Solubilized pharmaceutical composition for parenteral administration
A composition, parenteral technology, applied in the direction of drug combination, drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0148] Preparation of aqueous pharmaceutical compositions according to the invention
[0149] An aqueous solution for parenteral administration is prepared as follows Ingredients per ml (all are pharmacopoeia standards) Sescocalcitol (active substance) 10 μg disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate (buffer) 15.4 mg sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate (buffer) 2 mg sodium chloride 0.8 mg sodium ascorbate (antioxidant) 5 mg BASF's Solutol® HS15 (solubilizer) 5 mg water for injection to 1 ml
[0150] Solutol(R) HS 15 is dissolved in water for injection by heating it to a temperature of up to 80°C. Nitrogen protection. Buffer substances and sodium chloride are added and the solution is cooled to not more than 30°C. Sodium ascorbate is then added and finally secocalcitol is dissolved in the resulting solution.
[0151] The solution is sterile filtered and autoclaved under appropriate time-temperature conditions.
Embodiment 2
[0153] Chemical Stability of Sescocalcitol in Aqueous Pharmaceutical Compositions
[0154] The chemical stability of secocalcitol in aqueous solution was studied in order to measure whether commonly used pharmaceutically acceptable excipients had any influence on the stability. The pH of this aqueous solution was adjusted to pH=7.5. Ascorbate present but no N 2 During protection, the pH value drops to 7.1-7.2 in a short time.
[0155]Sescocalcitol is a vitamin D analogue that is readily degraded in aqueous acidic environments. Thus, the degradation rate decreased approximately 24-fold when the pH was shifted from acidic pH to neutral-slightly basic pH. Sescocalcitol can be degraded by allylic conversion when acid is contained, or sescocalcitol can be decomposed.
[0156] Sescocalcitol decay was monitored by HPLC using a 5 μm LiChrospher RP-18 compressed 125 mm x 4 mm column and acetonitrile:0.01 M phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 (60:40) as the mobile phase. The flow rate was 2ml...
Embodiment 3
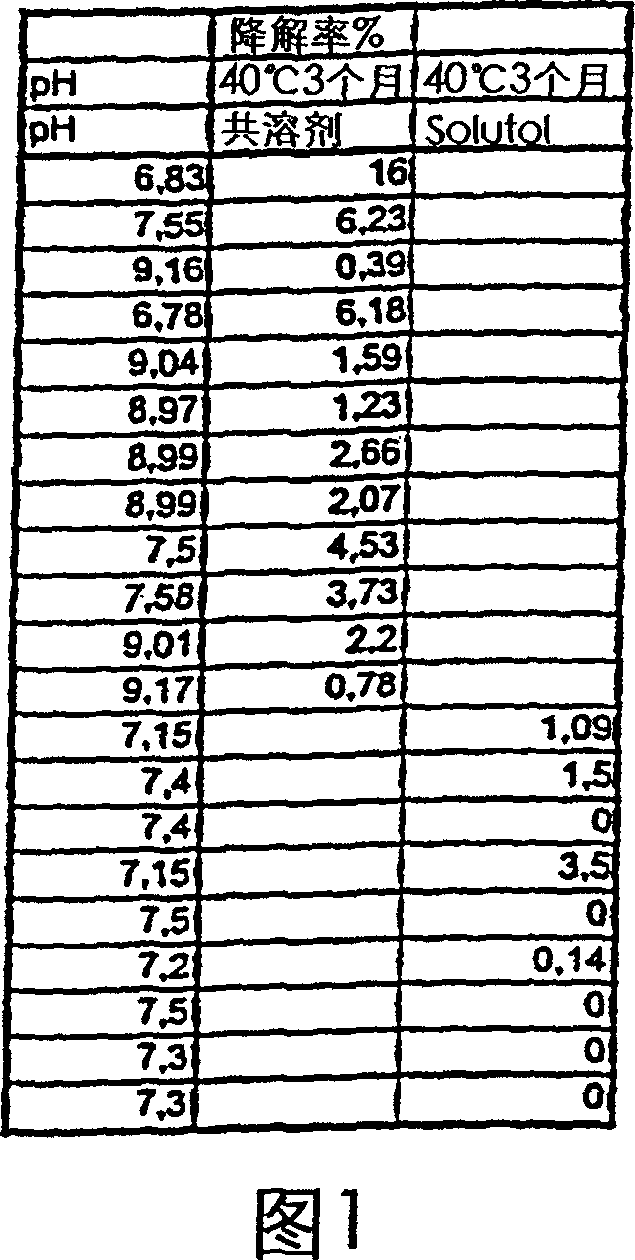
[0177] Improvement of Sescocalcitol Chemical Stability - Comparison of the Stability of Two Different Sescocalcitol Compositions
[0178] Stability of the composition of Example 2 containing Sescocalcitol dissolved in an aqueous vehicle containing Solutol® HS15 as solubilizer (Table 4) without any amount of organic solvent, compared with that containing ethanol-propylene glycol co-solvent (Table 5) Compared to the stability of Sescocalcitol compositions having a Sescocalcitol content of 10 or 30 μg. Compositions containing co-solvents were adjusted to specific pH values (range 6.8-9.2) in order to study the effect of pH on the stability of the compositions. The composition of an example co-solvent composition with a pH of about 9 is given below:
[0179] Sescocalcitol: 10 or 30 μg
[0180] Disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate: 1.8mg
[0181] Sodium chloride: 3.88mg
[0182] Benzyl alcohol: 15.675mg
[0183] 99.9% ethanol: 79.2mg
[0184] Propylene glycol: 414mg
[01...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com