Superconductive cable and superconductive cable line
A technology of superconducting cables and superconducting wires, which is applied to cable accessories of low-temperature cables, superconducting devices, superconducting/high-conducting conductors, etc. Problems such as increased cross-sectional area and increased cable cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
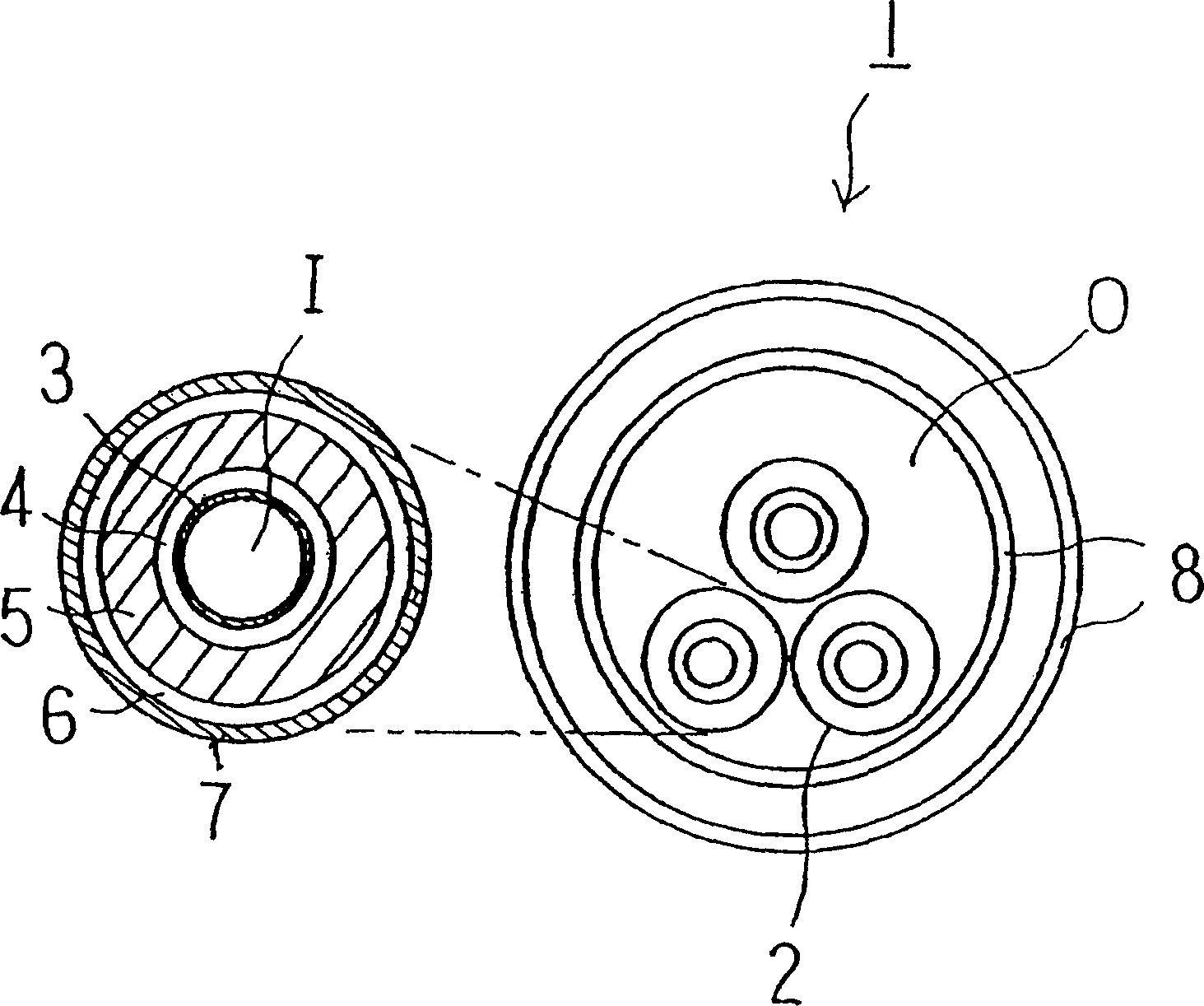
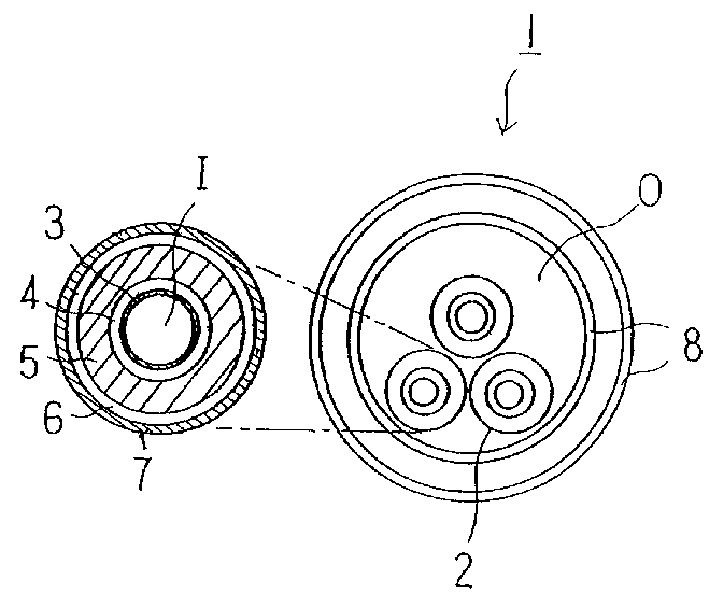
[0026] see below figure 1 The structure of the superconducting cable of the present invention will be described.
[0027] (the whole frame)
[0028] The superconducting cable 1 of the present invention is constructed such that the cable core wire 2 is housed in a heat insulating tube 8 . Each cable core 2 includes a former 3 , a first conductor layer 4 and an insulating layer 5 from inside to outside. It is also possible to sequentially arrange the second conductor layer 6 and the protective layer 7 on the periphery of the insulating layer 5 . Although a three-core high-temperature superconducting cable is used in this embodiment, a single-core cable may also be used.
[0029] (winding mode)
[0030] Aluminum, copper or stainless steel tubes are used as the winding die 3, which is the innermost part of the cable core wire 2. Alternatively, a strand of metal wire, such as thin copper wire, may be used, taking into account the mechanical properties of the cable. If tubes a...
no. 2 example
[0040] Ten pieces of YBa with a width of 5mm and a thickness of about 0.1mm are spirally wound around a stainless steel pipe with an inner diameter of 20mmφ, an outer diameter of 24mmφ, and a length of 2m at a pitch of 300mm. 2 Cu 3 o x (YBCO) superconducting stripline, thereby forming a single-layer Y-based superconducting cable conductor. The superconducting strip line is constructed so that a 2 μm-YBCO superconducting layer is formed on a stainless steel substrate with a width of 5 mm and a thickness of 0.1 mm through a 1 μm-YSZ intermediate layer, and the surface is covered with 5 μm of silver, and in liquid nitrogen The critical current is about 40A. The layers within a range of 30 cm from each end of the superconducting cable were integrated by welding with copper-lead alloy wires connected thereto for conducting current.
[0041] A DC current carrying test was performed by immersing the conductor in liquid nitrogen. The critical current determined by the development...
no. 3 example
[0046] Twenty pieces of HoBa with a width of 5mm and a thickness of about 0.1mm are spirally wound around a copper tube with an inner diameter of 26mmφ, an outer diameter of 30mmφ, and a length of 1m at a pitch of 400mm. 2 Cu 3 o x (HoBCO) superconducting stripline, thereby forming two layers of HoBCO superconducting cable conductors. The HoBCO superconducting stripline is constructed to form a 3 μm-HoBCO superconducting layer through a 1 μm-YSZ intermediate layer on a stainless steel substrate with a width of 5 mm and a thickness of 0.1 mm, and the surface of the layer is covered with 5 μm of silver, liquid nitrogen Their critical current is about 50A. An insulating layer with a thickness of 5 mm is formed by half-covering 10 layers of kraft paper with a thickness of 0.2 mm between the first and second layers. The first and second layers are wound in opposite directions. The layers within 30cm from each end of the conductor of the superconducting cable are integrated by w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com