Polylactate fiber
A technology of polylactic acid fiber and polylactic acid, which is applied in fiber processing, fiber chemical characteristics, single-component polyester rayon, etc., can solve problems such as poor mechanical properties at high temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1、2
[0173] After drying poly-L lactic acid with a weight-average molecular weight of 190,000 and an optical purity of 99% L lactic acid, melt spinning is carried out at 240°C, and the yarn is cooled and solidified by blowing cold air at 25°C through the ventilator 4, and then used The bundle oiling yarn guide 6 is coated with fatty acid ester as the main fiber oil, and the yarn is staggered by the interlacing guide 7 ( Figure 9 ). Then, the undrawn yarn 10 is taken up by the non-heated second drawing roll 9 with a peripheral speed of 5000 m / min (the spinning speed is 5000 m / min) by the non-heated first drawing roll 8 . The undrawn homopoly-L-lactic acid yarn had a crystal size of 7.7 nm in the (200) plane direction, a degree of crystal orientation of 0.96, a U% of 0.8%, and an elongation at 25°C of 50%. For this undrawn yarn 10 use Figure 10The device was stretched and heat-treated according to the conditions shown in Table 1 to obtain a stretched yarn of 84 dtex, 24 filaments...
Embodiment 3、4
[0176] Spinning and drawing were carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the spinning speed was 6000 m / min, to obtain a drawn yarn of 84 dtex and 96 filaments. The crystal size in the (200) plane direction of the undrawn yarn was 9.2 nm, the degree of crystal orientation was 0.96, the U% was 0.8%, and the elongation at 25° C. was 43%.
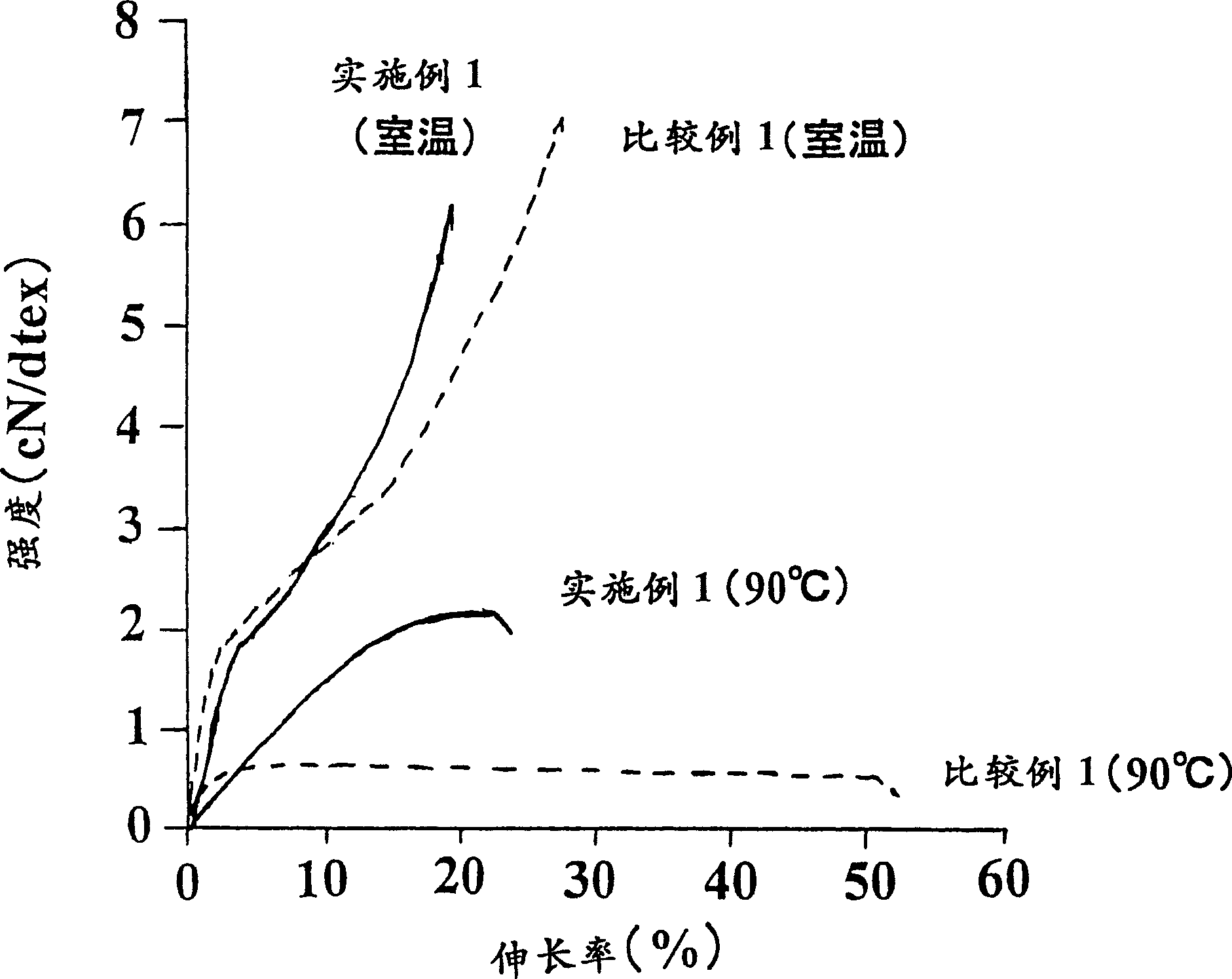
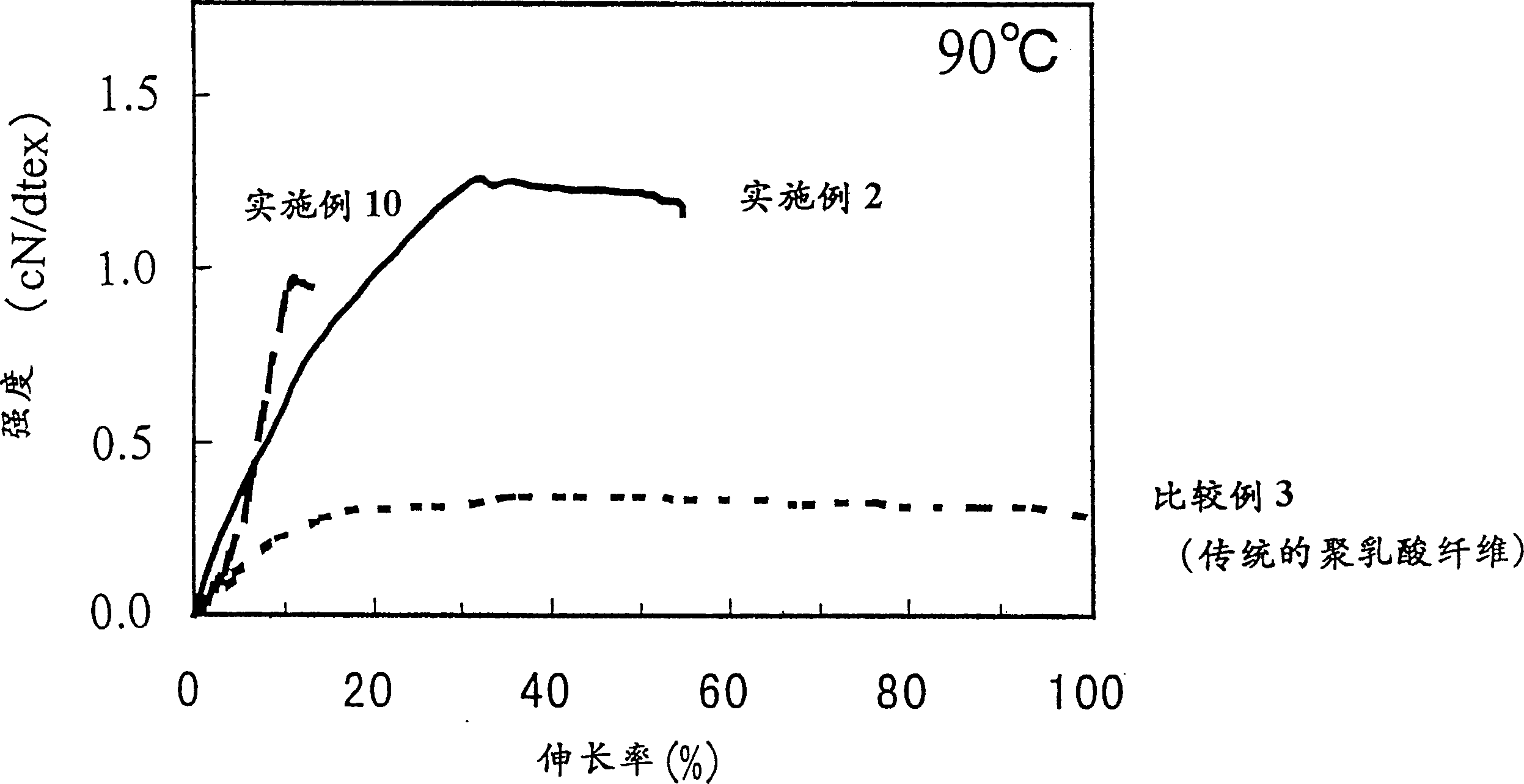
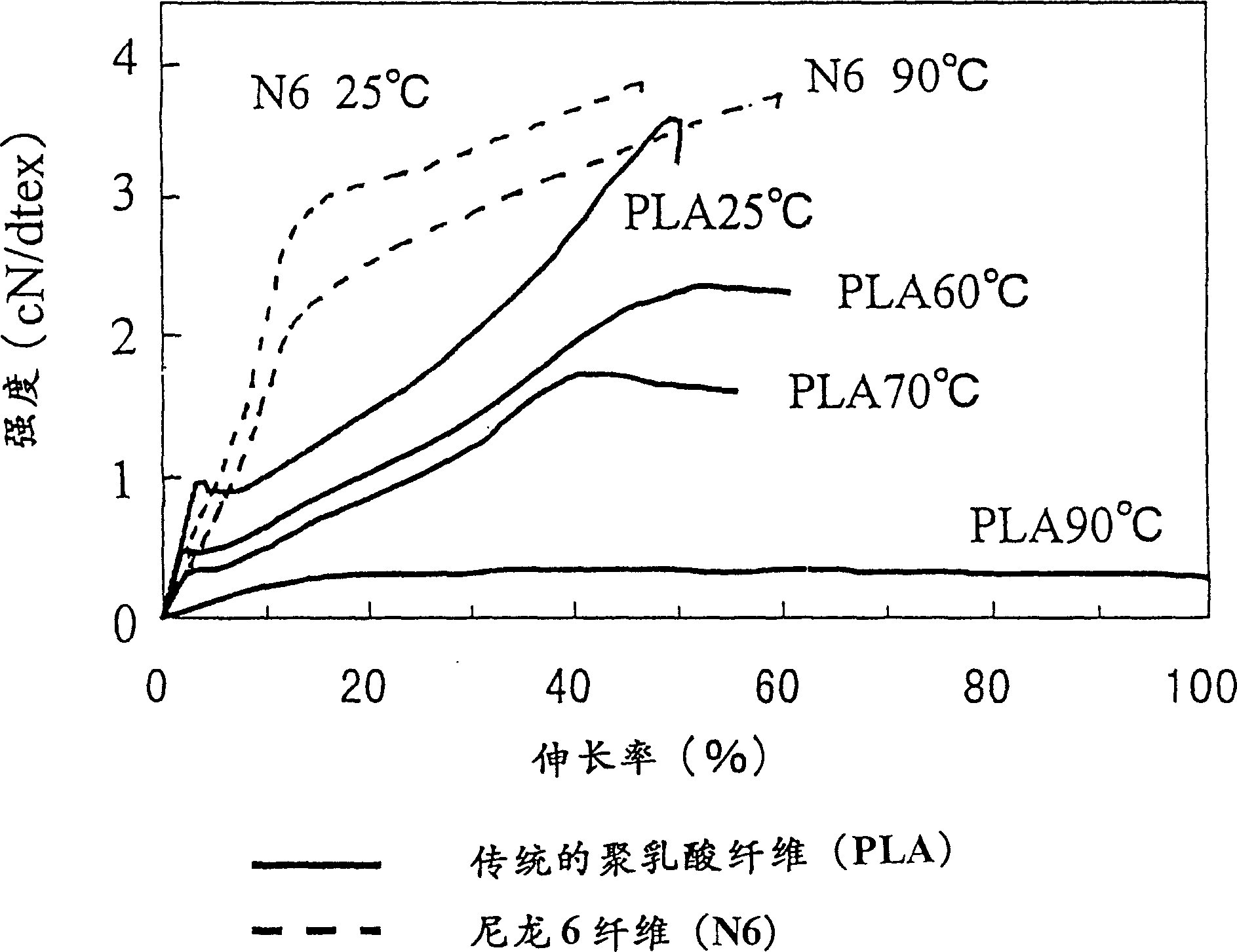
[0177] From the solid state NMR spectra of these stretched yarns it was confirmed that 3 1 spiral structure. In addition, its physical property values are shown in Table 1. Compared with the conventional high-strength polylactic acid fiber (Comparative Example 1), the mechanical properties at 90° C. were significantly improved.
Embodiment 5
[0179] Spinning was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the peripheral speed of the first pulling roll 8 was 4000 m / min, the temperature of the first hot roll 12 during stretching was 110° C., and the draw ratio was 1.6 times. And drawing, obtained the homopolylactic acid drawing yarn of 84detx, 36 monofilaments, trilobal section. The spun-coiled yarn had a crystal size of 6.8 nm in the (200) plane direction, a crystal orientation degree of 0.91, a U% of 0.8, and an elongation at 25° C. of 72%. From the solid NMR spectrum of the stretched yarn, it was confirmed that 3 1 spiral structure. In addition, the physical property values of this stretched yarn are shown in Table 1. Compared with the traditional high-strength polylactic acid fiber (Comparative Example 1), the mechanical properties at 90°C have been improved. In addition, the elongation of the fiber of Example 5 at 90° C. and a stress of 0.5 cN / dtex was 12%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com