Sphingol monospore bacterial strain and its application in anthraquinone dye waste water decolour
A sphingomonas, anthraquinone dye technology, applied in the fields of bioengineering and environmental engineering, can solve the problem of no evolution position, and achieve the effects of fast degradation speed, enhanced processing ability, and strong decolorization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The screening steps of the Sphingomonas bacterial strain provided by the invention:
[0043] The aerobic activated sludge samples were collected from the sewage outlet of the bromine production workshop of Zhaoyuan General Chemical Plant in Shandong Province, and used as a source of bacteria for domestication and enrichment. That is to say, the collected sludge is made into a suspension, and the supernatant is added to the activation enrichment medium for enrichment. The composition of the medium (g / l): beef extract 5, peptone 10, NaCl 5, wherein the medium is at 121 ℃, autoclaved for 20 minutes before use. Then transfer to the substratum with bromine as the only carbon source for acclimatization, substratum composition (g / l): (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2. KH 2 PO 4 1.3, Na 2 HPO 4 2. Trace elements 1ml / l, of which the composition of trace elements (g / l): (MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 39.9, ZnSO 4 9H 2 O 68.55, (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O 34.7. Acclimatization adopts the domest...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The application of the present invention to the decolorization research of bromic acid in nutrient-enriched medium, its steps are as follows:
[0059] [1] Add 50ml of LB medium to a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask, then add bromine to make the final concentration 100mg / l, and sterilize for later use.
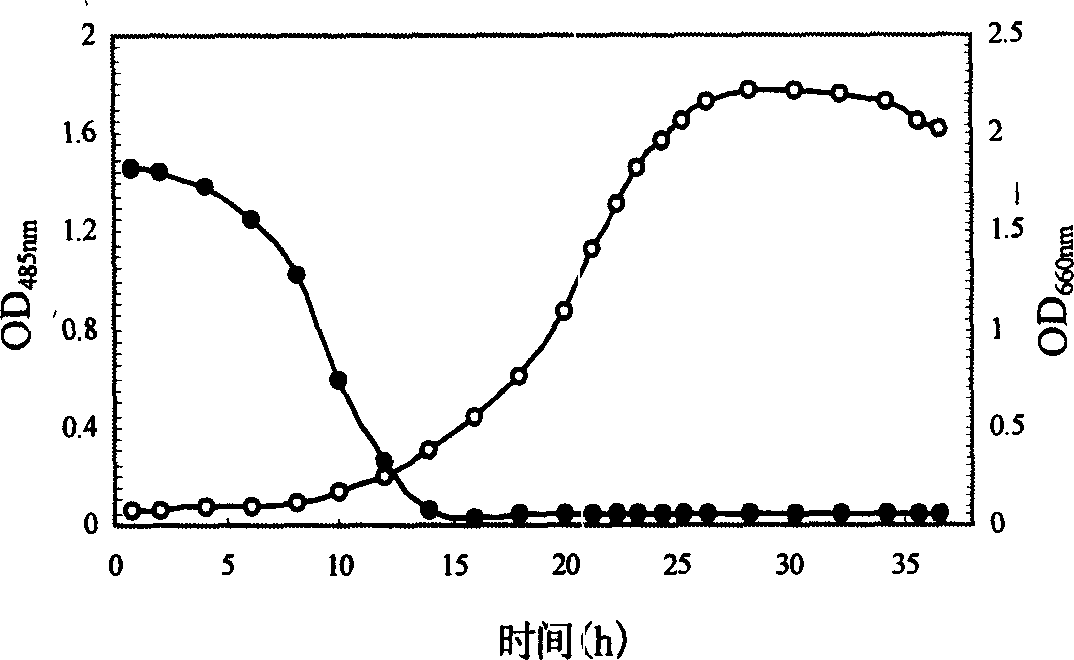
[0060] [2] Add the cell liquid culture of the sphingomonas strain prepared in Example 1 or the dormant cells of the sphingomonas strain prepared in the embodiment into the Erlenmeyer flask of the above [1] , 30°C, 150r / min, aerobic culture. Samples were taken every 12 hours. figure 1 is the growth of Sphingomonas strains in the enriched medium and the degradation of bromine; it can be seen from the figure that the degradation of bromine occurs in the early stage of the growth of the strain instead of the logarithmic phase; and it can be seen that the bacteria A small amount of body growth is enough to degrade bromine, and the decolorization rate of bromine is as high as 100% 14 ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Application of the present invention in decolorizing research on bromic acid in medium with bromic acid as the sole carbon and nitrogen source:
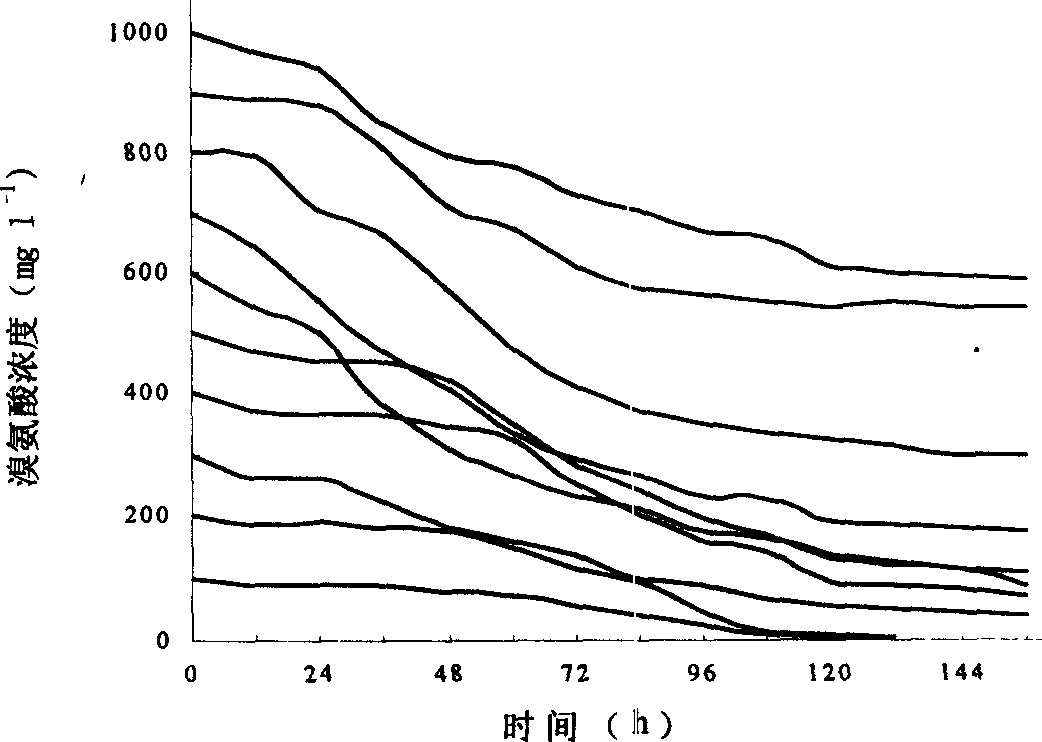
[0063] The LB medium in Example 1 was replaced with the basal medium with bromine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source, and other steps were the same as in Example 6. image 3 is the degradation situation of growing cells to different concentrations of bromine; image 3 It can be seen that the strain of Sphingomonas has a very strong decolorization ability to bromine, and can tolerate the concentration of bromine as high as 1000ppm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com