Method for producing hydrogen by coupling fermentation and photosynthesis of biomass and solid organic wastes
A technology of organic waste and biomass, applied in fermentation, chemical recycling, etc., can solve the problems of low energy conversion rate of hydrogen production by fermentation, inability to degrade organic acid to produce hydrogen, low energy conversion rate, etc., and achieve high fermentation and photosynthetic coupling The ability to produce hydrogen, reduce the cost of hydrogen production, and the effect of simple operation and management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
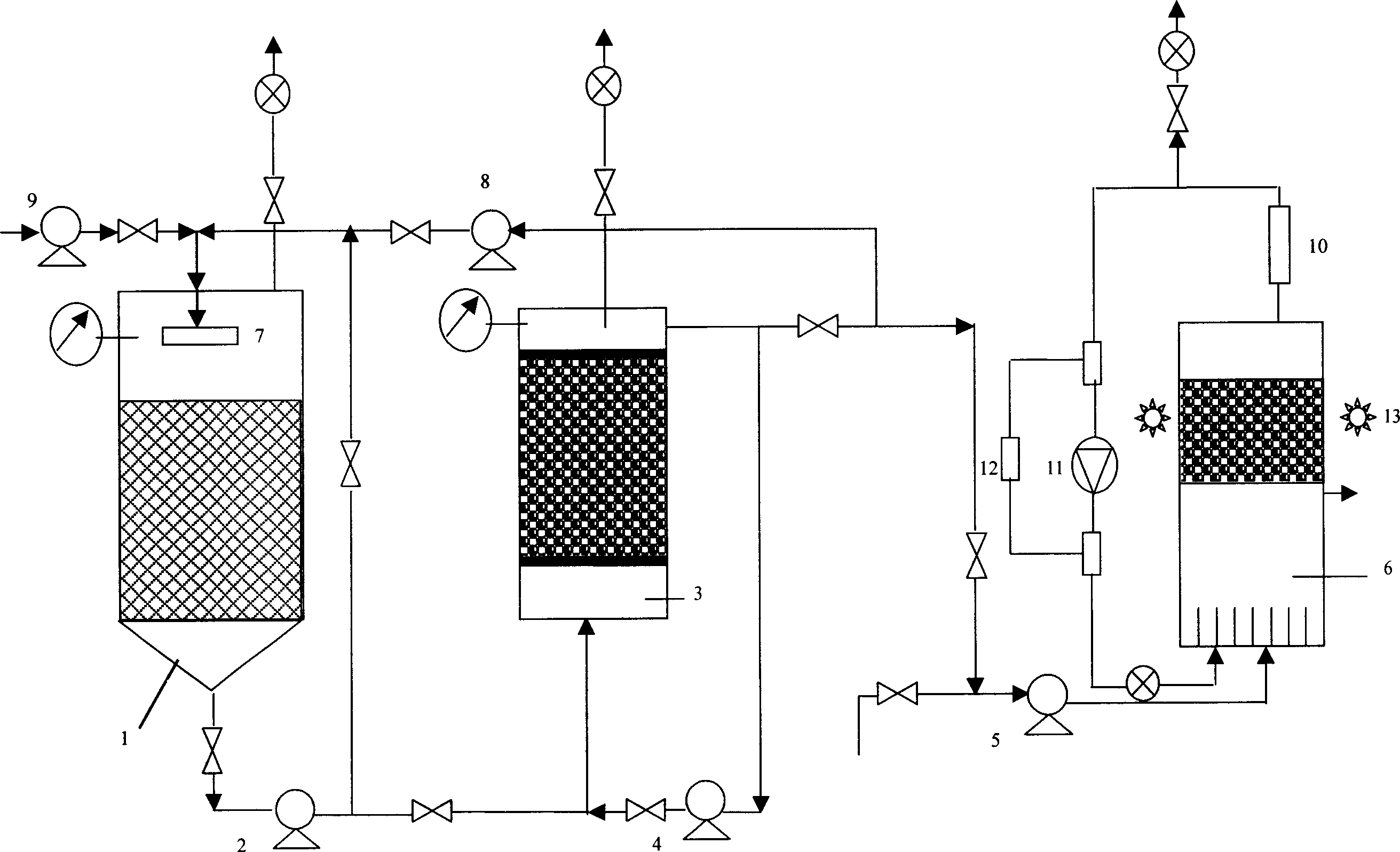
[0030] (1) The crushed potato is used as the fermentation base material, hydrolyzed and acidified under the conditions of temperature 35°C and pH value 5.0 to generate pyruvic acid, short-chain fatty acids and a small amount of H 2 , CO 2 .
[0031] The hydrolysis reaction and acidification reaction of this step are carried out in same hydrolysis and acidification reactor; reaction efficiency.
[0032] (2) Under the action of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria such as Clostridium butyricum, the mixture of pyruvic acid and short-chain fatty acids is fermented to produce a large amount of hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and small molecule organic acid by-products such as ethanol, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid. During the fermentation process, the temperature was controlled at 35° C., and the pH value was controlled at 5.0.
[0033] The fermentation hydrogen production reaction in this step is carried out in an organic acid fermentation hydrogen production reactor;...
specific Embodiment 2
[0037] The steps of this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1, wherein:
[0038] In the step (1) hydrolytic acidification reaction, the controlled temperature is 30°C and the pH value is 4.5; in the step (2) the controlled temperature is 30° C. in the hydrogen production reaction, and the pH value is 4.5; in the step (3) the controlled temperature in the photosynthetic hydrogen production reaction is 30°C, light intensity 2000lx, pH 6.0.
specific Embodiment 3
[0039] The steps of this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1, wherein:
[0040] In the step (1) hydrolytic acidification reaction, the controlled temperature is 60°C and the pH value is 7.0; in the step (2) the hydrogen production reaction is controlled at a temperature of 60°C and the pH value is 7.0; in the step (3) the photosynthetic hydrogen production reaction is controlled at a temperature of 40°C, light intensity 6000lx, pH 7.5.
[0041] Bacteria or strains used in the present invention are existing known strains, for example, fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria (Clostridium butyricum), photosynthetic hydrogen-producing bacteria (purple non-sulfur bacteria), wherein fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria (butyric acid Clostridium) is a large amount of bacteria carried by anaerobic activated sludge itself. Photosynthetic hydrogen-producing bacteria (purple non-sulfur bacteria) are commercially available strains. For example, purple non-sulfur bacteria ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com