Barrier layer for electroplating processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
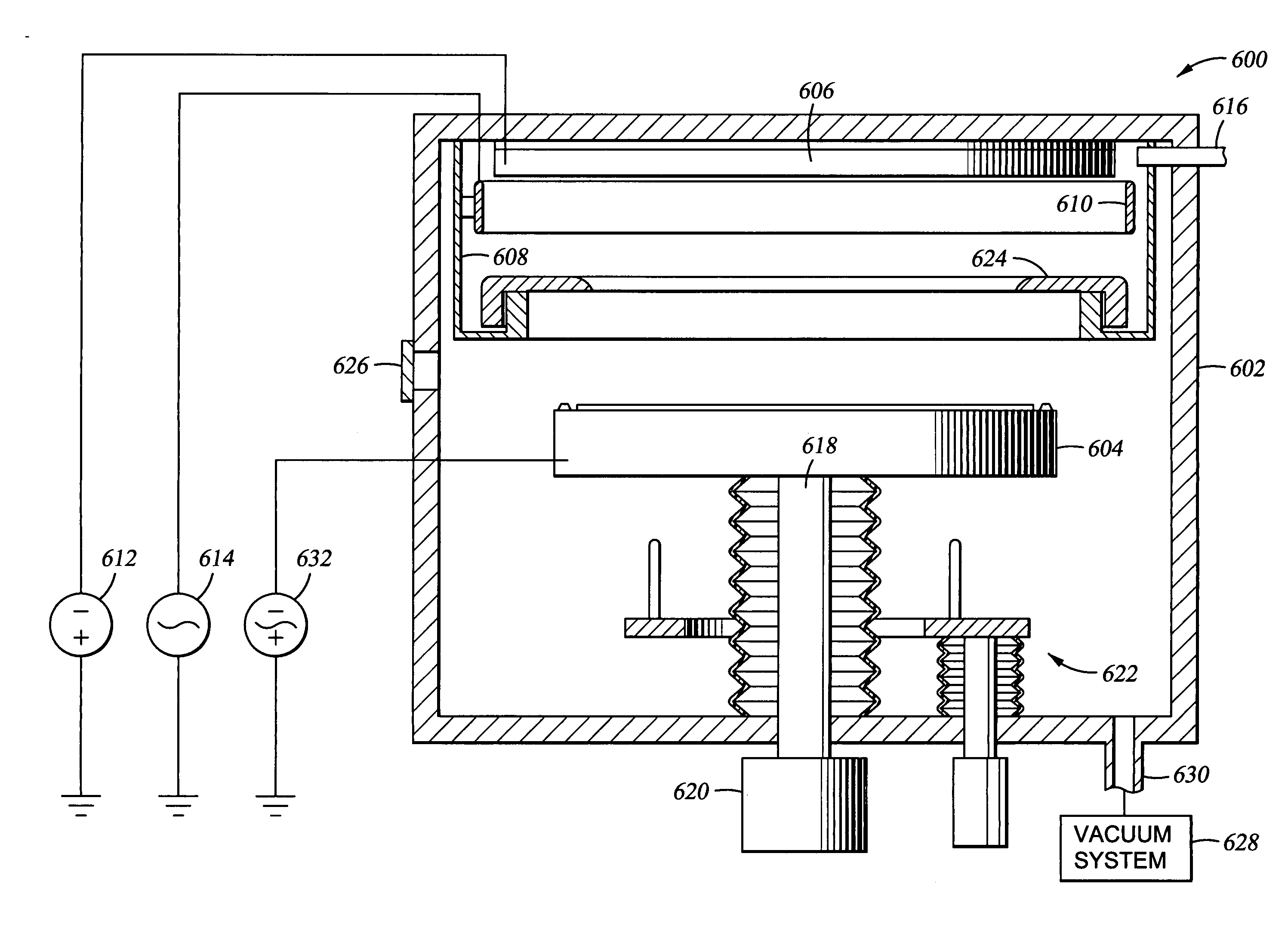
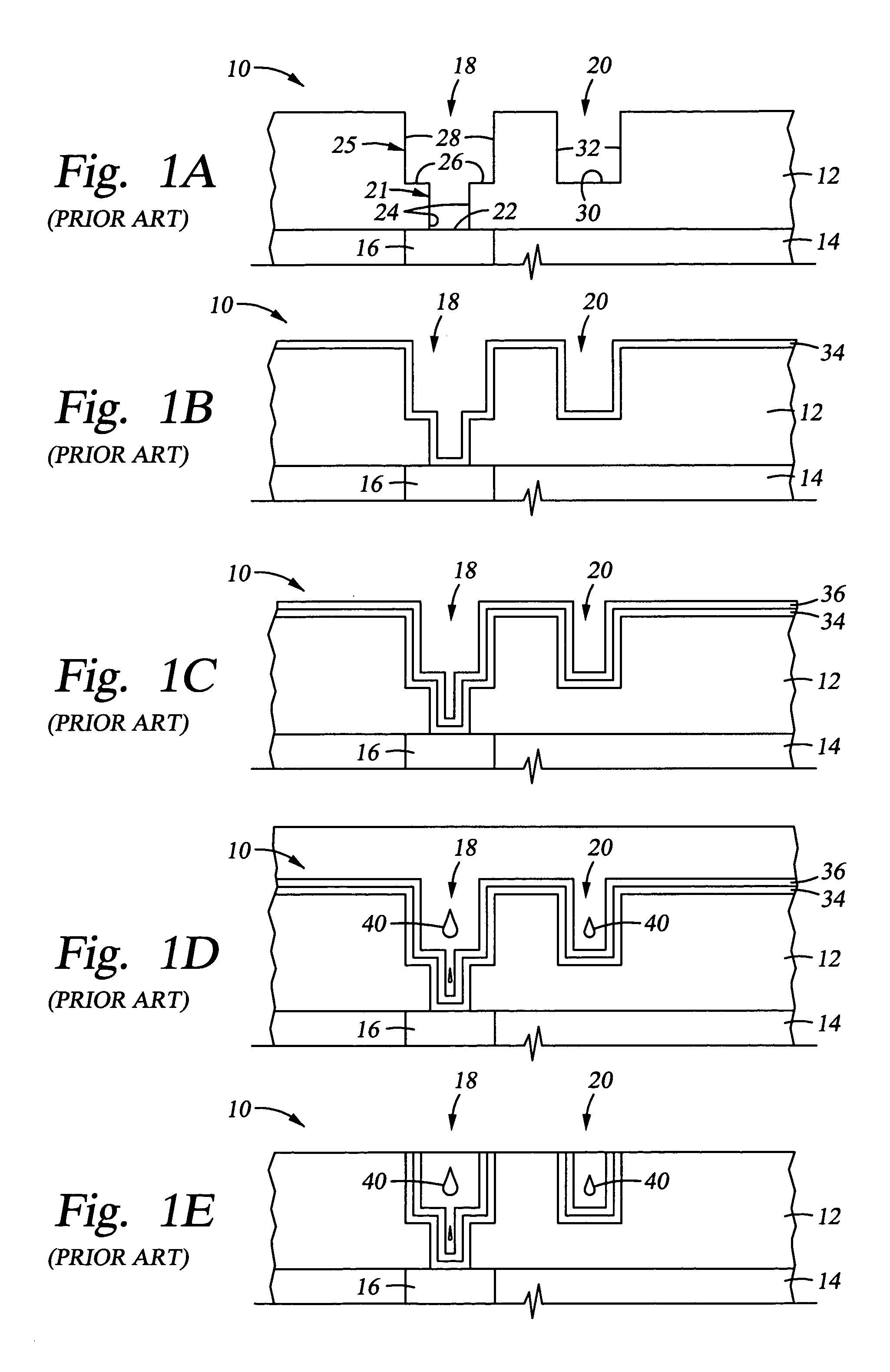
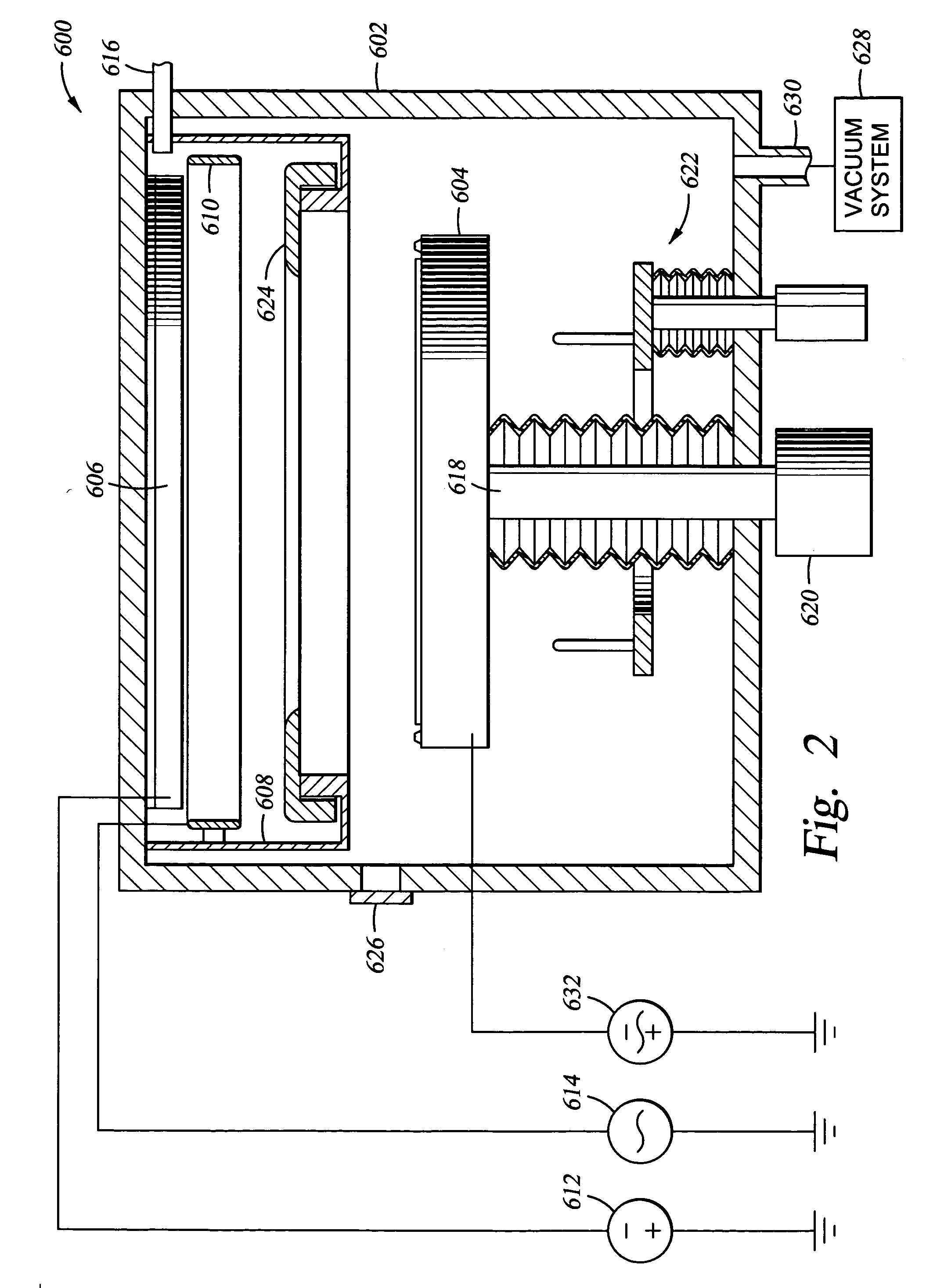
[0031] The present invention provides methods for improving the electroplating fill of high aspect ratio, sub-micron interconnect features. Although the invention is described using a dual damascene structure on a substrate, the invention contemplates applications in other interconnect features and other integrated circuit features (i.e., lines, vias, contacts, plugs, etc.) that require filling the features formed on a substrate with a metal. Also, although the invention is described using copper as the electroplated metal for metallization of the feature, the invention is applicable to other metals that can be electroplated onto a substrate.
[0032] Generally, a continuous metal seed layer is essential for conducting an electrical current to the surfaces to be plated by the electroplating process. Typically, the seed layer is deposited using PVD techniques, which has not provided satisfactory results for forming a uniform, continuous seed layer at the bottom of high aspect ratio, su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com