Immunogenic compositions for pneumonia chlamydia
A technology of Chlamydia pneumoniae and immunogenic fragments, which is applied in the field of immunology and vaccinology, and can solve the problem of incompleteness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[1493] Embodiment 1 (in vitro study)
[1494] Screening of antisera based on in vitro neutralizing properties
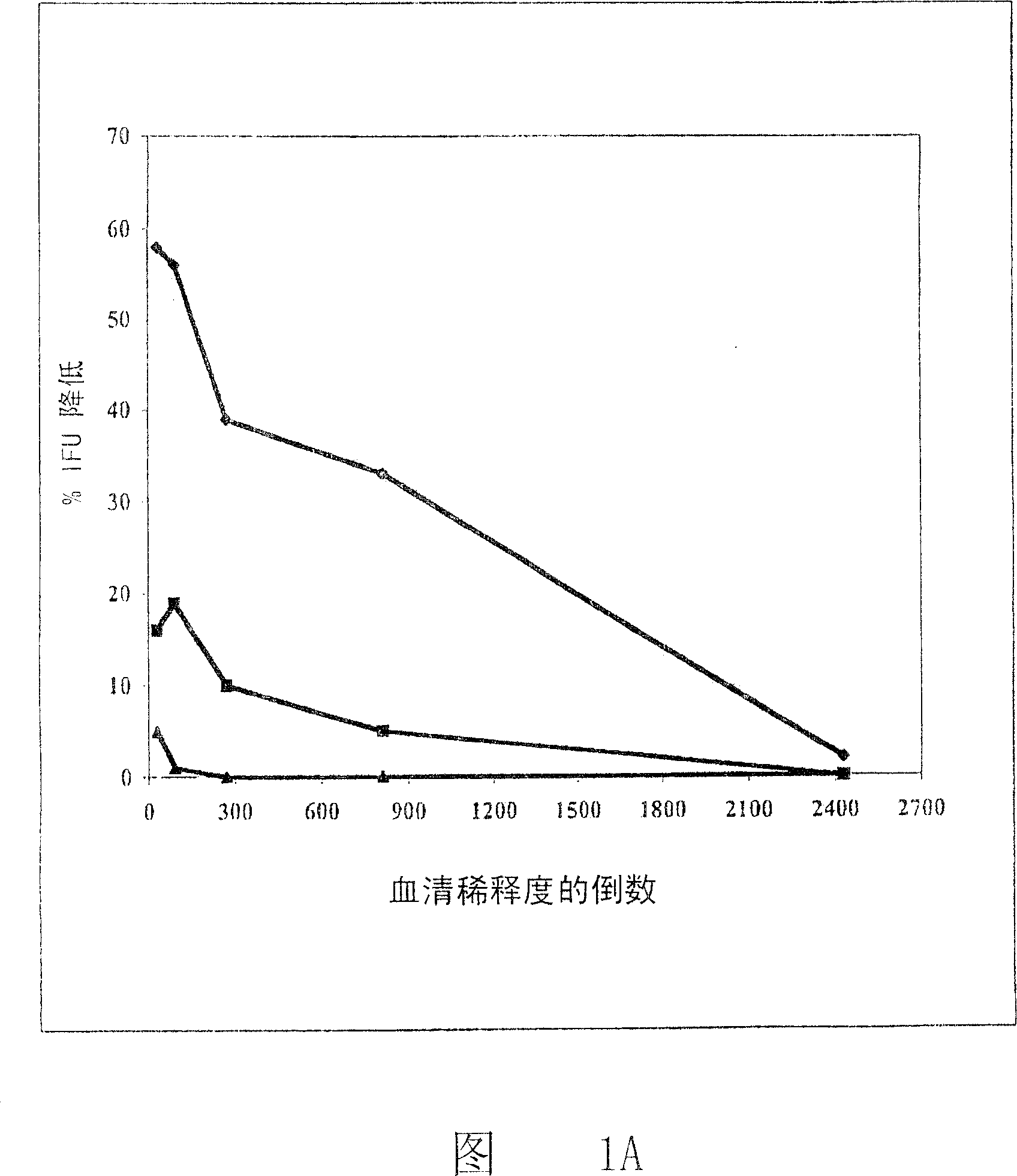
[1495]After a genome-wide screen for proteins likely to be located on the cell surface of C. pneumoniae, we recently reported (25) that antisera to 53 recombinant Chlamydia antigens were able to bind to the cell surface of C. pneumoniae in a FACS assay. In order to test whether some FACS-positive antigens can interfere with the infectivity of EBs in vitro, we prepared mouse antisera against recombinant FACS-positive antigens and evaluated the effect of each antiserum on the infectivity of purified EBs to LLC-MK2 cell monolayers. influences. First, infectious EBs were incubated with antiserum and then used to infect cell monolayers in 24-well multiwell titer plates, similarly to control samples where EBs were: i) treated with buffer only, or ii) treated with the same dilution The corresponding pre-immune mouse serum treatment.
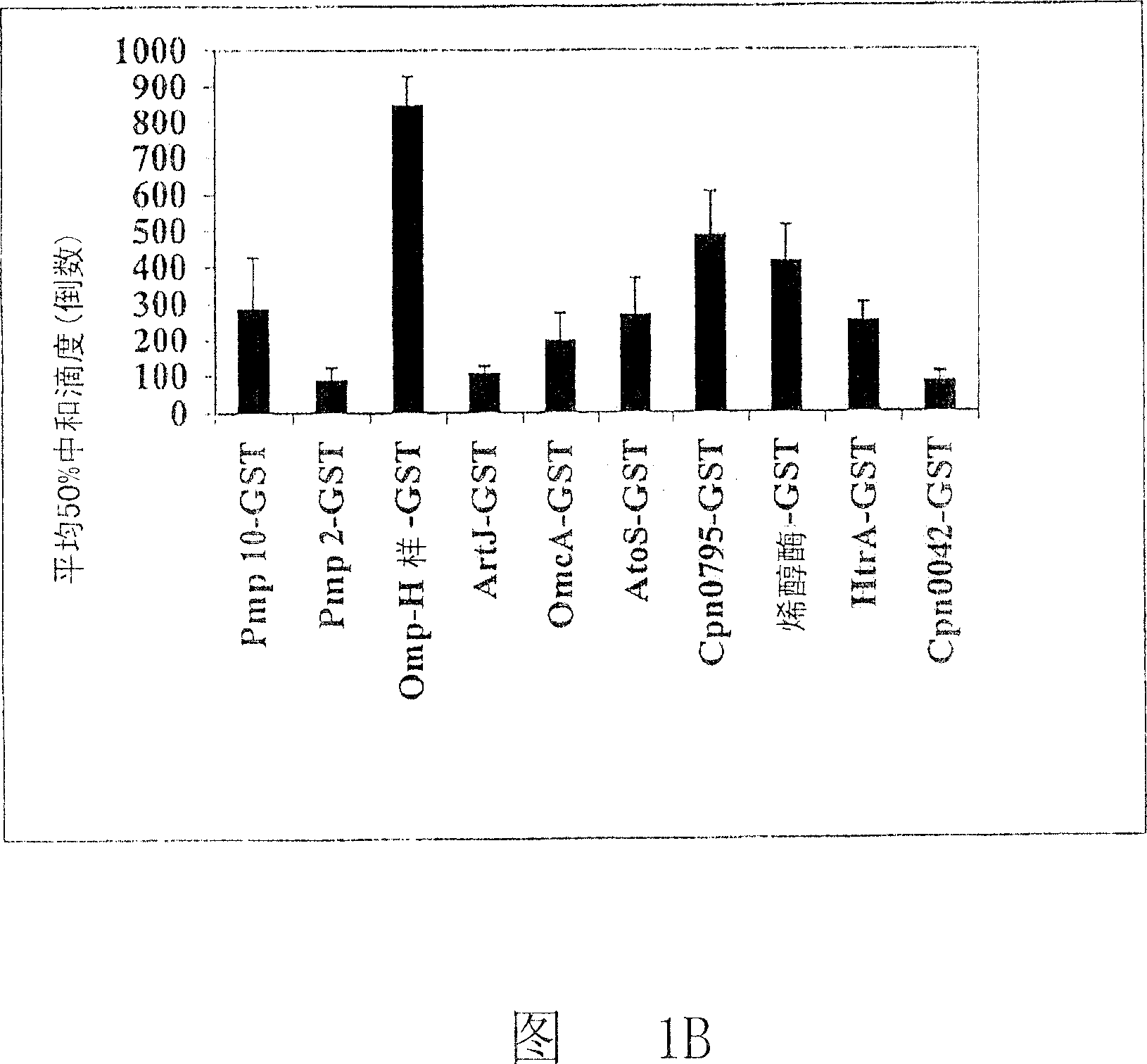
[1496] Result I
[1497] Using this...
Embodiment 2
[1507] Example 2 (in vivo studies)
[1508] Evaluation of antiserum specificity of Cpn protein extracts by 2D immunoblot analysis
[1509] To investigate whether the neutralizing activity observed in in vitro infection of LLC-MK2 cell monolayers was in fact due to antibody binding to selected C. The specificity of the antisera was evaluated by Western blot analysis.
[1510] Specifically, this analysis was performed on six antigens (Pmp2, Pmp10, Eno, ArtJ, HtrA and OmpH-like antigens) visible in the 2D map of EB total protein (Montigiani et al., 2002 Infection and Immunity 70:368-379). EB total protein was analyzed by 2D electrophoresis using two different pH intervals (pH 3-10 non-linear, pH 4-7, respectively), since it has previously been shown that one of the above pH intervals rather than the other is better for detecting the protein under study. some egg whites. Four gels were run in parallel at each pH interval. One gel was stained with Coomassie blue to visualize pr...
Embodiment 3
[1517] In vivo evaluation of in vitro neutralizing antigens in a hamster model of systemic infection
[1518] We recently described a novel hamster model of systemic C. pneumoniae infection in which replicating C. pneumoniae is disseminated by macrophages and accumulates in the spleen (34). We therefore asked the question whether the in vitro neutralizing antigens we identified were also protective in vivo in this model. To this end, 8 hamsters were immunized with 10 in vitro neutralizing recombinant antigens 3 times subcutaneously during 3 weeks, and two weeks later with 2 × 10 8 Cpn EB stimulation. Spleen infection was assessed 7 days after challenge. Protection specifically induced by putative vaccine candidates was measured as the difference between the mean number of infectious Chlamydia recovered from control animals and the number of Chlamydia recovered from animals immunized with recombinant Chlamydia antigens.
[1519] result 3
[1520] The results of spleen prote...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com