KCNQ1 gene mutant and use thereof
A gene and application technology, applied in the field of kits, constructs and recombinant cells for the detection of syndromic deafness, to achieve the effect of high early diagnosis rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Example 1 Determination of autosomal recessive deafness-causing mutations
[0080] 1. Sample collection
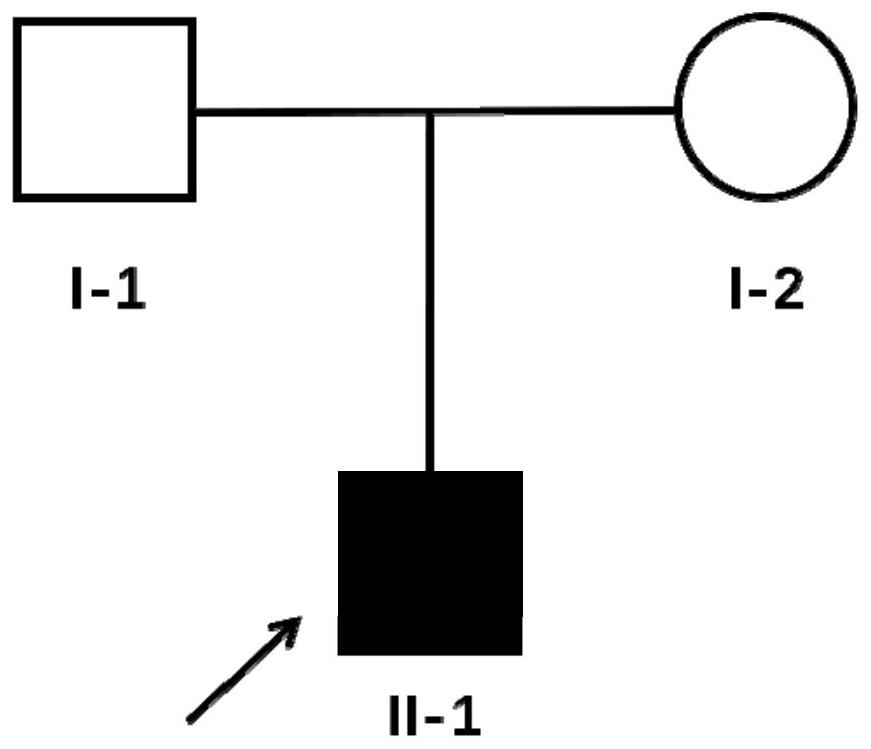
[0081] The inventor collected a Trio family (parents + proband) of a Chinese Han patient with autosomal recessive deafness, the family diagram is shown in figure 1 . Among them, ○ indicates a normal female, □ indicates a normal male, ■ indicates a male patient, and the arrow points to the proband.
[0082] Such as figure 1 As shown, the family contains 3 members, both parents are normal (i.e. I-1, I-2 in the pedigree diagram), and the son is a deaf patient (i.e. II-1 in the pedigree diagram), conforming to autosomal recessive genetic pattern.
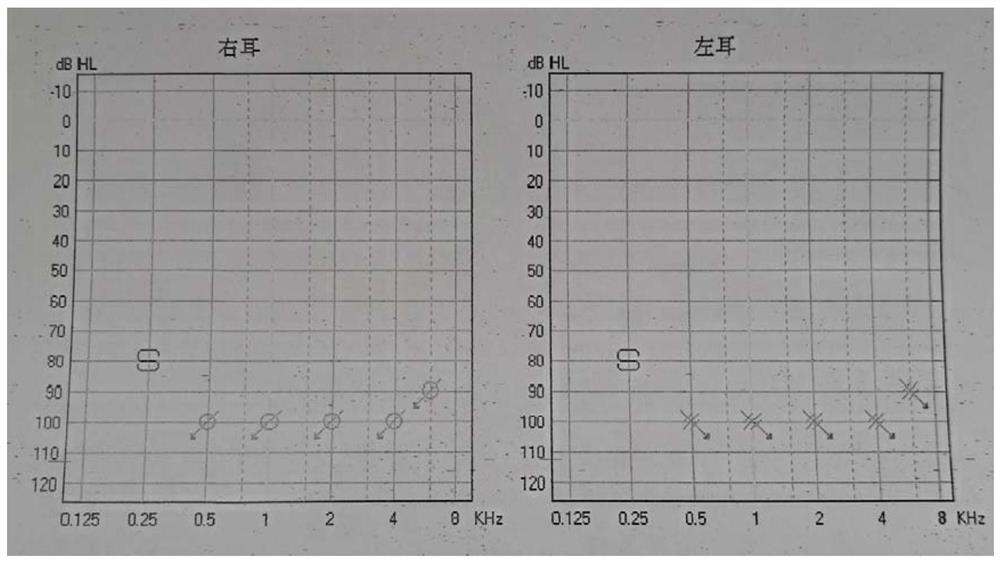
[0083] The pure tone audiometry results of the patients in this family can be seen in figure 2 . exist image 3 In the figure, the abscissa indicates the frequency of the pure tone, and the ordinate indicates the hearing level. If the hearing is normal, the threshold curve should float around 0, and the downward curve...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Example 2 Sanger method sequencing verification
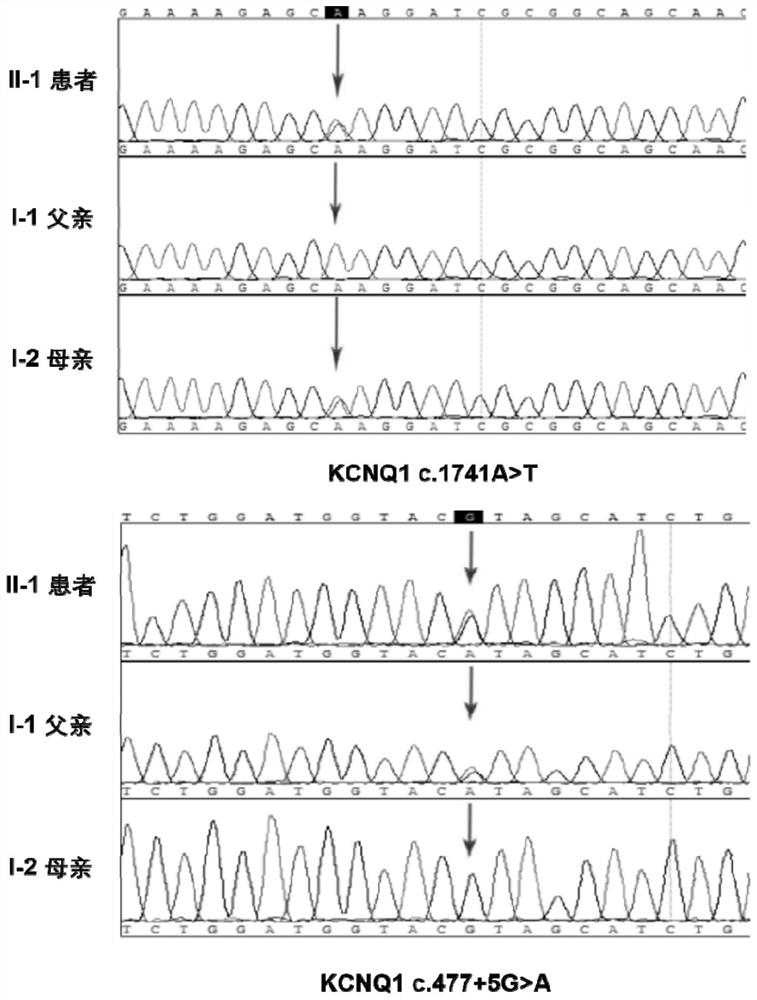
[0092] Detect the KCNQ1 gene of all family members (including patients and parents with normal hearing) in the autosomal recessive deafness patient family described in Example 1: c.1741A>T mutation and c.477+ for the KCNQ1 gene Design primers for the 5G>A mutation, then obtain the relevant sequence of the mutation site by PCR amplification, product purification and sequencing, and verify whether the c.1741A>T mutation and the c. Whether the .477+5G>A mutation was detected in the sample.
[0093] Specific steps are as follows:
[0094] 1. DNA extraction
[0095] According to the DNA extraction method described in Example 1, the genomic DNA in the peripheral venous blood of the subject was extracted for future use.
[0096] 2. Primer design and PCR reaction
[0097] First, referring to the human genome reference sequence GRCh37 / hg19, specific primers for the c.1741A>T mutation and c.477+5G>A mutation of the KCNQ1 gene ...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Embodiment 3 detection kit
[0115] A detection kit is prepared, which comprises primers capable of detecting the c.1741A>T mutation of the KCNQ1 gene, and is used for screening biological samples susceptible to autosomal recessive deafness. The corresponding primers are KCNQ1 gene exon-specific primers, the sequences of which are shown in Example 2 as SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3, etc.
[0116] The specific steps for screening biological samples susceptible to autosomal recessive deafness using the above kit are as follows:
[0117] According to the method described in step 2 of Example 1, the DNA of the test subject is extracted, and the DNA extracted is used as a template to carry out a PCR reaction with the exon-specific primers of the above-mentioned KCNQ1 gene (see Example 2 for the PCR reaction system and reaction conditions, The PCR product was purified according to conventional methods in the art, and the purified product was sequenced.
[0118] By observing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com