Data transmission method for high-speed downlink packet access service
A data transmission method and technology for accessing services, which are applied in the data transmission field of high-speed data packet access services, can solve problems such as overloading of data processing units, and achieve the goal of ensuring liquidity, normal operation, and preventing the impact of data transmission quality. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
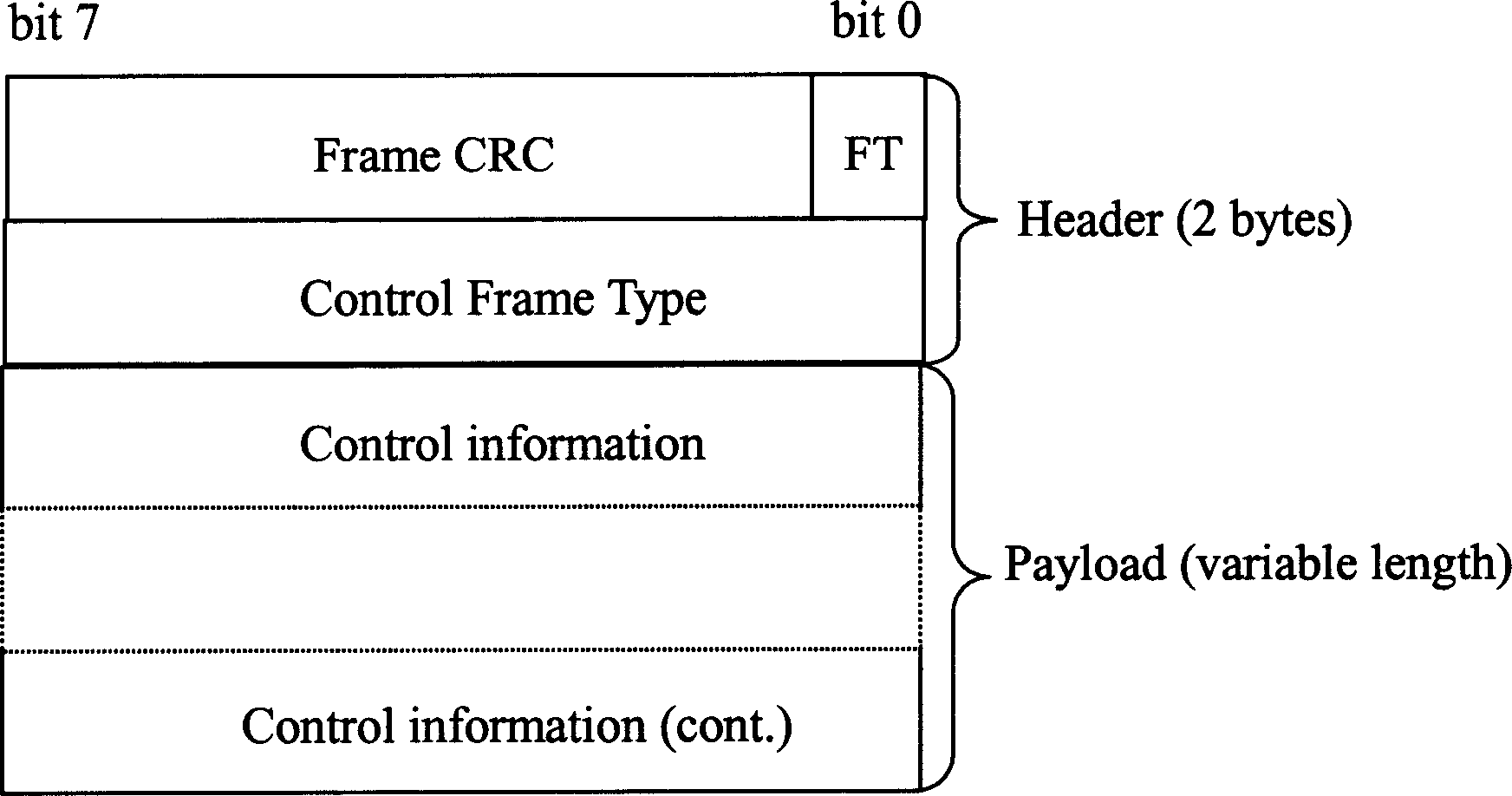
[0038] Examples, such as Figure 6 As shown, the processing flow after data overload occurs:
[0039] S10. When overload occurs, the RNC data processing unit notifies the MAC-d entity of the overload information.
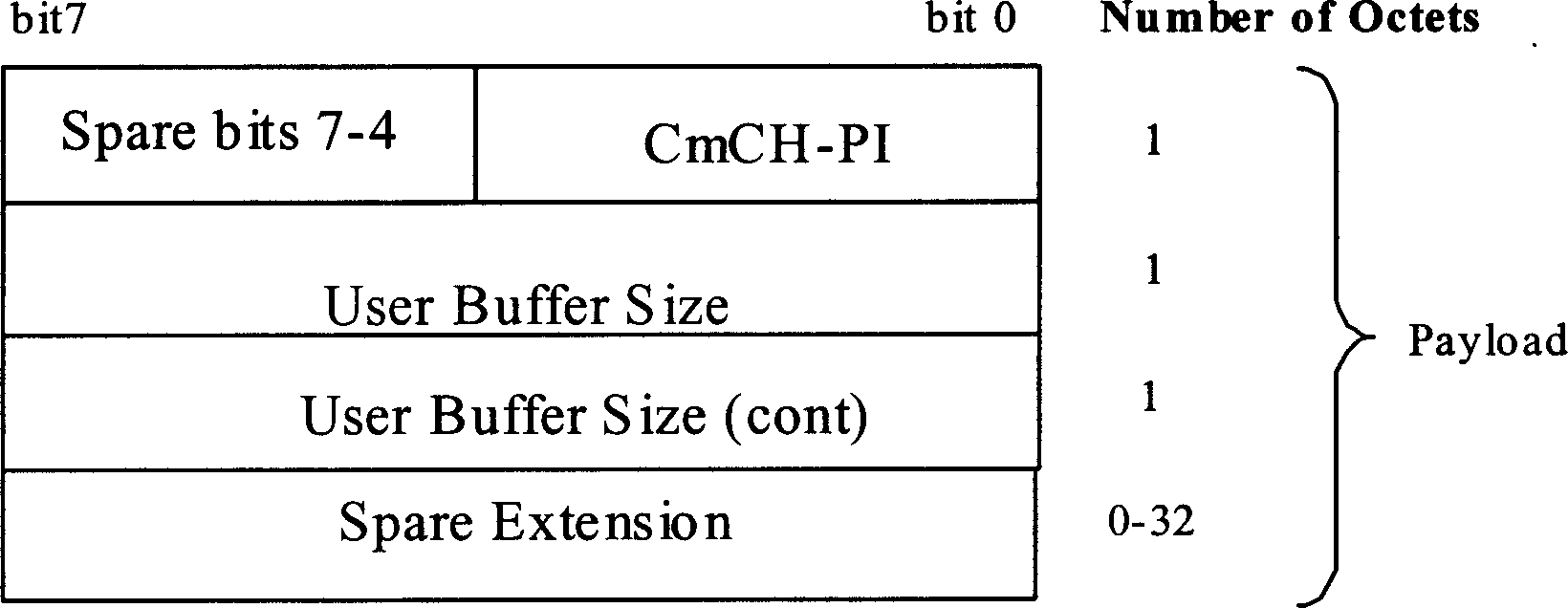
[0040]After the NodeB sends the traffic allocation message to the RNC, the MAC-d entity in the RNC will receive the NodeB traffic allocation message and send data on the corresponding HS-DSCH according to the traffic allocated in the traffic allocation message, each HS- DSCH has no relation to each other. Because the NodeB often only allocates traffic according to its own air interface capability or state when performing traffic allocation, without considering other factors such as Iub interface transmission resources, it may happen that the RNC is requested to send a large amount of traffic on a certain HS-DSCH at certain moments. data, which may cause the burst traffic overload on the certain HS-DSCH to cause the overload of the RNC data processing unit or the o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com