Method for enciphering and deciphering code of packet, and encipherer and decipherer
A technology of encryption and decryption and block cipher, applied in the field of method and its encryption and decryption device, can solve the problems of no introduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Explanation of the program design of permutation code with n=4
[0068] 1. Establish a permutation code table with n=4
[0069] Key 0 1 2 3
[0070] 0 0 1 2 3
[0071] 1 0 1 3 2
[0072] 2 0 2 1 3
[0073] 3 0 2 3 1
[0074] 4 0 3 1 2
[0075] 5 0 3 2 1
[0076] .........
[0077] 23 3 2 1 0
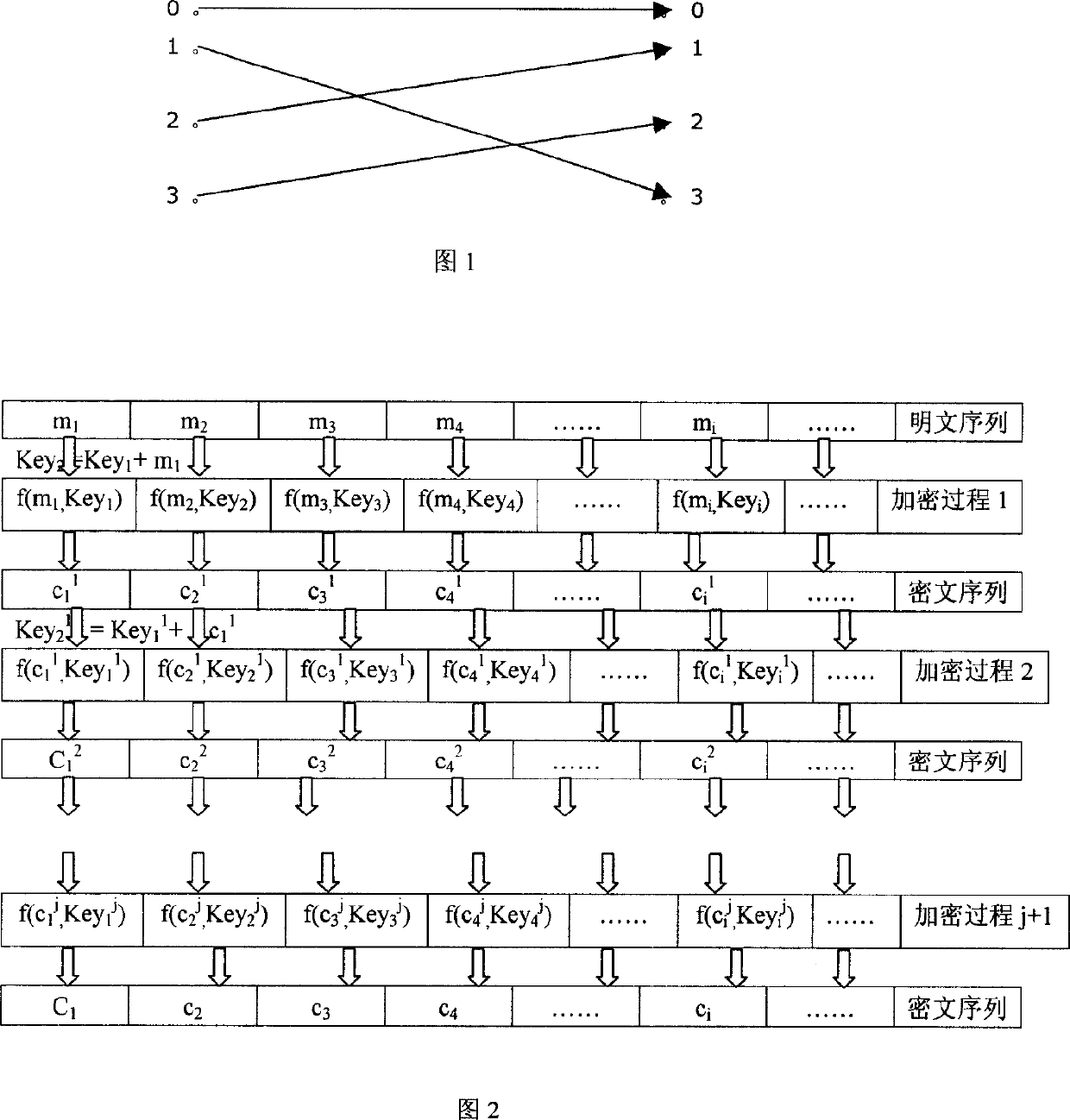
[0078] Such a table has 24! , we randomly build 256 of them. When Key=4, there is the following mapping relationship: 0→0, 1→3, 2→1, 3→2. Figure 1 depicts a schematic diagram of bit exchange when Key=4.
[0079] In order to save storage space, 0→00, 1→01, 2→10, 3→11, and Key are represented by storage addresses. Such a permutation code table occupies 24 bytes.
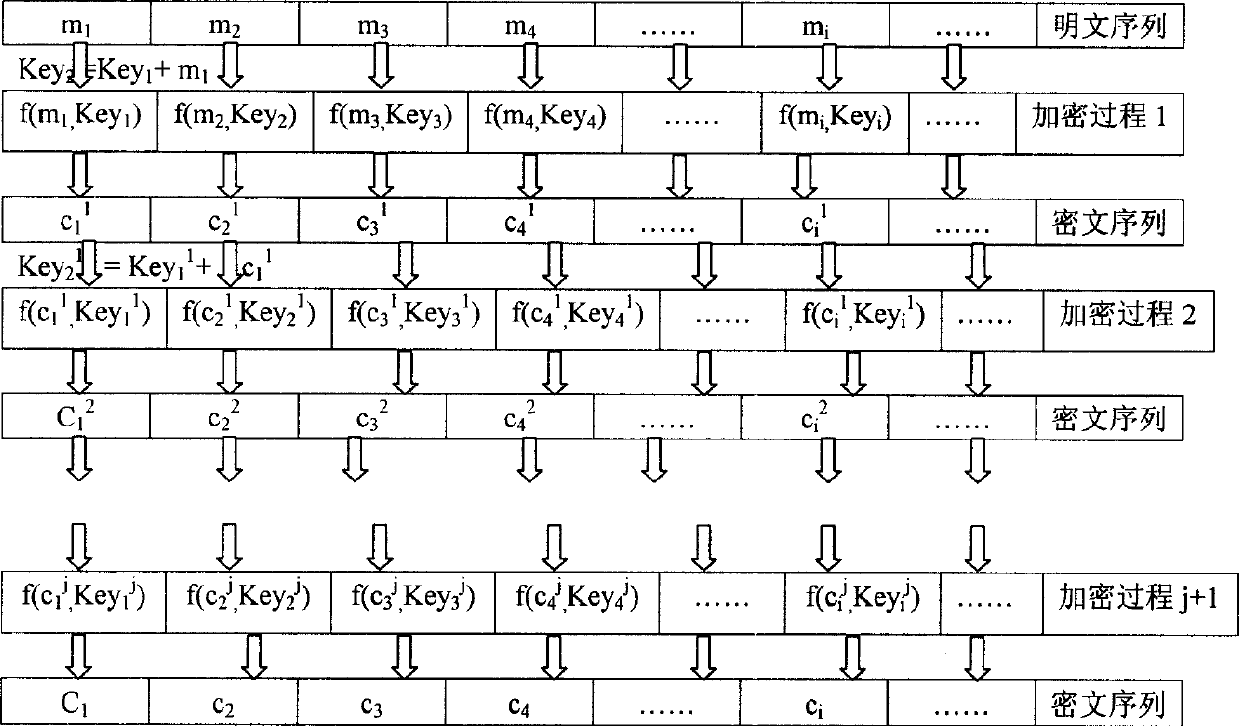
[0080] Figure 2: Schematic diagram of the encryption process; Figure 3: Schematic diagram of the decryption process; Note: The order of encryption and decryption can be performed by row or by column.
[0081] 2. Key design
[0082] Use 1 byte as an integer, and the range it represents is 0-255. Just can det...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Application of Key Sequence as Logical Ruler in Encryption and Decryption
[0093] Encryption and decryption are two opposite processes, which can be encrypted first and then decrypted, or decrypted first and then encrypted. We can use 1-bit binary 0 or 1 as a key to control whether to run the encryption module or the decryption module at present. That is: the input key sequence Key can be used as a logic rule to control which passes are encrypted and which passes are decrypted during the multi-pass encryption and decryption process.
[0094] The following notation conventions are now used in this embodiment:
[0095] To perform one pass of encryption requires a k bit key, then perform j passes of encryption and decryption, and you can input a key with a length of j*k bits; use the k bits in the key sequence Key in sequence for each pass of encryption and decryption; you can also input a key with a length less than j * A key with a length of k bits. In this case, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Application of Key Sequence and Plaintext Group as Logic Ruler in Encryption and Decryption Process
[0120] In each example of embodiment 2, the key sequence Key is used as the logical rule to control which pass to execute the encryption module and which pass to execute the decryption module; in this embodiment, the key sequence and plaintext grouping are used as the logical rule.
[0121] Figure 12 describes the application of the key sequence and plaintext as a logical ruler in the process of longitudinally encrypting plaintext. In this figure, for each plaintext group m 1 , m 2 ,... m L Carry out vertical encryption; first use the key sequence Key as a logical ruler, and when the key sequence Key is used up as a logical ruler, use the plaintext group m 1 Each bit of each bit continues to be used as a logic rule to control which pass performs encryption and which pass performs decryption. If the plaintext group m 1 still not enough, then when m 1 After running ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com