Optical device and spectroscope and polarization separating device using the device
An optical device and beam technology, applied in the field of optical devices and beam splitter devices, can solve the problems of large device size and inability to realize polarization separation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
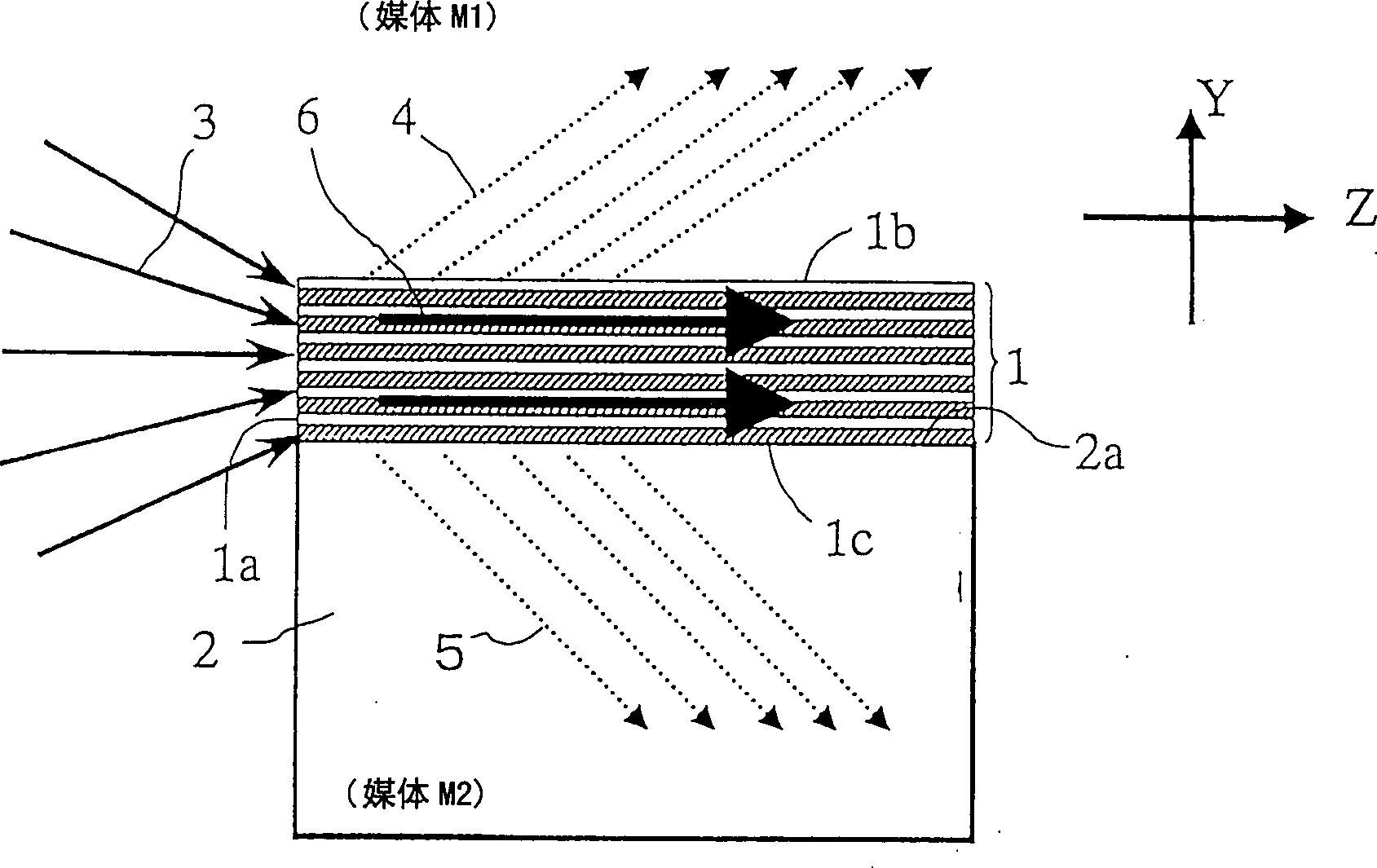
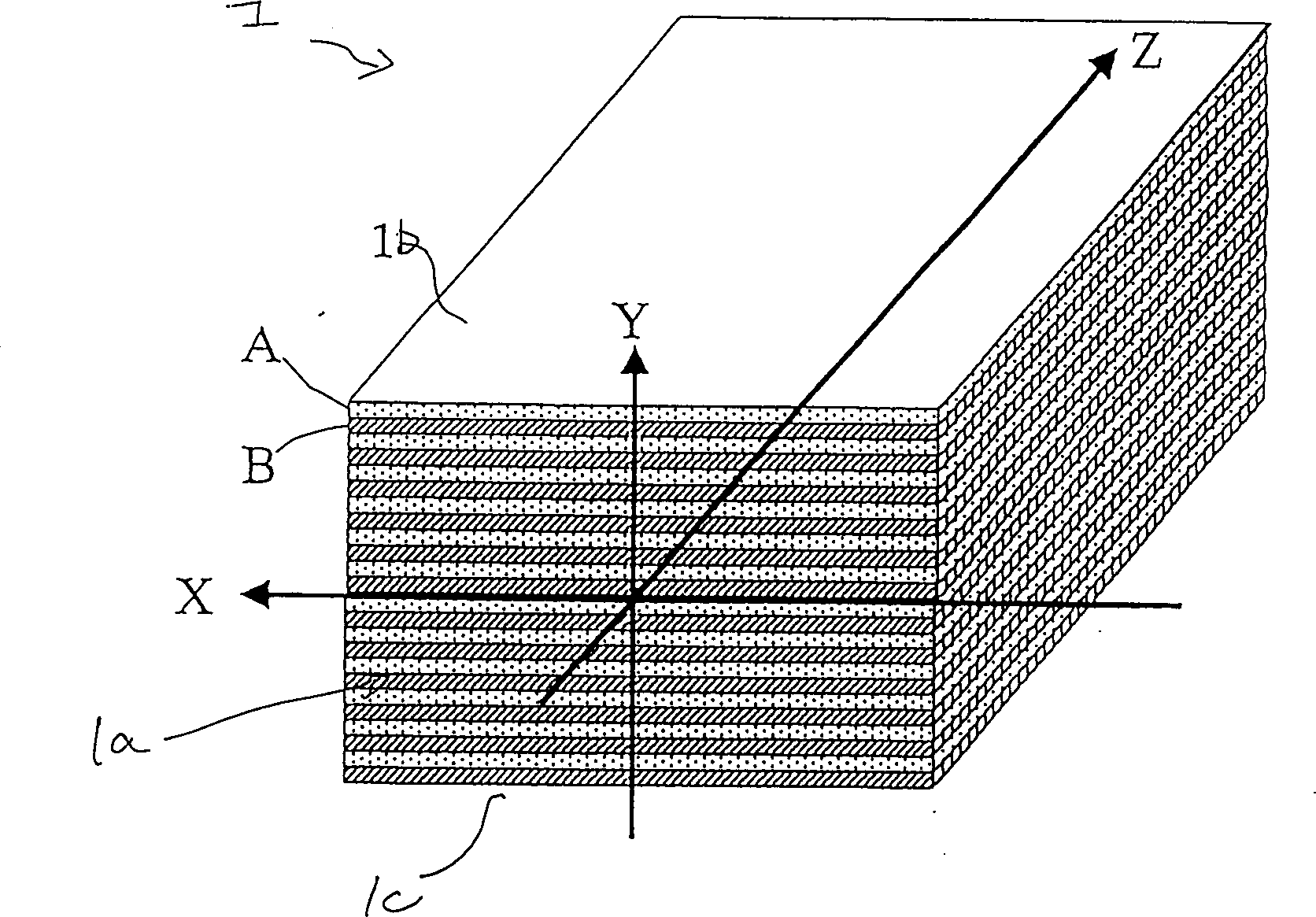
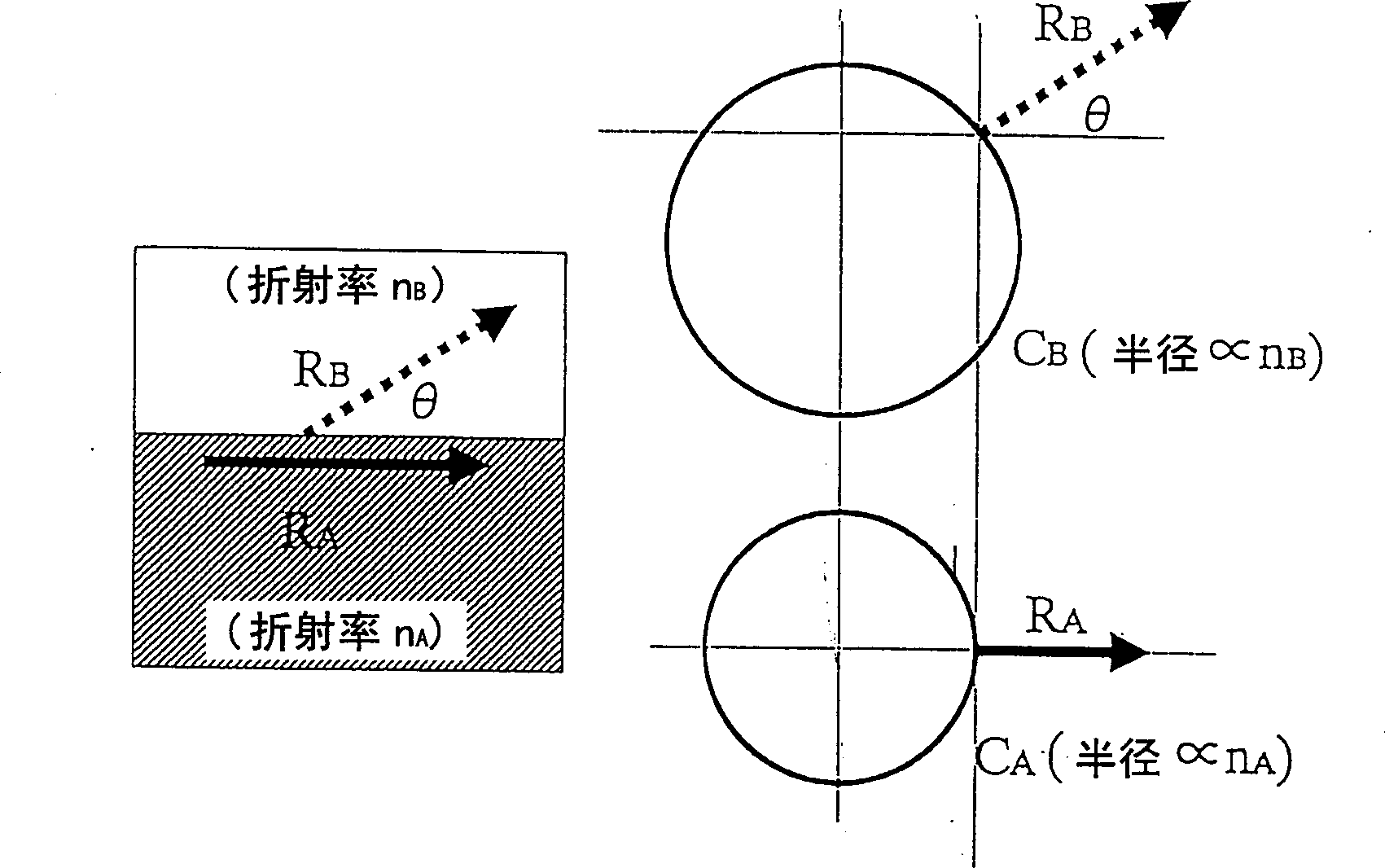
[0136] Such as Figure 15 As shown, a multilayer film 1 is formed on the surface of a parallel plane substrate 2 (soda lime carbonate glass) having a thickness of 1 mm. The thickness of the substrate 2 can generally be selected within the range of 0.1 to 2 mm. Silicon dioxide film (thickness t 1 =150nm) and titanium oxide film (thickness t 2 = 150nm) are successively formed on the substrate surface to form a period. After repeating this operation for a total of 20 cycles (40 layers), a silicon dioxide film with a thickness of 2 μm was attached thereto as protective film 7 .
[0137] Two opposite end faces 2c of the substrate were cut perpendicular to the other surfaces of the substrate and polished to a width of 10 mm. The optical system shown in FIG. 16 was used so that the laser beam was incident on the end face 1a of the multilayer film portion (6 µm thickness).
[0138] A wavelength-tunable laser is used as laser source 11 . After the laser beam 20 is emitted from th...
example 2
[0141] A multilayer film 1 is formed on the surface of a parallel plane substrate 2 (quartz glass) having a thickness of 1 mm. Titanium oxide film (thickness t 1 =212nm) and silicon dioxide film (thickness t 2 = 212nm) are successively formed on the substrate surface to form a period. This operation is repeated for a total of 20 cycles (40 layers). The surface of the multilayer film 1 tangential to the air is a silicon dioxide layer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com