Method for constructing well structures for hybrid optical waveguide and the optical waveguide
A technology of optical waveguide and optical core, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, light guide, optics, etc., can solve the problem of reduction of optical signal transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
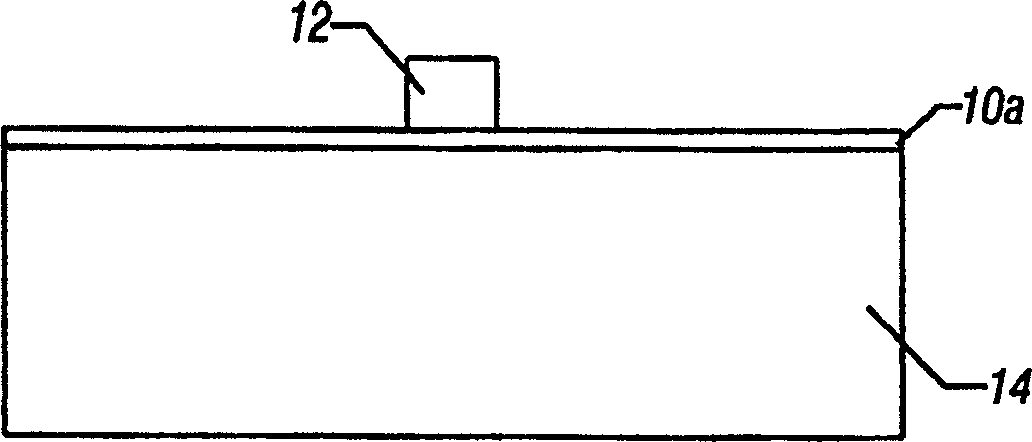
[0036] Reference attached figure 1 In the cross-sectional view of , the substrate 14 may be covered by the lower cladding layer 10 . The lower cladding layer can be a material such as silicon. The optical core 12 may form ridges or lines on the lower cladding 10 . Such as figure 1 As shown, the axis of the ridge is positioned perpendicular to the transverse plane. The optical core can be, for example, a silicon doped with germanium or an oxynitride material.
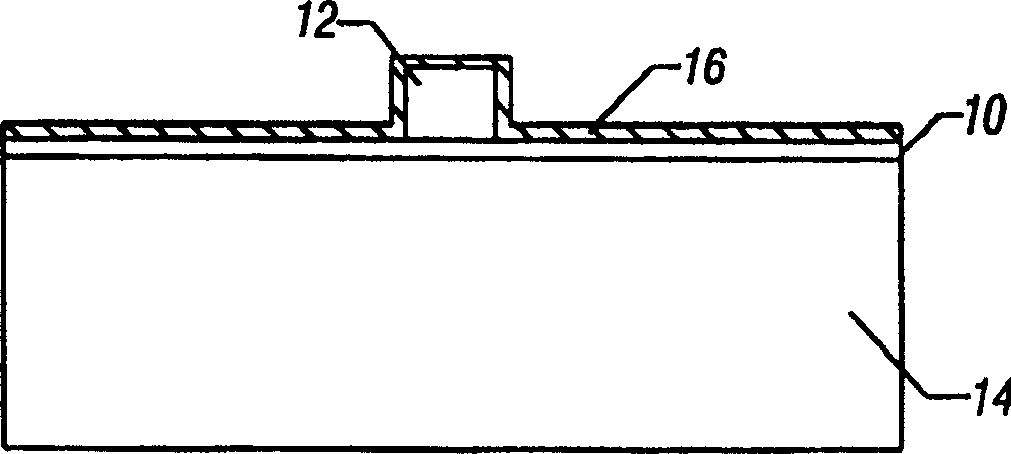
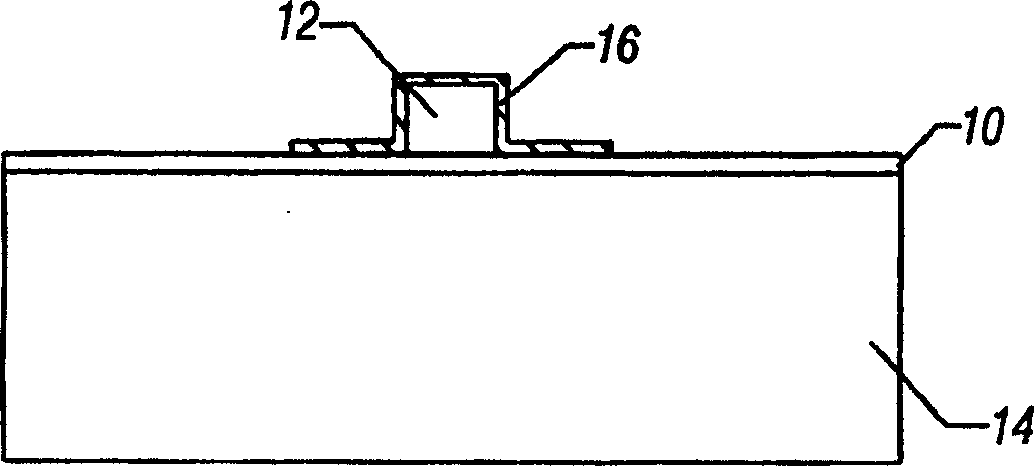
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, a thin seed layer 16 of metallic material such as nickel is formed across the optical core 12 and lower cladding layer 10 . In one embodiment, the metal 16 may be deposited. A first mask is formed on the seed layer 16 using standard photolithography processes. Then the seed layer 16 is etched into the required pattern, as attached image 3 Shown in cross section. Wet etching is very advantageous for this etching process because the seed layer 16 can be completely removed from t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com