Rotary drag-type drill bits and methods of designing such bits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
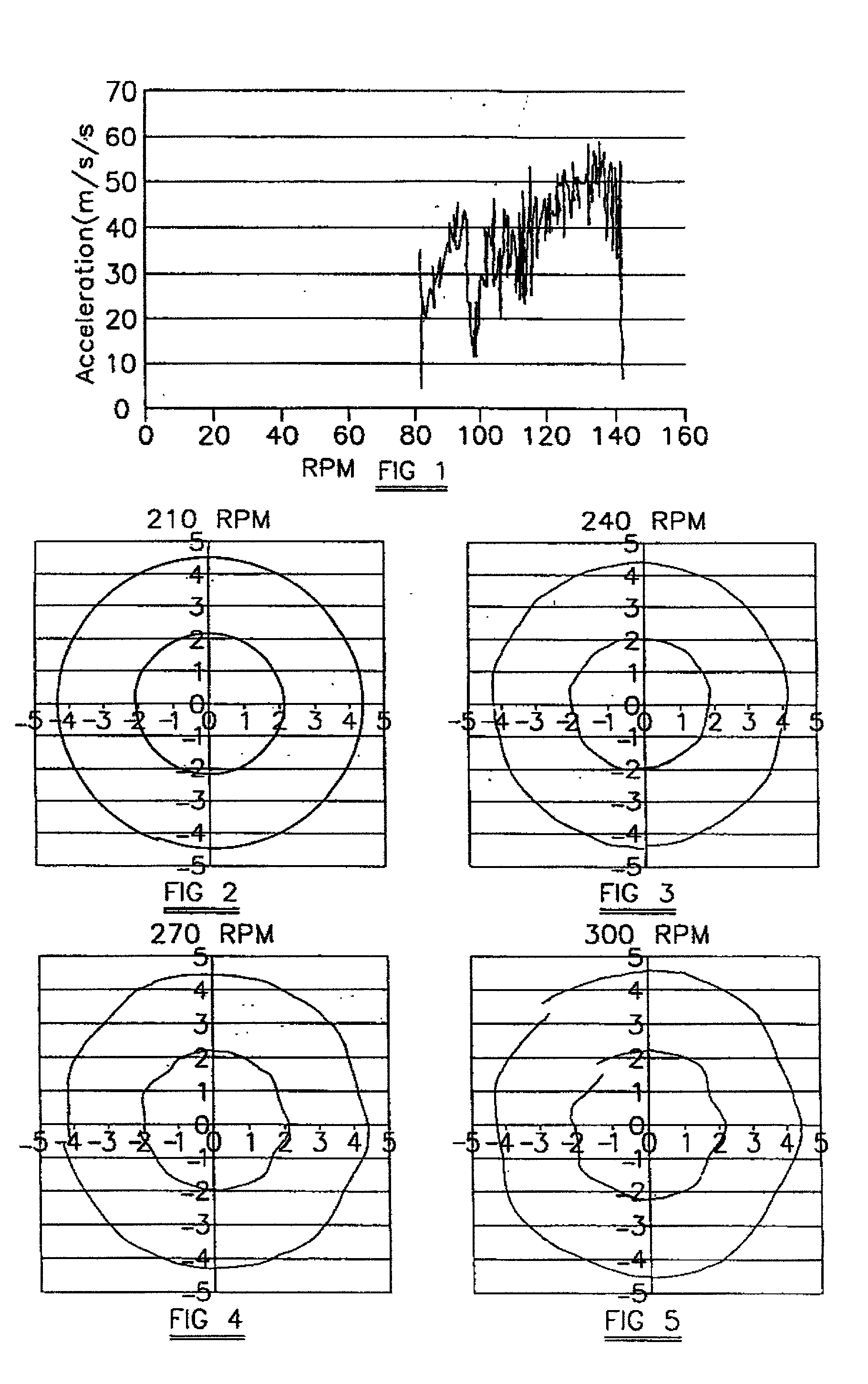
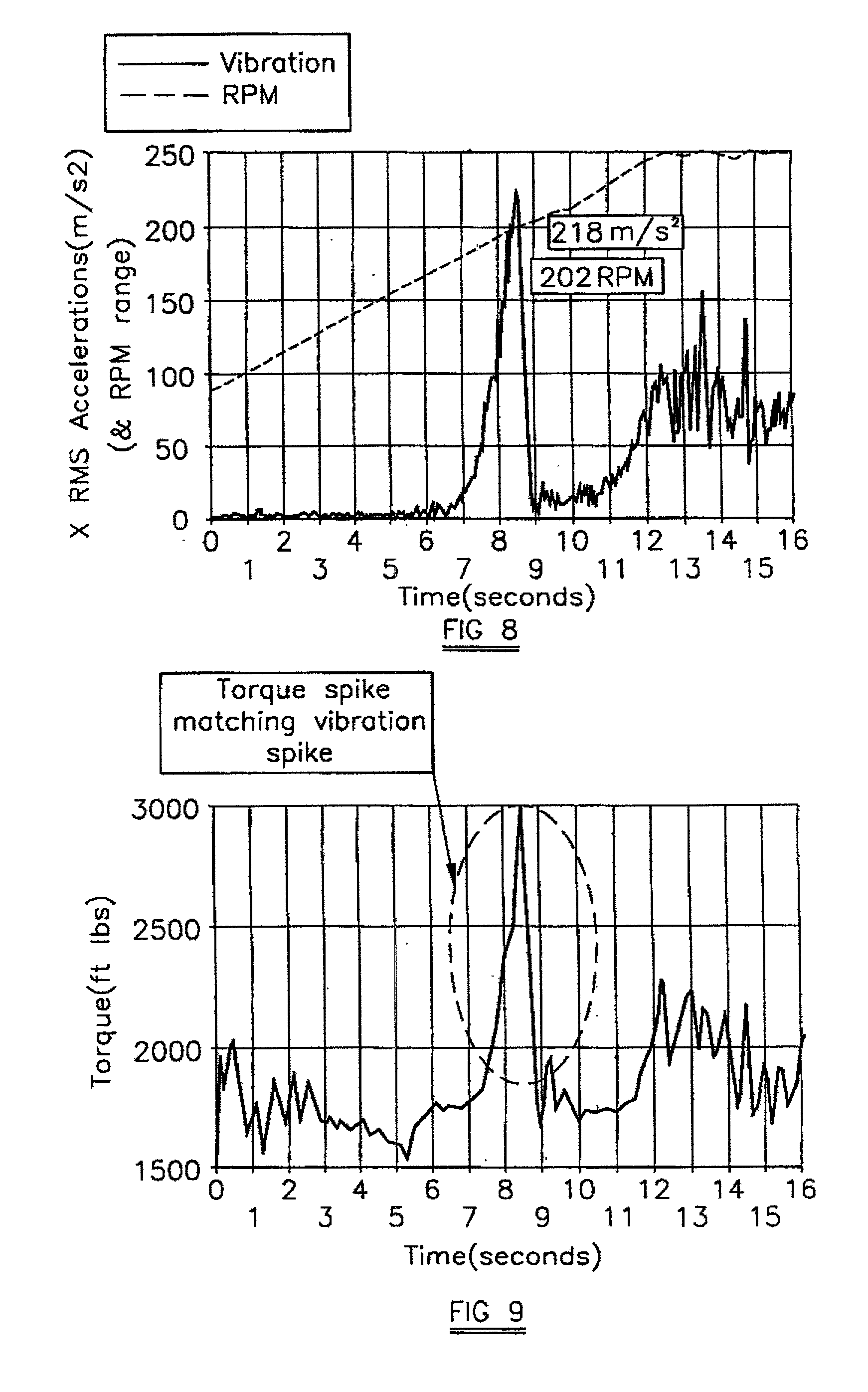
[0045] FIG. 1 shows the lateral vibration of a particular drag-type rotary drill bit (Bit A) plotted against rpm, the vibration being plotted as lateral acceleration in meters / s / s, and the data being acquired in laboratory drilling tests. This shows that Bit A is not stable, experiencing lateral vibration that rises quickly with rotary speed to 60 m / s / s. However, contrary to the conventional teaching in the drill bit art, which considers that bit stability is required in order to reduce torsional vibrations, Bit A is found to exhibit a very low incidence of stick-slip while drilling.
[0046] This characteristic has been found in other PDC drill bits; and FIGS. 2-5 show the patterns of lateral vibration in an 81 / 2 inch unbalanced drill bit (Bit B) with increase of rotary bit speed from 210 rpm to 300 rpm.
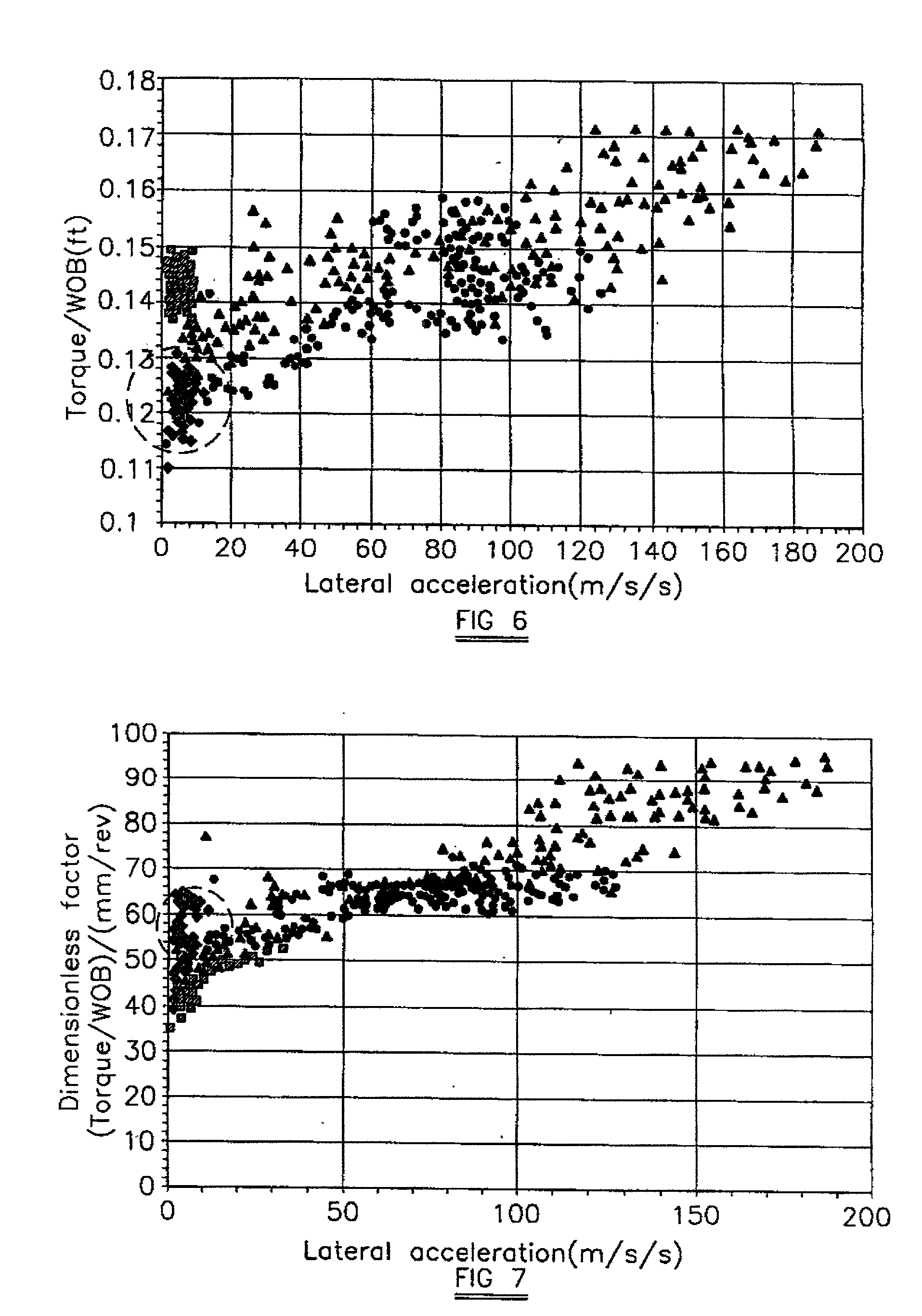
[0047] FIGS. 6 and 7 show the correlation between lateral vibration and torque in Bit B. In FIG. 6 torque / weight-on-bit, in feet, is plotted against lateral acceleration, in m / s / s, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com