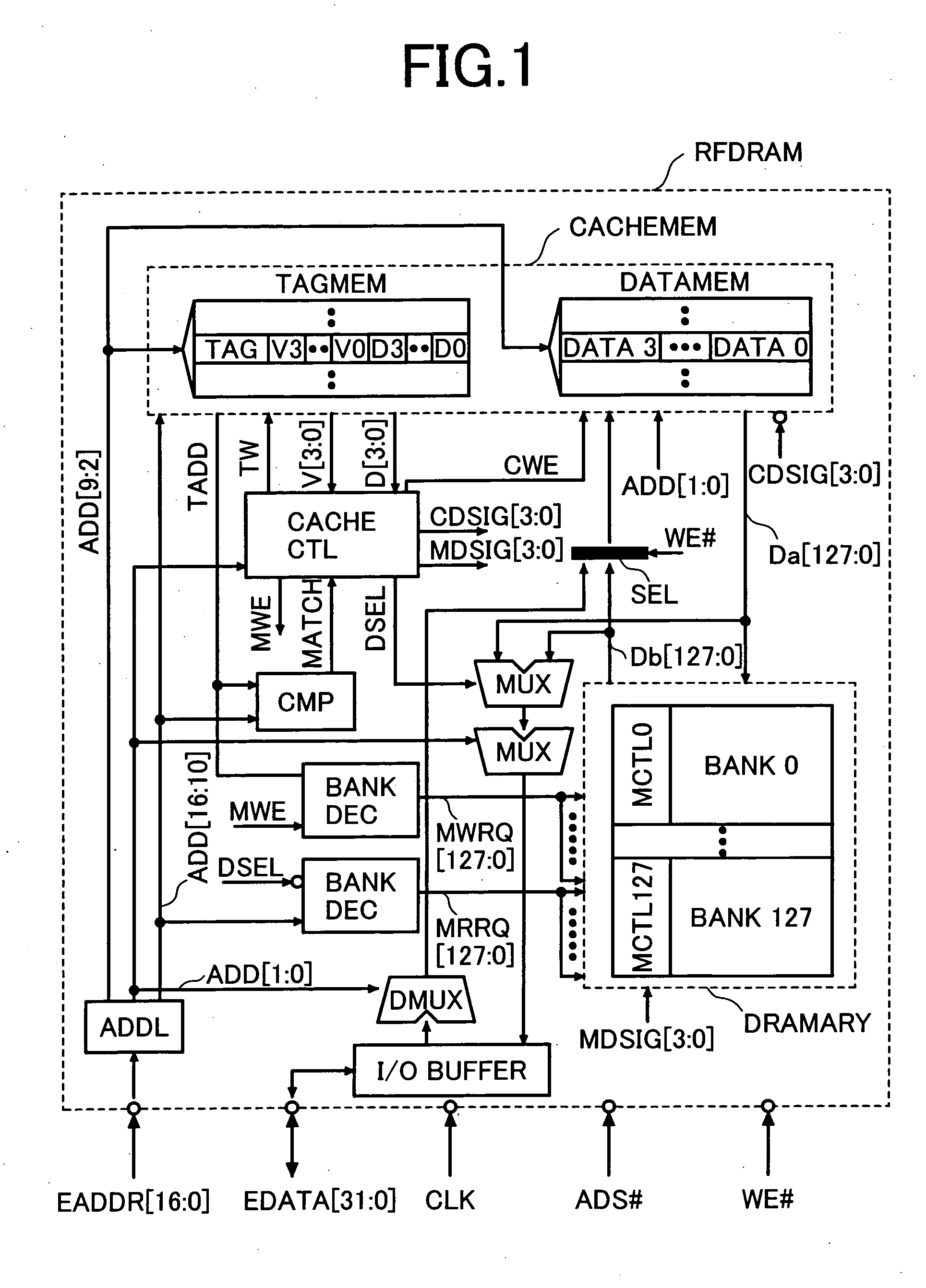
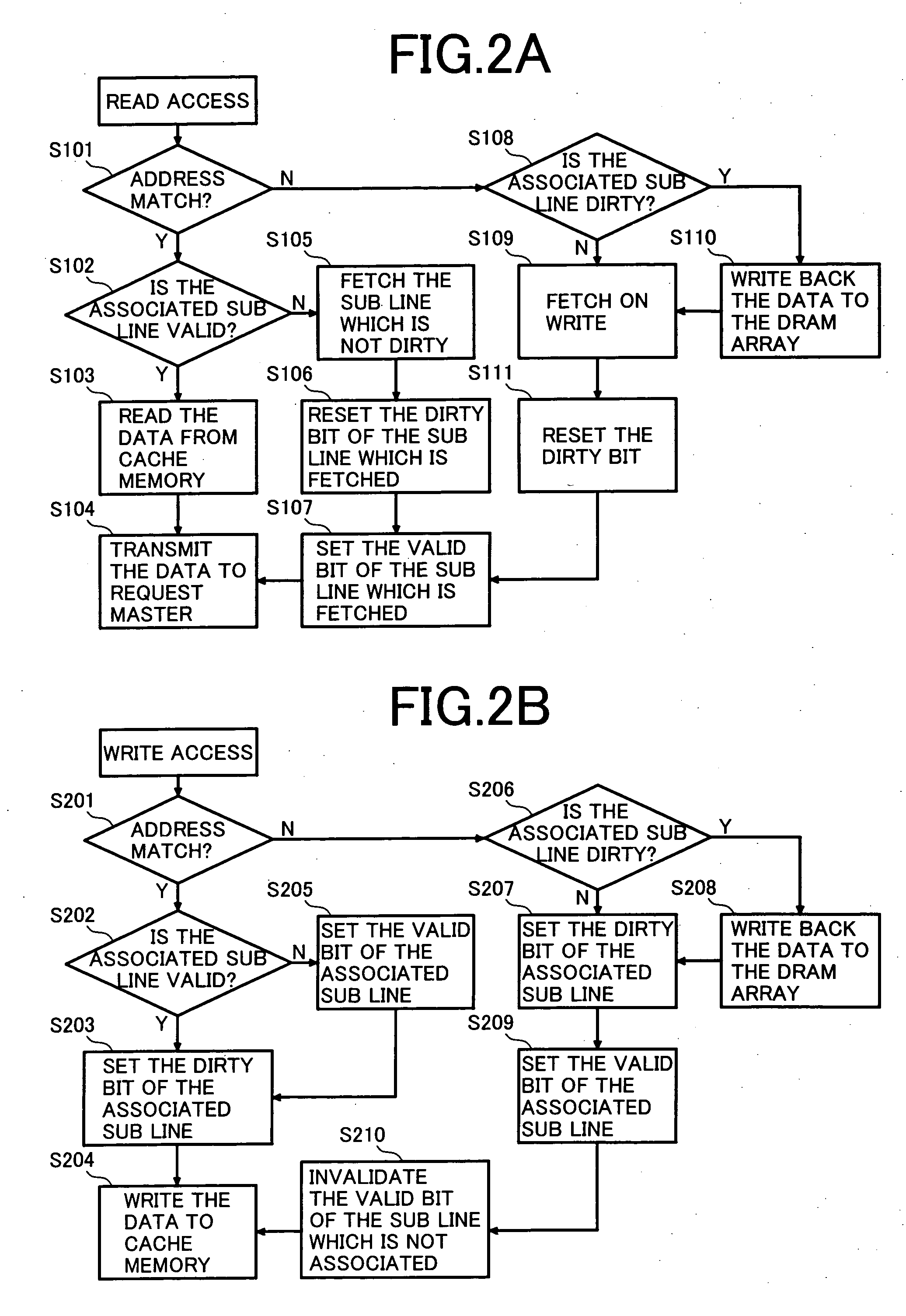
[0026]FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of a refresh free dynamic memory RFDRAM (referred to as RFDRAM hereinafter), which is a memory device in an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 shows a flowchart of the operation of the RFDRAM. FIG. 3A and 3B show embodiments of a cache memory and FIGS. 4A and 4B show embodiments of a DRAM memory array used in the RFDRAM shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 5 shows a timing chart of the RFDRAM denoting that it is possible to avoid a confliction between an access and a refresh operation requested to the DRAM array concurrently.
[0027] As shown in FIG. 1, the RFDRAM is composed of a cache memory CACHEMEM and a DRAM array DRAMARY, which consists of a plurality of DRAM banks (128 banks (bank 127 to bank 0)) In the example shown in FIG. 1, the capacity of one bank is 32k bits and the total capacity of the memory is 4M bits. The capacity of the cache memory CACHEMEM is equivalent to that of one bank. In FIG. 1, the cache memory consists of 16-byte wide cache li...
second embodiment
[0073]FIG. 6 shows the second embodiment of the RFDRAM of the present invention. The cache memory in this embodiment is controlled by the direct mapped caching scheme. The main difference from the first embodiment is that the external data bus EDATA[127:0] and the internal data bus Da[127:0] / Db[127:0] is equal in data width. In other words, the data width is the same among the data input / output to / from the DRAM array DRAMARY, the cache line, and the external data bus EDATA[127:0]. This configuration can eliminate dividing of a cache line into sub lines, so that the tag memory TAGMEM requires only a valid bit and a dirty bit. In addition, because the minimum unit of data management is equal to the data width of the cache line, the cache data control signal CDSIG[3:0] and the memory data control signal MDSIG[3:0] can be omitted. The address match signal MATCH is used instead of the data select signal DSEL that is inputted to the multiplexer MUX.
[0074] The memory operation in the seco...
third embodiment
[0083]FIG. 7 shows the third embodiment of the RFDRAM of the present invention. The main difference from the first and second embodiments is that the cache memory CACHEMEM is composed of a plurality of tag memories TAGMEMa and TAGMEMb, as well as a plurality of data memories DATAMEMa and DATAMEMb and the set associative method is employed to control the cache memory CACHEMEM in this embodiment. The cache hit decision method in this embodiment also differs from that in other embodiments. In addition, the RFDRAM is provided with a write buffer WBUFFER, a write back buffer WBB, a hit way signal HITWAY, a way selector signal WAYSEL, and a write tag address bus WTADD, etc.
[0084] On the other hand, there in no need to divide a cache line into sub lines in this third embodiment, so that the cache data control signal CDSIG[3:0] and the memory data control signal MDSIG[3:0] are omitted just like in the second embodiment. Just like in the second embodiment, each cache line is provided with a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com