Optical fiber preform and manufacturing method therefor
A technology for optical fiber preforms and glass rods, which is applied to manufacturing tools, glass manufacturing equipment, glass production, etc., can solve the problems of increased processing times, increased optical fiber manufacturing costs, and increased optical fiber preform manufacturing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
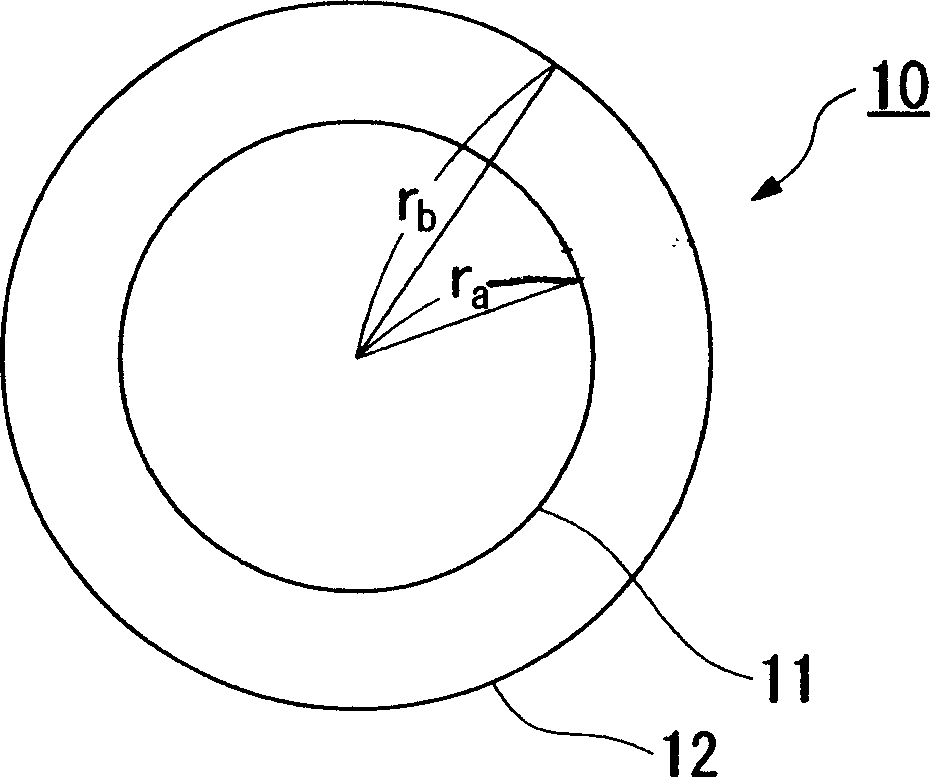
[0066] A glass rod including a core and a cladding portion was formed using a VAD (Vapor Axial Deposition) method, and drawn to obtain a central glass rod with a diameter between 23-34 mm.
[0067] Afterwards, use the same process to obtain multiple central glass rods.
[0068] The surface of each central glass rod was fire-polished, wherein an oxyhydrogen flame was emitted from a burner moving along the longitudinal direction of each glass rod.
[0069] The moving speed of the burner was set at 30 mm / min.
[0070] As shown in Table 1, several sets of different values (Conditions A-E) were set for the temperature of the oxyhydrogen flame, the flow rate of oxygen supplied to the burner, and the flow rate of hydrogen supplied to the burner.
[0071] Next, fine glass grains are deposited on the outer surface of each central glass rod, and each central glass rod with deposited fine glass grains is dehydrated and vitrified in an electric furnace to form an outer cladding, thereb...
example 2
[0082] A glass rod including a core and a cladding portion was formed using a VAD method, and the glass rod was drawn to obtain a central glass rod with a diameter of 23-34 mm.
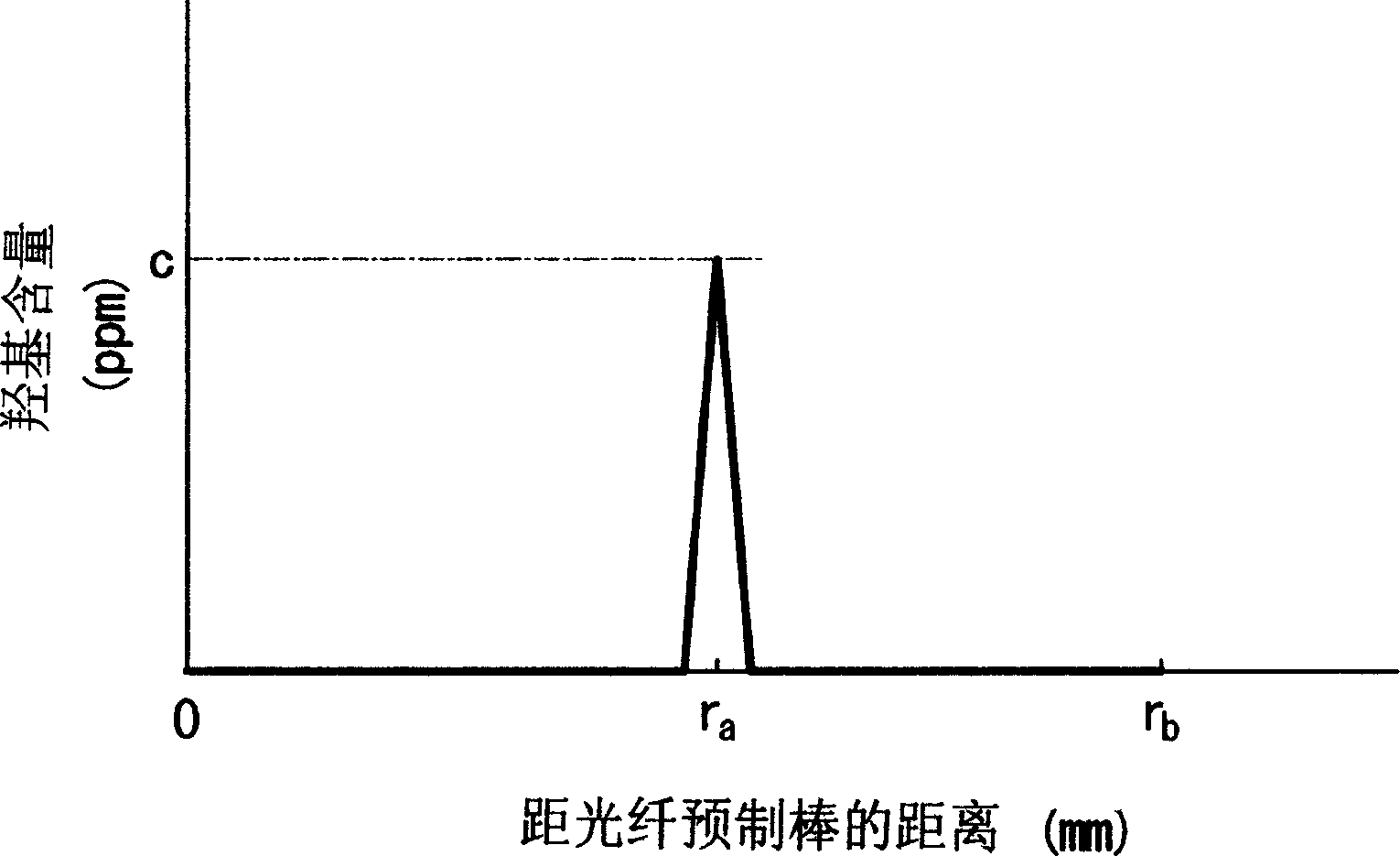
[0083] Using the above-mentioned central glass rod, in the same manner as in Example 1, under conditions A-1 to A-3, and B-1 to B-3 shown in Table 2, optical fiber preforms of cylindrical shape were obtained. In Table 2, r a Indicates the radius of the central glass rod, r b Indicates the radius of the fiber preform.
[0084] Maximum hydroxyl content
c(ppm)
r a / r b
r a / r b / c
Condition A-1
130
0.248
0.0019
Condition A-2
130
0.352
0.0027
Condition A-3
130
0.416
0.0032
Condition B-1
180
0.320
0.0018
Condition B-2
180
0.368
0.0020
Condition B-3
180
0.496
0.0028
[0085] ...
example 3
[0089] Central glass rods were produced in the same manner as in Example 2, and using these central glass rods, cylindrical optical fiber preforms were obtained under conditions C, D-1, D-2 and E shown in Table 3.
[0090] Maximum hydroxyl content c(ppm)
r a / r b
r a / r b / c
Condition C
50
0.288
0.006
Condition D-1
32
0.288
0.009
Condition D-2
35
0.416
0.012
Condition E
20
0.288
0.014
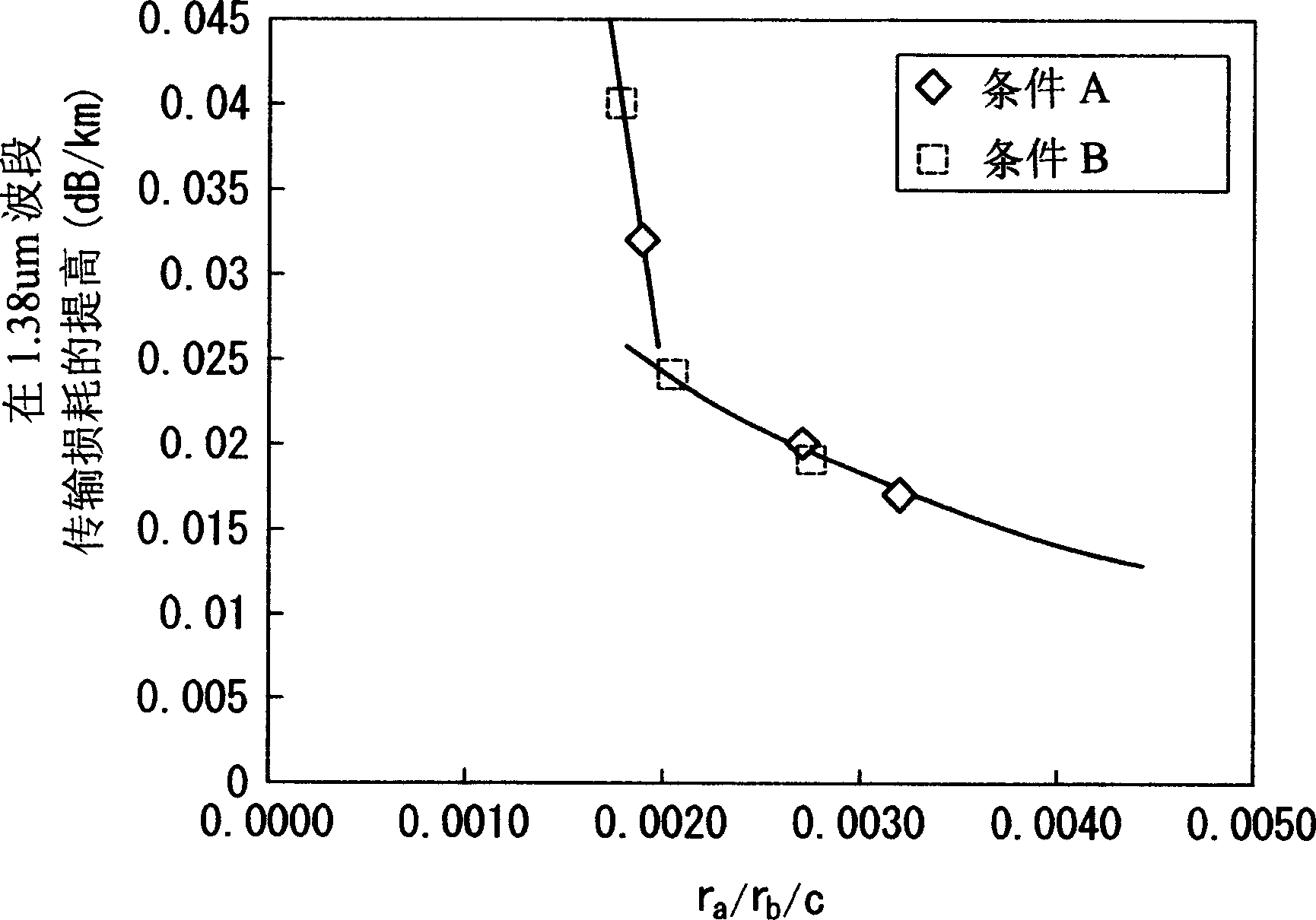
[0091] Optical fibers were formed by drawing the optical fiber preforms produced under the conditions shown in Table 3. The drawing speed was set at 1000 m / min.
[0092] Measure the transmission loss in the 1.38um band caused by hydroxyl in the optical fiber. Measurement results such as Figure 4 shown.
[0093] Such as Figure 4 As shown, even when the ratio r a / r b When / c is set to be greater than 0.01, it is also impossible to reduce t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com