Method for measuring environment of electric charge in environmental scanning electron microscope
A technology of environmental scanning electron microscope and measurement method, which is applied in the field of measurement of charge environment in environmental scanning electron microscope, and can solve the problems of inability to measure and monitor the charge environment of sample chambers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: In high vacuum mode, measure the sample current (I SC )
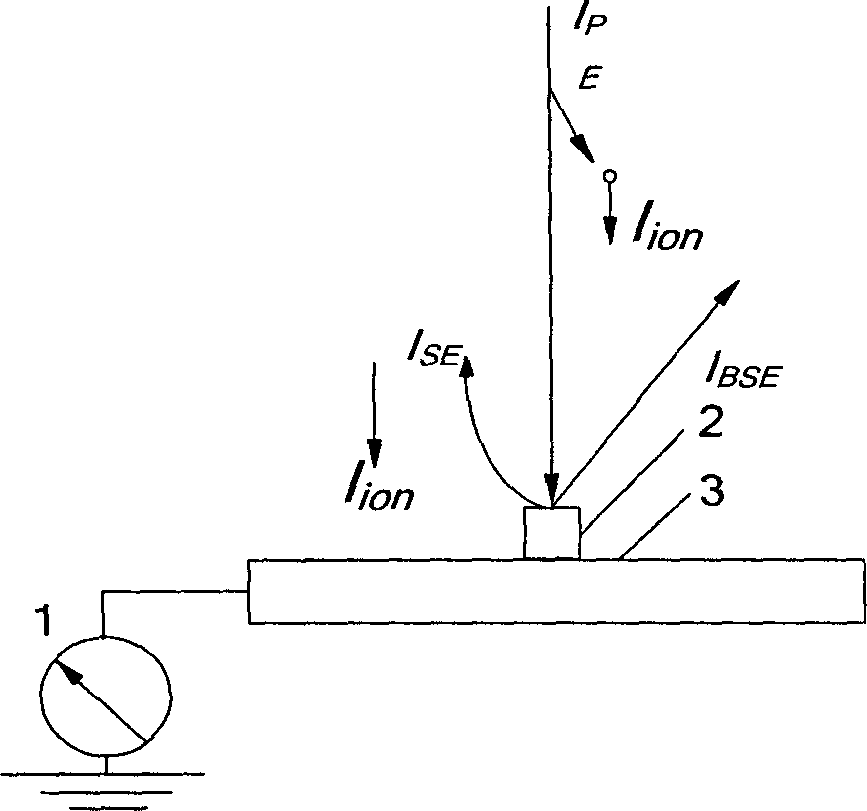
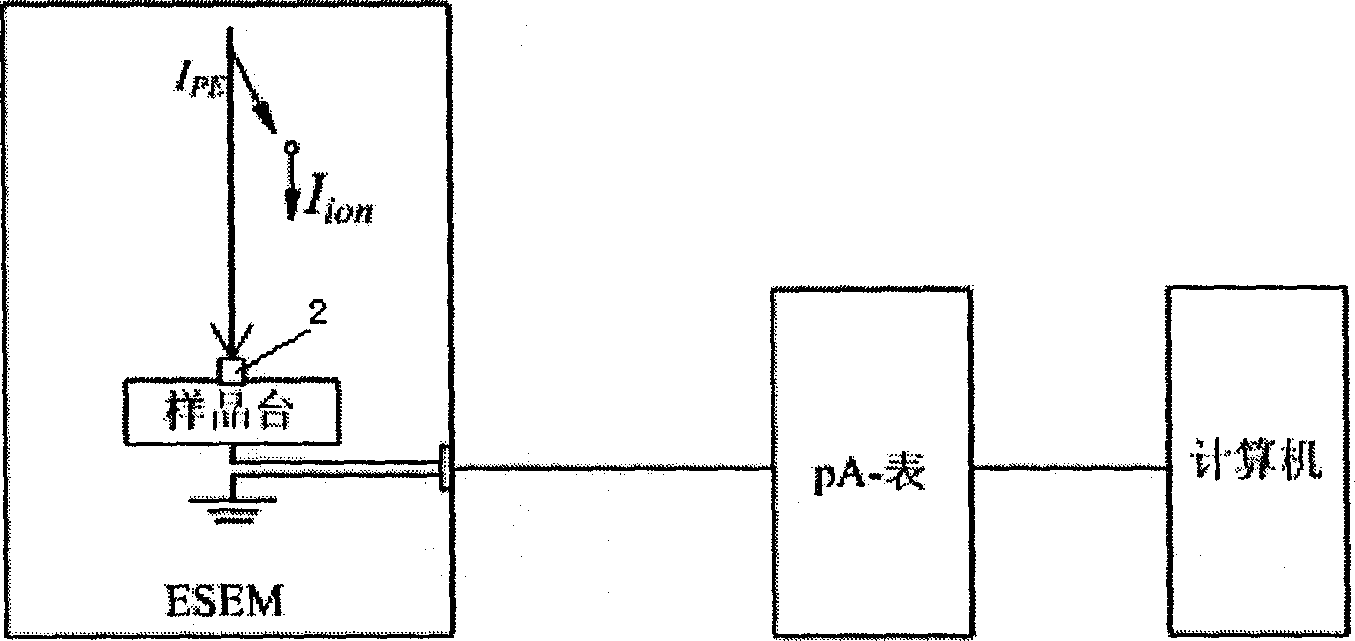
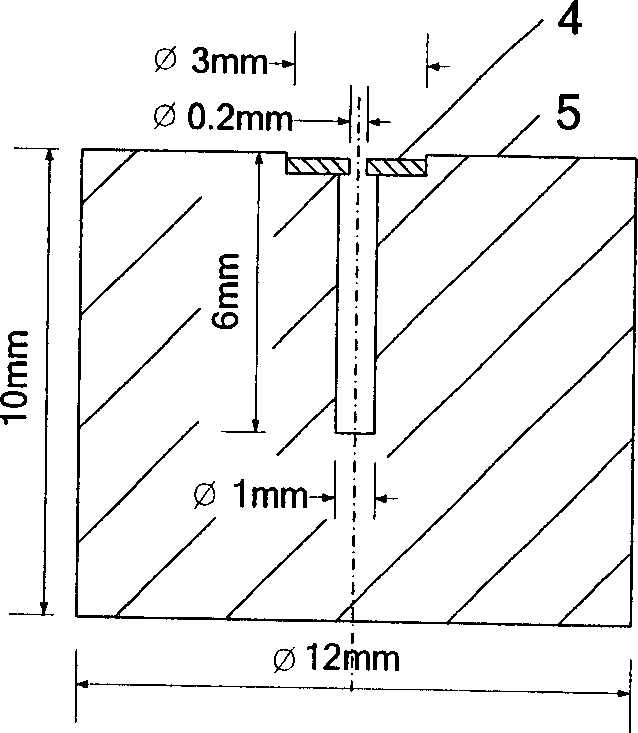
[0040] 1) This embodiment utilizes figure 2 , image 3 The test device shown is realized by the following method. Place the Faraday cup on the sample stage 3 in the sample chamber of the Environmental Scanning Electron Microscope (ESEM), connect it to the sample stage through conductive tape or conductive glue, and make the Faraday cup pass through the sample stage to be well grounded. In this embodiment, the ESEM is Quanta 200 from FEI Company, and the working distance, that is, the distance from the lower surface of the environmental scanning electron microscope objective lens to the sample is 7.7mm.
[0041] 2) Vacuum the ESEM. In the high vacuum operation mode of the ESEM, when the ambient pressure is lower than 10 -4 After Pa, apply an accelerating voltage of 30kV to the electron gun to emit electrons. Under the action of an accelerating voltage of 30kV, the electrons emitted by the electron ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: In ambient vacuum mode, measuring the space charge current (I SP )
[0047] The test procedure is the same as in Example 1, except that the ambient pressure is adjusted to 130Pa, 200Pa, 300Pa, 400Pa, 500Pa, 600Pa and 700Pa; the ambient gas is water vapor and oxygen; the accelerating voltage is 30kV; the working distance is 7.7mm, 10mm, 12.5 mm and 15mm.
[0048] (1) Water vapor environment, changing pressure and working distance, Faraday Cup I SP see test value Figure 5 ,the result shows:
[0049] (i)I SP Both are positive values, 10 -7 A~10 -8 A, Reflecting that the charge environment in the sample chamber is dominated by ion currents. This is because in a higher pressure environment, a large number of electrons are scattered, so that the incident electrons directly detected in the Faraday cup are significantly reduced, while the ion current generated by the scattered electrons is significantly increased.
[0050] (II) I SP The change of reflects t...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: In ambient vacuum mode, measure the space current (I SP )
[0055] I for testing metals, semiconductors and insulators SP The condition is the same as that of testing the Faraday cup in water vapor in Example 2, except that the Faraday cup is changed into a sample and placed on the sample stage 3.
[0056] (1) I of the metal sample SP : I of Cu-Zn alloy SP Test results such as Figure 7 shown. I SP The variation law of is similar to that of the Faraday cup. The difference is that different pressures and different working distances of I SP The peak value is higher than that of the Faraday cup, the highest is 2.5×10 -7 a. This reflects that the ionization of gas molecules by the secondary electrons and backscattered electrons overflowing from the sample increases the total ion flow in the sample chamber, making I SP improve.
[0057] (2) I of the semiconductor sample SP : I of the single crystal Si sample SP see test value Figure 8 . ISP The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com