Human auricular fibrillation pathogenic gene, encoding protein and use thereof
A gene coding, atrial fibrillation technology, applied in genetic engineering, animal/human peptides, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as undisclosed or reported human atrial fibrillation pathogenic genes, no disclosure or suggestion of KCNQ1, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0114] Mapping of Human Atrial Fibrillation Genes
[0115] Genomic DNA of peripheral blood leukocytes is extracted through standard procedures, and the present invention uses the second version of the ABI Prism polymorphic microsatellite linkage marker kit to scan the whole genome. First do rough positioning, and then do fine positioning of key areas. The microsatellites used for the fine positioning of key regions were selected from the Généthon linkage map, and the microsatellite amplification primers were synthesized according to the Généthon set.
[0116] Microsatellites were amplified by multiplex PCR with a reaction volume of 5 ul, containing 20 ng of genomic DNA, 3.0 mM MgCl, 5-15 pairs of primers (each primer concentration 0.04 uM) and 0.2 U AmpliTaq Gold™ enzyme (PerkinElmer Applied Biosystems). Use the Touchdown method to do PCR, and the PCR cycle is as follows: first, 94°C for 12min; then 94°C for 30sec, 63°C for 1min (each cycle decreases by 0.5°C), and 72°C for 1...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Identification of Human Atrial Fibrillation Genes
[0121] The strategy adopted in the present embodiment to identify human atrial fibrillation pathogenic genes is: (1) in the positioning interval, first check whether the known ion channel genes (including genes such as KCNQ1 and CHRNA10) have mutations; (2) if No mutations are found in the known ion channel genes, and DNA fragments that are highly homologous to known ion channel genes will be searched in the positioning interval, and then these fragments will be used as probes to screen the cardiac cDNA library to clone new ion channels Next, detect whether these newly cloned ion channel genes are mutated in the family; (3) If no mutations are found in these known ion channel genes and newly cloned ion channel genes, then the arrhythmia The pathophysiological mechanism of the disease, determine other candidate genes that fall in this interval, and conduct mutation detection, and finally clone the pathogenic gene of idi...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Establishment of Hereditary Atrial Fibrillation Mouse Model Using Knock-in Technology
[0140] In this example, an animal model of hereditary atrial fibrillation was established by gene knock-in, and the atrial fibrillation-inducing effect of the S140G mutation was confirmed in the animals.
[0141] Comparing the homology of the human and mouse KCNQ1 genes, it is found that the KCNQ1 gene is highly conserved, and exons 1-8 in humans correspond to exons 2-9 in mice. The exon corresponds to the mouse exon 2, its nucleotide homology is 90%, and its amino acid homology is 100%. Therefore, changing the A to G in the 32nd nucleotide of exon 2 in mice should cause hereditary atrial fibrillation in mice.
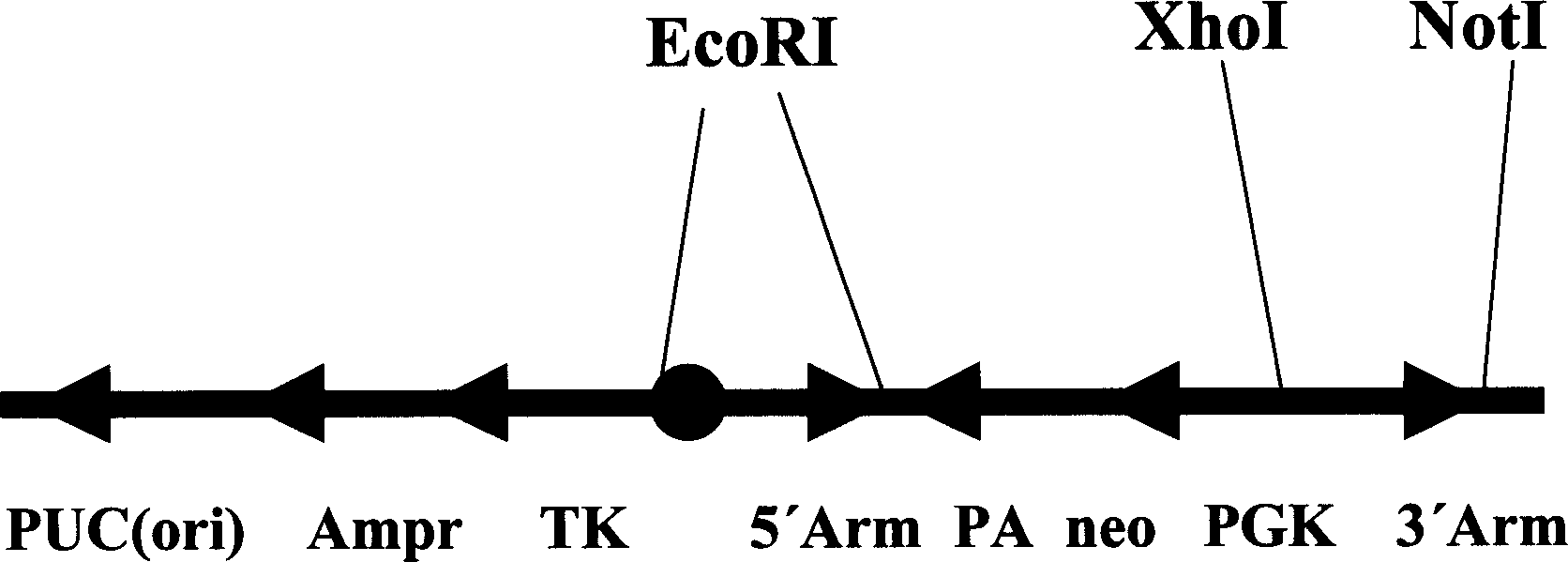
[0142] Through restriction analysis of the genome sequence of the mouse KCNQ1 gene, the two homologous recombination arms used for gene targeting were designed between the 2nd and 3rd exons (including part of the 2nd exon), that is, the 5' arm 44807-47832, 3'arm 40739-43790...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com