Superconductive current lead welding method
A technology of wire welding and superconducting current, applied in welding equipment, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as loosening and brazing melting, and achieve the effects of reducing the chance of heating, easy operation, and low temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
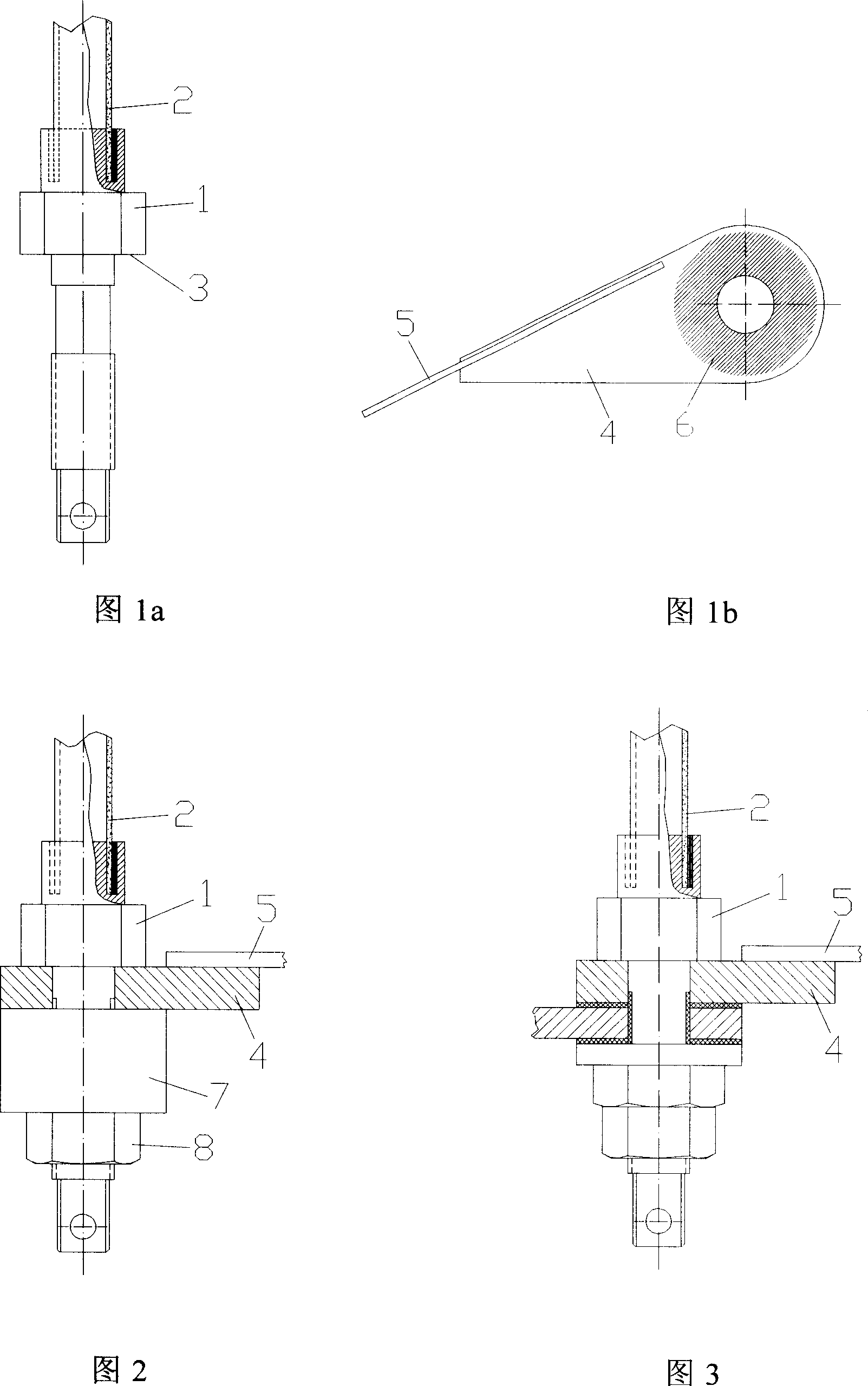
[0014] As shown in FIG. 1 a , the copper pillar 1 is first soldered to the tubular high-temperature superconductor 2 by tin brazing, and at the same time solder is hung on the plane 3 of the copper pillar 1 . As shown in Figure 1b, the copper block 4 is first soldered to the lead-out wire 5 of the superconducting magnet with tin brazing. , which is the shaded area shown in Figure 1b, quickly wipe over to remove excess solder on this area.
[0015] In Fig. 2, the copper pillar 1 and the high-temperature superconductor 2 that have been welded together are put on a lathe to turn the solder layer on the plane 3 until only a thin layer of solder is left on the plane 3, and the thickness of the solder layer is equal to that on the plane 3. The color of copper is not exposed. After using a file to scrape off the excess solder on the edge of the roun...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com