Treatment of i (C. Difficile) toxin B associated conditions
A technology for Clostridium difficile toxins and toxins, which can be applied in the directions of antitoxins, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, and can solve problems such as interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
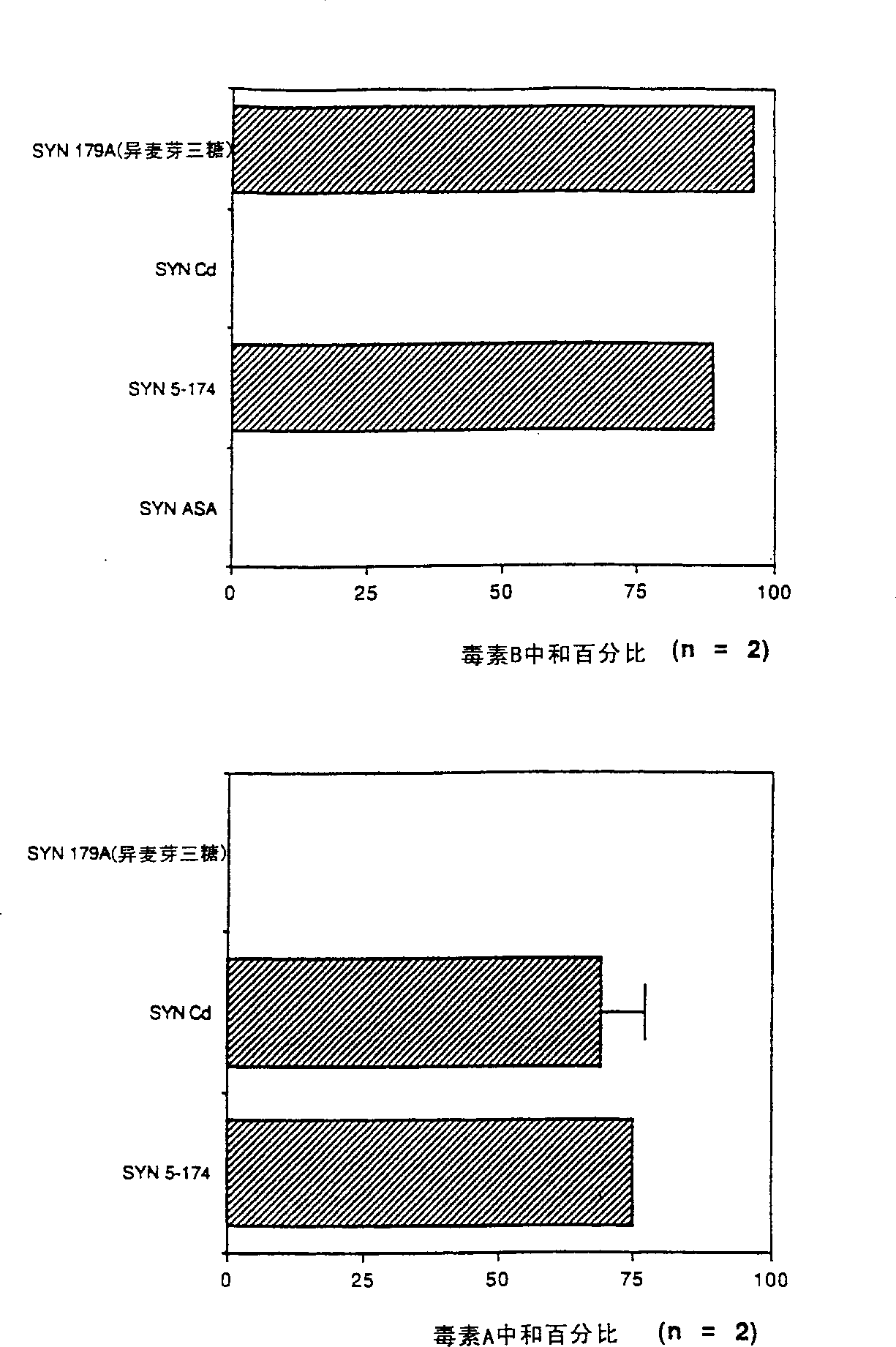
[0150] Example 1 Determination of the conditions for the combination of toxin B and isomaltotriose SYNSORB
[0151]By incubating 20 mg of isomaltotriose SYNSORB (5-128) or Chromosorb sample with 1 mL of purified toxin B solution in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube on a vertical cylinder rotor for 1, 2 and 4 hours at room temperature, Conditions required for toxin B binding were determined. Control tubes containing toxin B solution but without SYNSORB or Chromosorb were incubated simultaneously. The optimal amount of isomaltotriose SYNSORB required for maximal toxin B neutralization was determined by incubating immobilized isomaltotriose (10, 20 or 40 mg) with 1 ml of toxin B for 2 hours at room temperature. The amount of toxin activity in each sample was determined using CHO cells. After incubation, SYNSORB is pelleted to the bottom of the tube and the supernatant is carefully removed. Serial 5-fold dilutions of supernatants were prepared and assayed for cytotoxicity endpoints...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Screening for oligosaccharides that neutralize toxin B
[0154] In a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube, a solution containing purified toxin B (1 ml) was added to various SYNSORBs containing different oligosaccharide sequences listed in Table 1 and incubated on a vertical cylinder rotor at room temperature for 4 Hour. The amount of neutralization for each sample was determined by comparing the CHO cell cytotoxic endpoint titers of the samples with and without SYNSORB.
[0155] As shown in Table 1, with the exception of βGlc, all tested oligosaccharides effectively neutralized toxin B cell toxicity. Therefore, oligosaccharides αGlc(1-2)βGal, αGlc(1-4)βGlc (maltose), βGlc(1-4)βGlc (cellobiose), αGlc(1-6)αGlc(1-6)αGlc( Isomaltotriose), αGlc(1-6)αGlc (isomaltose), and βGlcNAc(1-4)βGlcNAc (chitobiose) bind toxin B.
Embodiment 3
[0157] Toxin A neutralization assay using isomaltose and isomaltotriose SYNSORB In a 0.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, a solution containing purified toxin A (1 mL) was added to isomaltose or isomaltotriose SYNSORB (10 or 20 mg), incubate for 1 hour at 4°C or room temperature on a vertical cylinder rotor. After incubation, SYNSORB is pelleted to the bottom of the tube and the supernatant is carefully removed. Serial two-fold dilutions of supernatants were prepared in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) and the hemagglutination endpoint determined as described above. The reduction in endpoints in the presence of either SYNSORB was determined as compared to a control in which no SYNSORB was added. We did not detect any binding of toxin A to isomaltose or isomaltotriose SYNSORB, suggesting that toxin A has binding specificity distinct from toxin B.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com