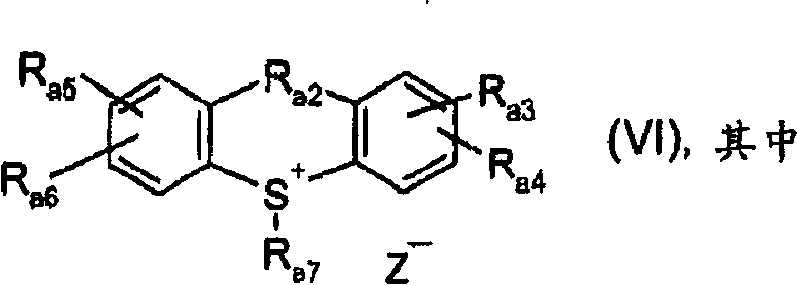
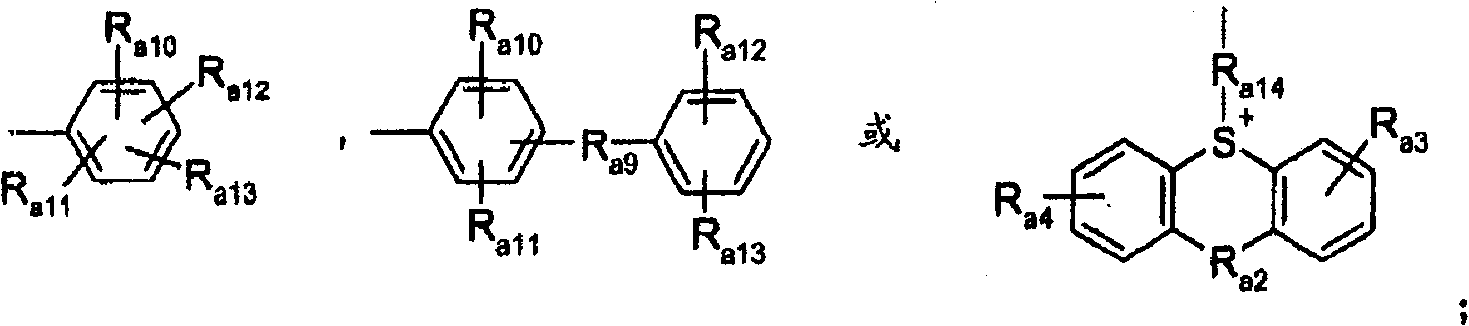
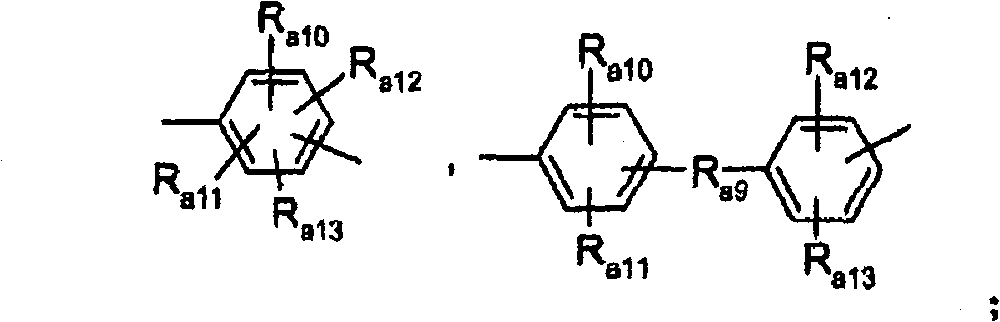
Process for the photoactivation and use of a catalyst by an inverted two-stage procedure
A photocatalyst and photoalkali technology, applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as feasibility and effectiveness without any explanation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0524] In the production of foamed plastics, foaming is often performed in a mould. In such cases, the reaction mixture is placed into a mold, for example, after irradiation and addition of the water component. Suitable mold materials are metal, typically aluminum, or plastic, typically epoxy. In the mold, the foamable reaction mixture rises and forms the molded article. The foam molding can be carried out in such a way that the resulting molding has a microporous surface structure or, alternatively, the molding has a dense skin and a microporous core. In this regard, sufficient quantities of the foamable reaction mixture can be placed in the mold such that the resulting foam just fills the mold. However, it is also possible to place more foamable reaction mixture in the mold than is required to fill the interior of the mold with foam. In the latter case, the operation is then carried out under overfill conditions.
[0525] In the case of foam molding, known external m...
Embodiment 1
[0530] The following preparations are made by mixing the corresponding ingredients:
[0531] Component A
[0532] 54.78 parts of hydroxyl-functional polyacrylate (Desmophen A VP LS 2350, provided by Bayer AG)
[0533] 0.70 parts leveling agent Byk 333 (10% in butyl acrylate, polyether modified polydimethylsiloxane, supplied by Byk Chemical Company)
[0534] 0.50 parts leveling agent Byk 335 (polyacrylate solution, supplied by Byk Chemical Company)
[0535] 0.55 parts of antifoam Byk 141 (polysiloxane, supplied by Byk Chemical Company)
[0536] 18.47 parts of a mixture of xylene / methoxypropyl acrylate / butyl acrylate in a ratio of 1:1:1,
[0537] Component B
[0538] 20.08 parts of aliphatic polyisocyanate (Desmodur N 3390, supplied by Bayer)
[0539] 2.8% photolatent base Can be well dissolved in component A. Before application, component B was added to the sample and homogenized. The coating preparation thus prepared was then placed in a petri dish...
Embodiment 2
[0544] Example 2: Preparation of Polyether and Polyurethane Soft Foam Plastics
[0545] 0.08g (0.05%, based on polyols) amine catalyst, 1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (DBN)
[0546] 0.24g (0.15%, based on polyol) photolatent catalyst PLB-1 dissolved in 160g polyether polyol [Lupranol 2082 (RTM) hydroxyl value 48mg KOH / g, water content less than 0.1%, acid value less than 0.1 mg KOH / g]. Subsequently, the sample was exposed for 2 minutes to a Panacol UVA lamp UVF 450W with a blue light filter.
[0547] Add 9.6 g of solution containing 1.92 g of polysiloxane polyoxyalkylene block copolymer foam stabilizer ( BF 2370; supplied by Goldschmidt, Germany) and 7.68 g deionized water, then the reaction mixture was vigorously stirred at 2600 rpm for 10 s. Then add 0.32g stannous octoate ( 29; supplied by Goldschmidt, Germany), then, the reaction mixture was vigorously stirred at 2600 rpm for 18 s. Subsequently, 94.54 g of isocyanate ( T80, supplied by BASF; mixtur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com