Multi-path dynamic routing algorithm
A path and routing technology, which is applied in the direction of data exchange, calculation, computer, etc. through path configuration, and can solve problems such as congestion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
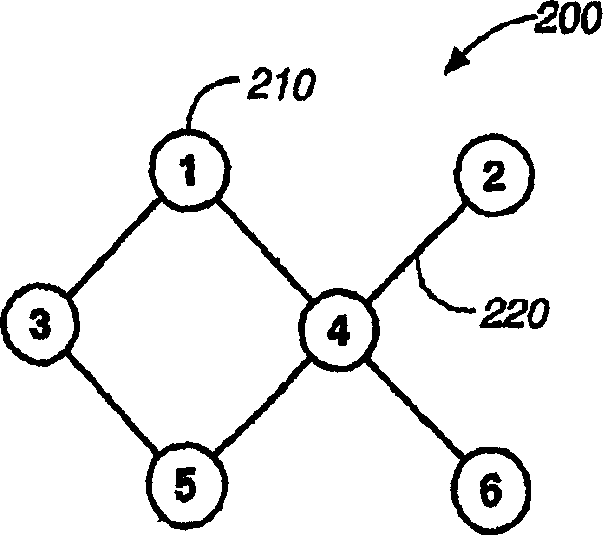
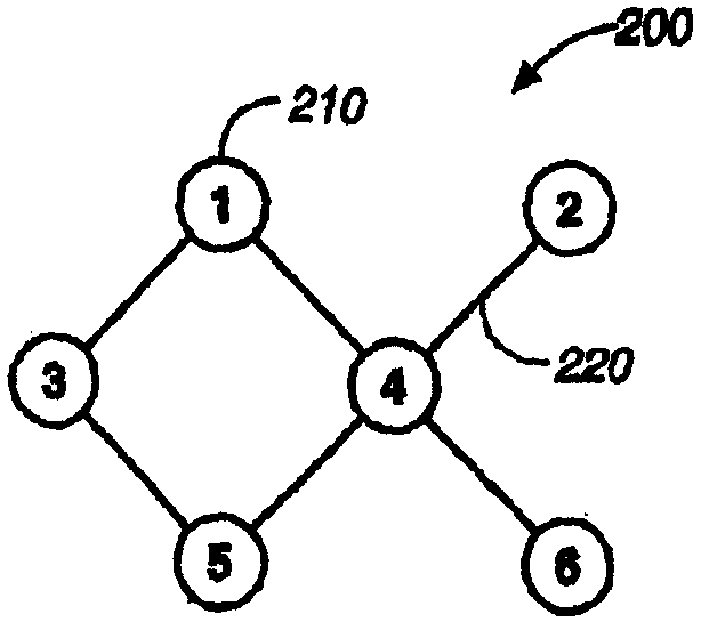
[0013] refer to figure 2 , compute the metric of the path from node 1 to node 5 via node 4 by summing the node metrics of all intermediate nodes. Here, node 4 is the only intermediate node on the path, so its metric is also the path metric of the path. Other methods for combining node metrics of intermediate nodes on a path can also be used to compute the path metric.
[0014] The node bandwidth of a node 210 is the maximum processing rate of a node 210 in the network 200 . Since a node 210 can only communicate with one other node 210 at any one time, the bandwidth of a node 210 is shared by all of its links. Assuming node 4 has a bandwidth of 100 Mbps, then this bandwidth can be shared among its four links to nodes 1, 2, 5 and 6. In other words, the sum of the data communication rates of the node 4 on these four links must be 100 Mbps or less. Generally speaking, let R(i, j) represent the communication rate on the link i-j, then R(4,1)+R(4,2)+R(4,5)+R(4,6)<= 100Mbps, whe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com