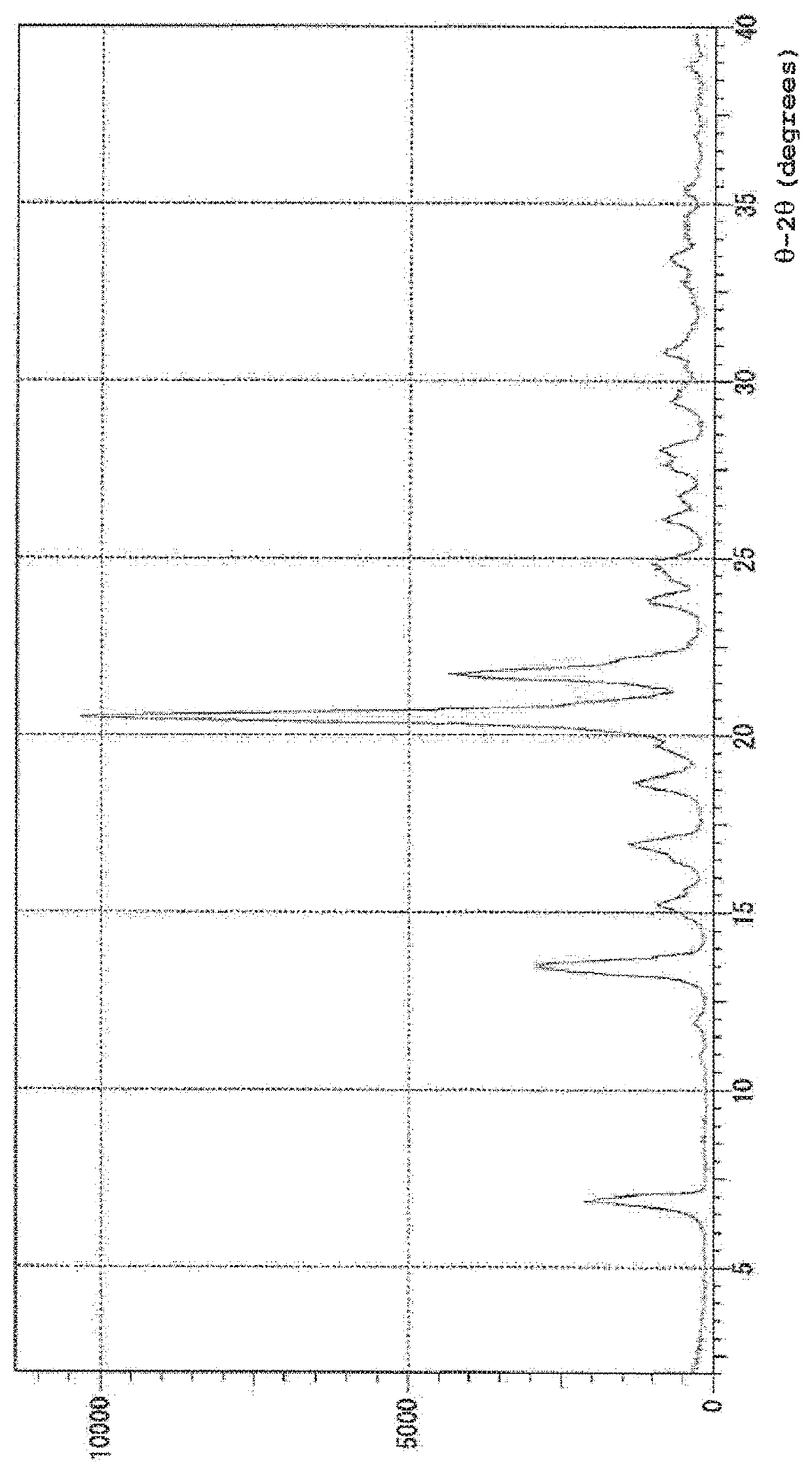
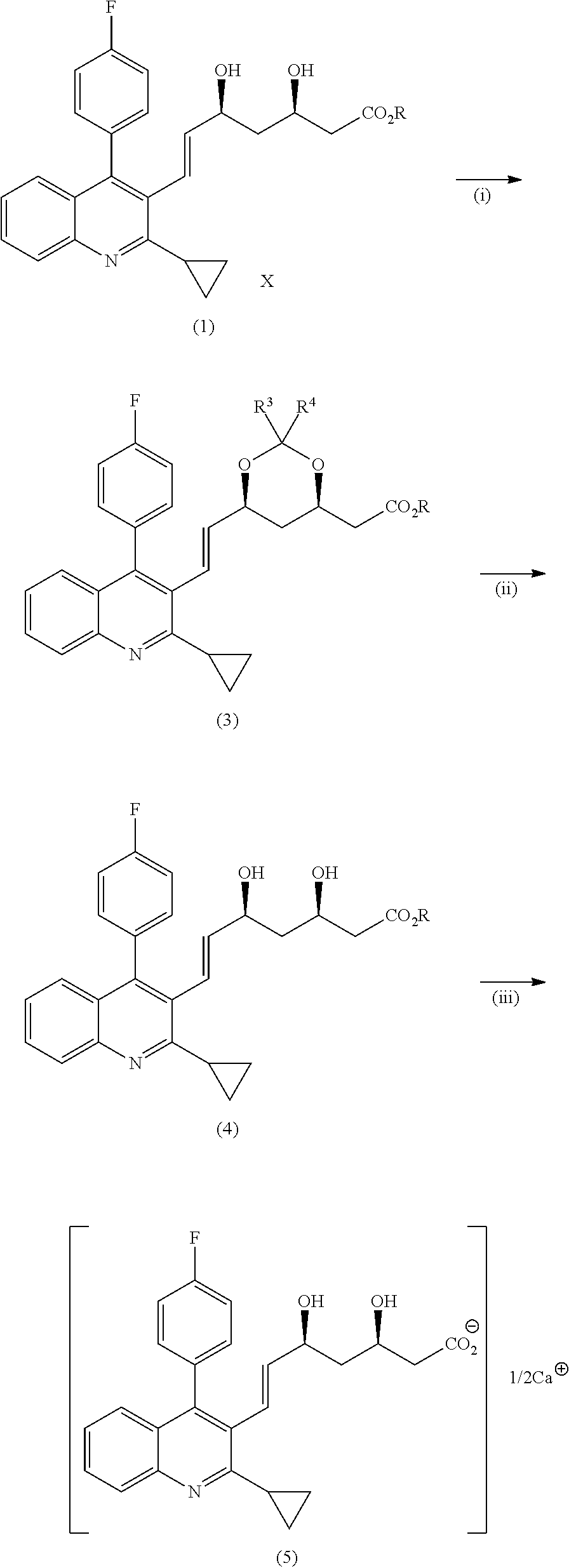
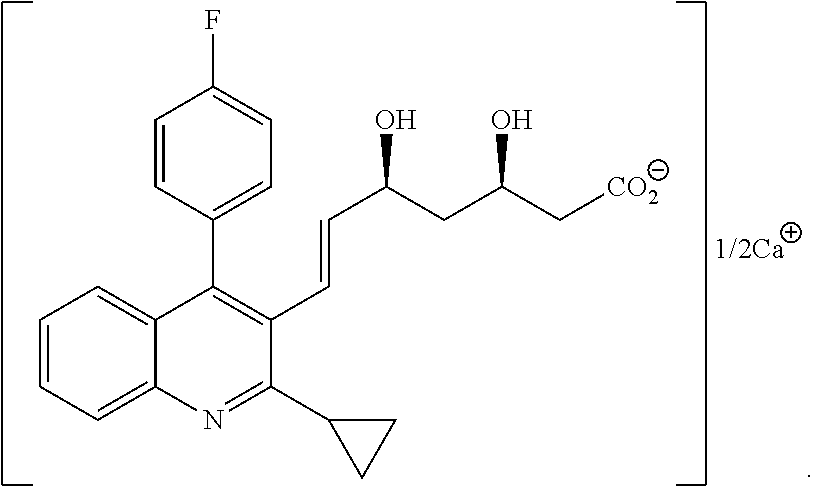
Method for producing pitavastatin calcium
a production method and technology of pitavastatin, applied in the field of improved production methods of pitavastatin calcium, can solve the problems of high cost, insufficient production of 2 types of pitavastatin, and concern about costs, and achieve the effects of low cost, high selectivity, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 (
Production of PT-DOXE)
[0249]
[0250]Under a nitrogen atmosphere, sodium hydride (20.8 g, purity 59.5%, 515 mmol) and THF (200 mL) were charged in a flask and cooled to 17° C. To this mixture was added dropwise a solution of DHAB (53.9 g, purity 91.9%, 247.1 mmol) in THF (200 mL) over 2 hr, and the solution after completion of the dropwise addition was stirred at 25° C. for 13 hr.
[0251]To the solution after stirring was added dropwise a solution of PT-ALD (40.0 g, 137.3 mmol) in THF (400 mL) over 4 hr, and the solution after completion of the dropwise addition was stirred at 25° C. for 1 hr. The solution after stirring was analyzed by HPLC to find that the conversion ratio to PT-DOXB was 99.2%.
[0252]To the solution after stirring were added dropwise n-heptane (200 mL) and water (400 mL) at 25° C. and partitioned. Thereafter, the organic layer was washed with 4 wt % aqueous sodium chloride solution, 10 wt % aqueous citric acid solution and 10 wt % aqueous sodium chloride solution. The o...
example 2 (
Production of PT-DOXB)
[0255]
[0256]Under a nitrogen atmosphere, sodium hydride (15.6 g, purity 59.5%, 386 mmol), THF (150 mL) and N,N-dimethylformamide (75 mL) were charged in a flask and cooled to 5° C. To this mixture was added dropwise a solution of DHAB (40.4 g, purity 91.9%, 185.4 mmol) in THF (150 mL) over 2 hr, and the mixed solution after completion of the dropwise addition was stirred at 8 to 10° C. for 14 hr.
[0257]To the mixed solution after stirring was added dropwise a solution of PT-ALD (30.0 g, 103.0 mmol) in THF (225 mL) over 3 hr, and the solution after completion of the dropwise addition was stirred at 8 to 10° C. for 6 hr. The solution after stirring was analyzed by HPLC to find that the conversion ratio to PT-DOXB was 98.5%.
[0258]To the solution after stirring were added dropwise n-heptane (150 mL) and water (150 mL) at 10° C. and partitioned. Thereafter, the organic layer was washed with 4 wt % aqueous sodium chloride solution, 10 wt % aqueous citric acid solution...
reference example 1 (
Preparation of Bacterial Cells)
[Preparation of Recombinant Escherichia coli 7M109 / pKV320CR1-GDH Co-Expressing Carbonyl Reductase (Hereinafter OCR1) and Glucose-1-Dehydrogenase (Hereinafter GDH)]
(1) Cloning of Gene
[0259]Primers ocr1_F (SEQ ID NO: 3) and ocr1_R (SEQ ID NO: 4) for amplifying full-length ocr1 gene were designed and synthesized based on the gene sequence (ocr1) encoding OCR1 (SEQ ID NO: 2 described in JP-B-4270918) derived from Ogataea minuta variant nonfermentans (Ogataea minuta var. nonfermentans) NBRC (former IFO) 1473. Then, PCR was performed according to a conventional method and using chromosome DNA of Ogataea-Minuta variant nonfermentans (Ogataea minuta var. nonfermentans) as a template to give an about 0.8 kbp DNA fragment.
[0260]Then, based on a gene sequence (hereinafter gdh (SEQ ID NO: 5)) encoding GDH (SEQ ID NO: 6), which is glucose-1-dehydrogenase encoded by a gene (GeneBank Accession No. AL009126.3) derived from Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) wherein...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| carbon number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com