Equalizer and equalizing method
An equalizer and equalization technology, which is applied in equalizers, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, baseband system components, etc., can solve problems such as incorrect equalization, large errors, and inability to remove noise components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
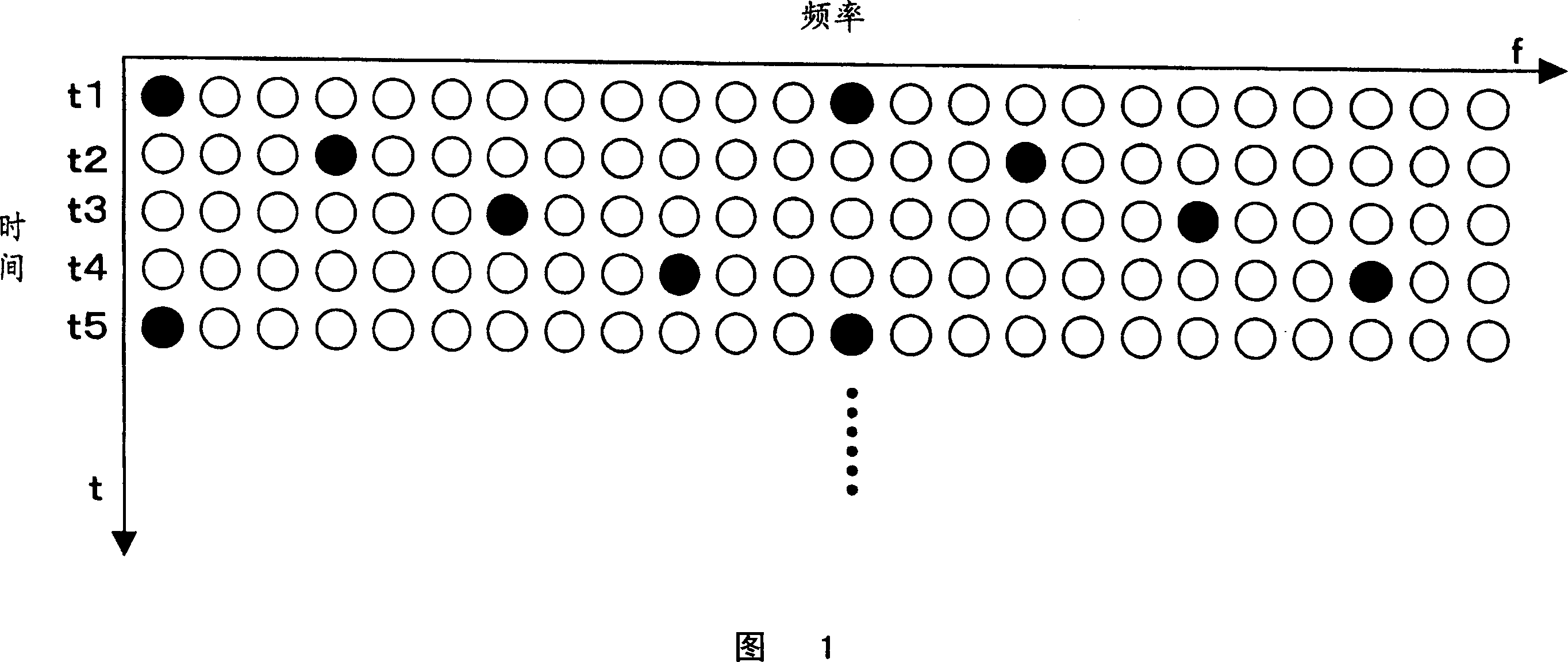
[0033] Next, the equalizer and equalization method of Embodiment 1 will be described. When using Fig. 1 to illustrate the concept of the equalizer and the equalization method of Embodiment 1, the equalizer and the equalization method of Embodiment 1 use the pilot symbols of the current (for example t3) OFDM symbol to decipher the current OFDM symbol Tune.
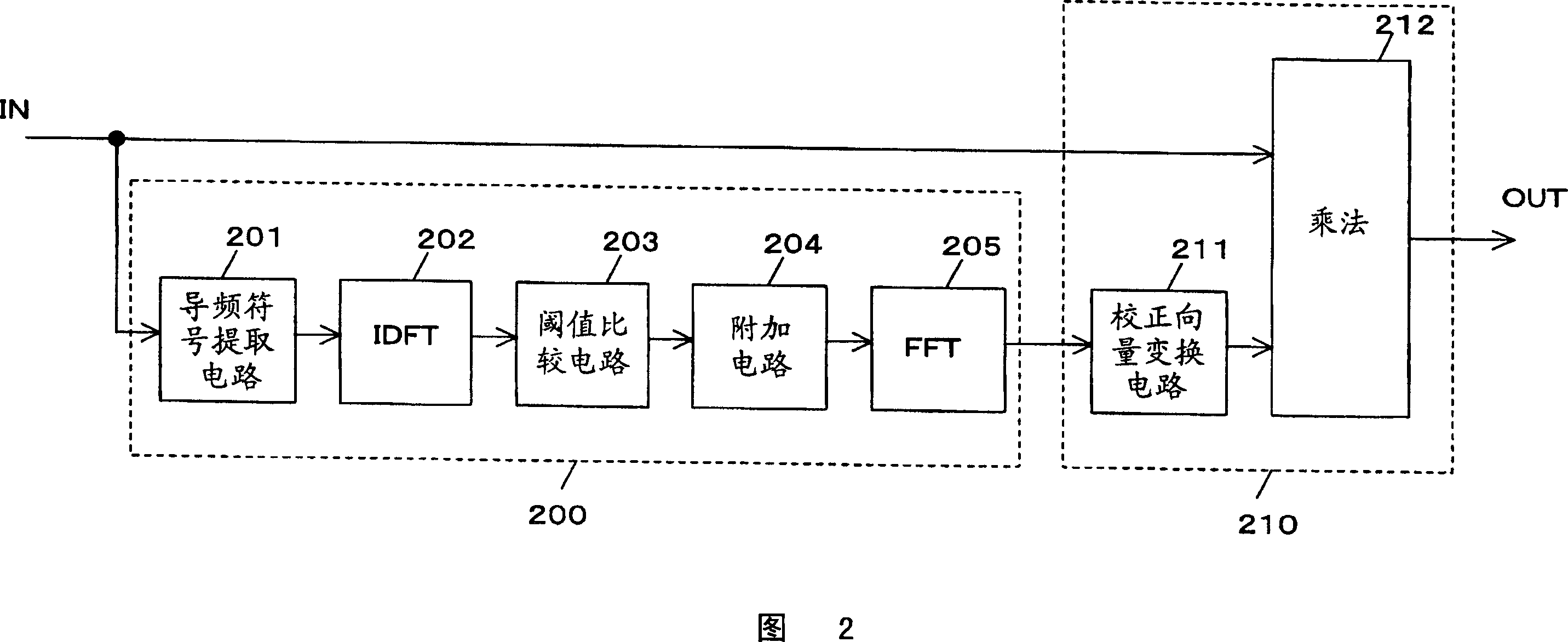
[0034] FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the structure of the equalizer of the present invention. The equalizer of the present invention includes a channel estimation unit 200 and an equalization calculation unit 210 that receive a Fourier-transformed input signal IN. Here, the input signal is a signal subjected to Fourier transform in units of one OFDM symbol.
[0035] The channel estimation unit 200 includes a pilot symbol extraction circuit 201 , an inverse discrete Fourier transform circuit 202 , a threshold comparison circuit 203 , an addition circuit 204 , and a fast Fourier transform circuit 205 .
[0036] Pilot s...
Embodiment 2
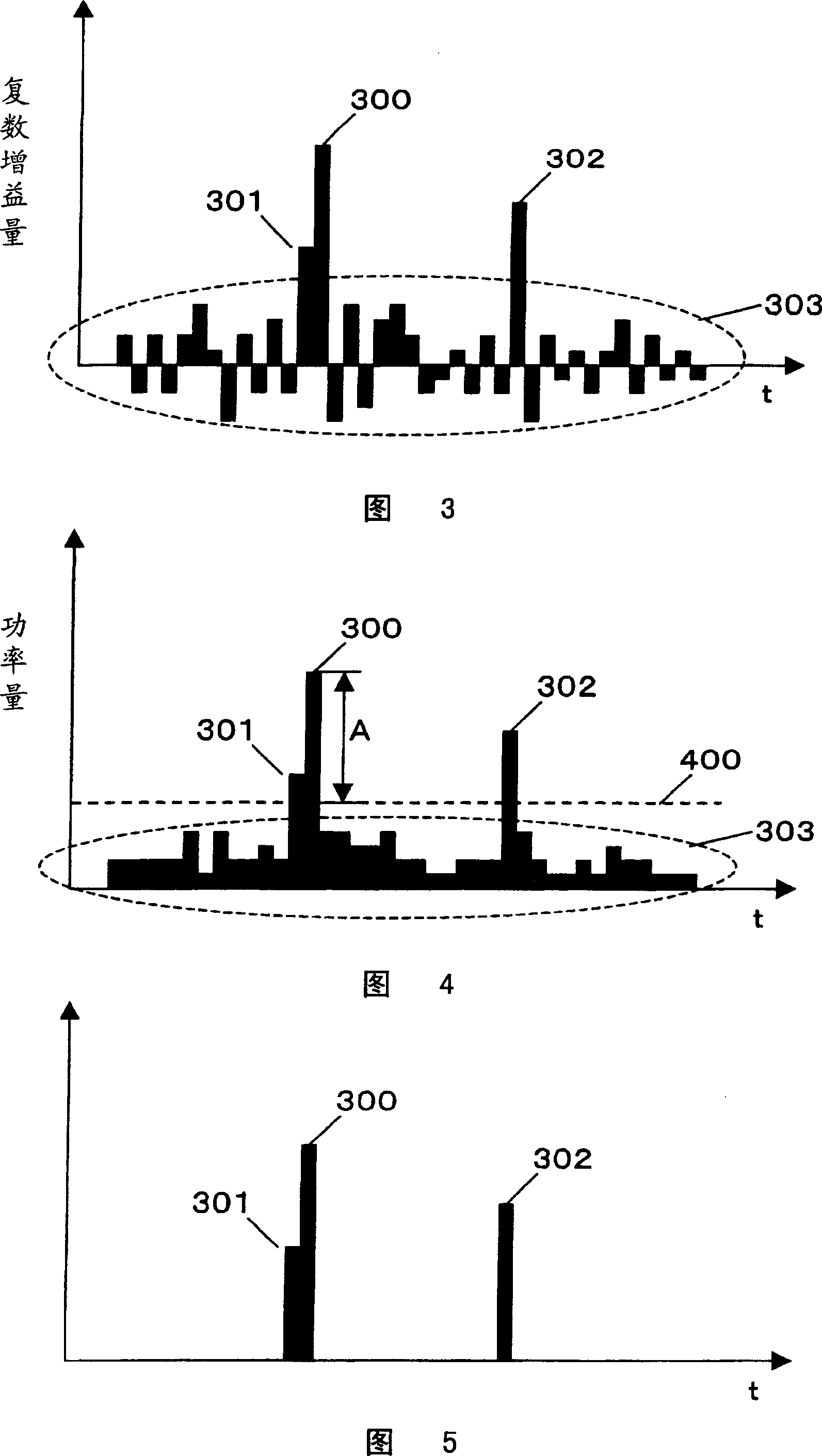
[0056] The path extraction method of the equalizer and the equalization method in the second embodiment are different from those in the first embodiment. In the threshold comparison circuit of the first embodiment, the path is extracted using the power amount obtained by squaring the complex gain amount. On the other hand, in the threshold comparison circuit of Embodiment 2, paths are extracted using the absolute values of the real and imaginary numbers of the complex gain amount.
[0057] Specifically, the threshold comparison circuit of the second embodiment obtains the absolute value of the real number and the imaginary number of the complex gain amount of each path obtained in the discrete Fourier inverse transform circuit 202, and adds the absolute values of the real number and the imaginary number for each path. operation. The threshold comparison circuit extracts a path having the largest complex gain amount as a result of addition. Then, the threshold comparison ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The method of transforming the correction vector of the equalizer and the equalization method of the third embodiment is different from the first and second embodiments. The correction vector conversion circuits of Embodiments 1 and 2 extract only the phase components corresponding to the channel estimates of the respective subcarriers. On the other hand, the correction vector conversion circuit of Embodiment 3 extracts the phase component and the amplitude.
[0064] More specifically, the correction vector conversion circuit of the third embodiment generates a correction vector that is the reciprocal of each subcarrier using the following formula.
[0065] (Formula 5)
[0066] SubC _ T = Re [ SubC ] - jIm [ SubC ] Re [ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com