Comparator circuit and bias compensator
A technology for comparing circuits and compensating devices, which is applied in the fields of physical parameter compensation/prevention, electrical components, analog/digital conversion calibration/testing, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulties, increased occupied area of semiconductor devices, and low power consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
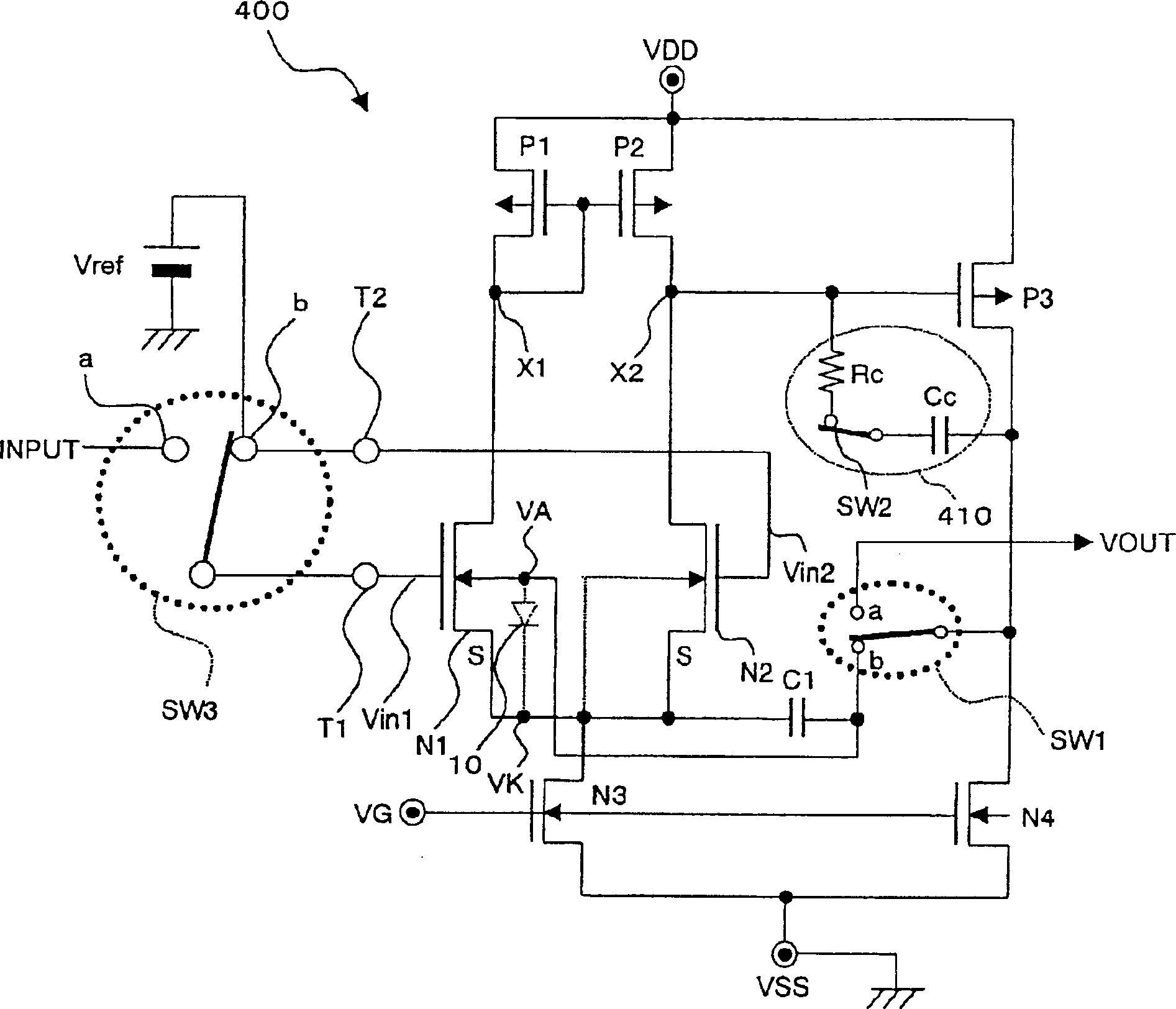
[0059] figure 1 is a circuit diagram showing the structure of the comparison circuit according to the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the comparison circuit (hereinafter also referred to as "comparator") is configured with: NMOS transistors M1 and M2 for forming a differential pair; constant current source transistor N3; load transistors (PMOS transistors) P1 and P2, Used to form a current mirror; and an output stage transistor (composed of a PMOS transistor P3 and a constant current source transistor N4), used to form a push-pull output stage circuit. This comparison circuit is also configured with: a phase adjustment resistor Rc; a phase adjustment capacitor Cc; a phase adjustment circuit 410 composed of a switch SW2 which becomes ON when bias is adjusted; a DC cut capacitor C1; a switch SW1; a switch SW2; another switch SW3; an input T1; and another input T2.
[0060] In this case, an input voltage (INPUT) or a reference voltage (also re...
no. 2 example
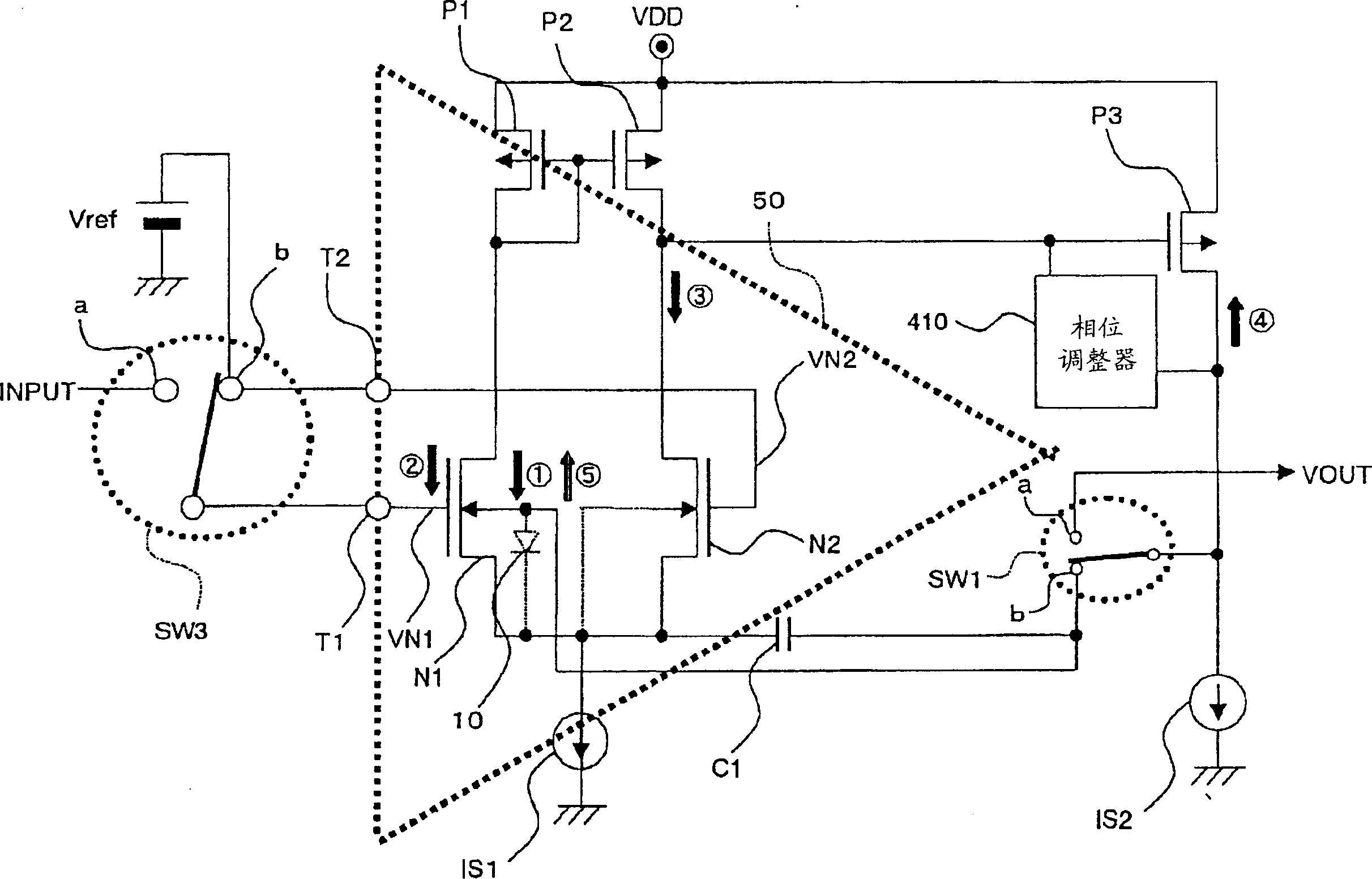
[0116] Figure 10 A structural circuit diagram of the bias compensation device according to the second embodiment mode of the present invention is shown. The offset compensating device of this second embodiment can cancel a DC offset by using a comparator having an offset adjustment function.
[0117] In this second embodiment, for the comparator, the comparator 400 equipped with the offset adjustment function as described in the first embodiment is used. Before canceling the bias of the D / A converter 500a (500b), the switch SW4 provided at the input stage of the comparator 400 is switched to the "a" side terminal in order to adjust the right / left current bias. The differential output (negative) of the D / A converter 500a (500b) is input to the "a" terminal.
[0118]As a result, the comparison voltage used in the comparator 400 is equivalent to the difference between the reference voltage "Vref" connected to the non-inverting terminal of the comparator 400 and the D / A convert...
no. 3 example
[0128] Figure 11 A structural circuit diagram of a bias compensation device according to a third embodiment mode of the present invention is shown. It should be understood that the same reference numerals shown in the second embodiment are used to denote the same or similar circuit elements used in the third embodiment. In the offset compensation device of the third embodiment, the correction value generation circuit 430 is composed of an addition and subtraction circuit (up / down counter) 432 and a latch 434, and the value from the addition and subtraction circuit 432 can be selected by the switch SW5. Any one of the output signals is used as an input signal to the adder 420 . Other circuit configurations of this bias compensation device are similar to Figure 10 The structure of the circuit shown.
[0129] In this embodiment, for the comparator, the comparator 400 equipped with the offset adjustment function as explained in the above-mentioned first embodiment is used. B...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com