Semiconductor device manufacturing process
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc., can solve the problems of limited miniaturization, improve reliability, simplify procedures, and prevent loosening Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
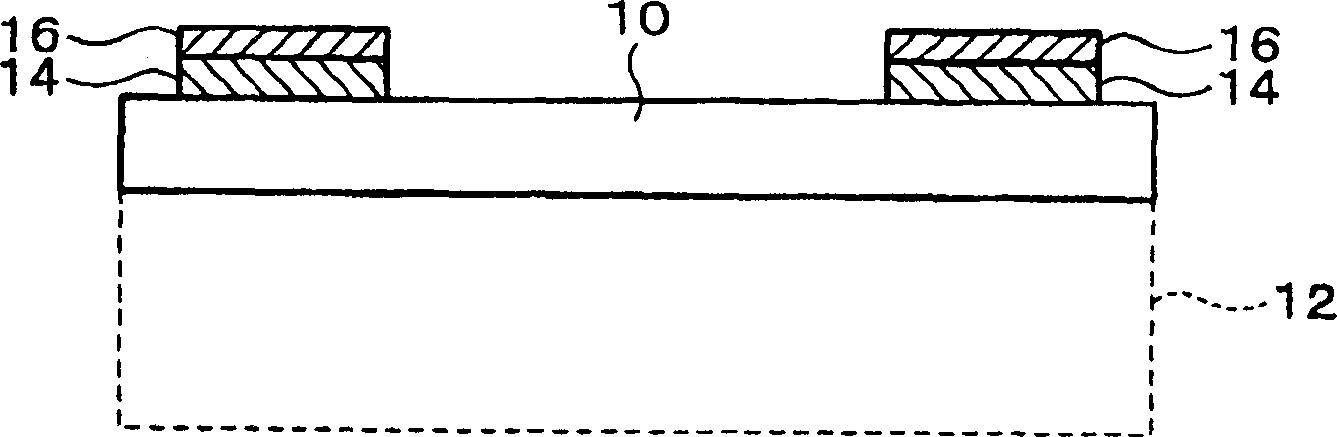
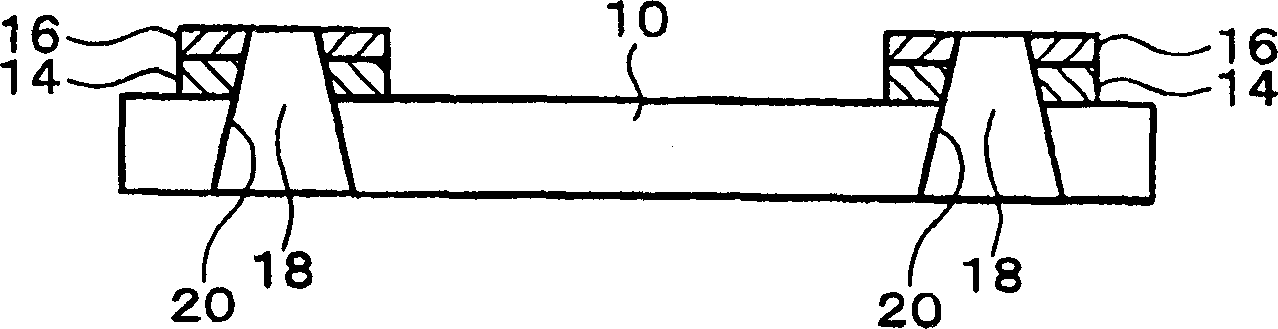
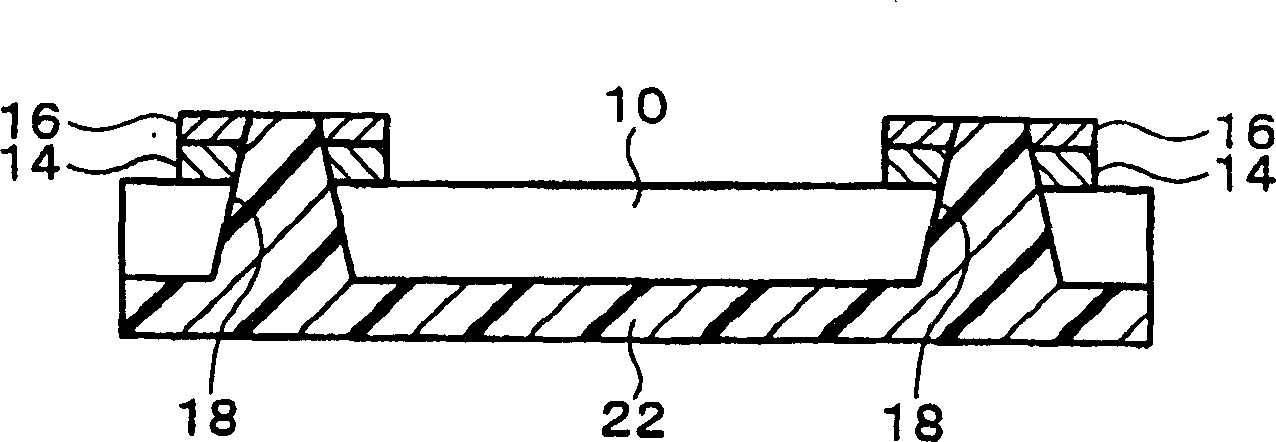
[0051] Figure 1A ~ 2C It is a schematic diagram of the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Figure 1Ais a schematic diagram of a semiconductor chip 10 (semiconductor element) used in this embodiment. In the example shown in this embodiment, a semiconductor wafer diced into a plurality of semiconductor chips 10 side by side is used. The semiconductor chip 10 is generally a rectangular parallelepiped (including a cube), but its shape is not limited and may be spherical.
[0052] The semiconductor chip 10 is formed by thinning the thickness of the original semiconductor chip 12 (or semiconductor wafer). Specifically, the surface of the semiconductor chip 10 opposite to the surface on which the integrated circuit is formed (active surface) is polished. The thickness of the semiconductor chip 10 can be reduced as much as possible as long as the portion forming the integrated circuit remains. The thickness...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0092] Figure 4A and Figure 4B It is a schematic diagram of a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the method of forming the conductive member 28 is different from the above.
[0093] like Figure 4A As shown, in this embodiment, first and second semiconductor chips 11 and 13 are provided. The first and second semiconductor chips 11 and 13 can form the second through-holes 24 penetrating through at the positions of the electrodes 14 of the respective semiconductor chips through the above steps. In this embodiment, the conductive member is solid and disposed inside the second through hole 24 of the second semiconductor chip 13 . The conductive member may also be a bump 32 . The bumps 32 can be formed of solder, gold, or the like.
[0094] The bumps 32 are provided and connected to the electrodes 14 (plating layer 16 ) of the first semiconductor chip 11 . Specifically, when the firs...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0108] Figure 6A and 6B It is a schematic diagram of the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device according to the third embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the form of the second through hole 25 is different from the above.
[0109] like Figure 6A As shown, in this embodiment, the second through hole 25 is formed with a conical surface. Specifically, the second through hole 25 may be formed with a conical surface 27 that becomes smaller as it is farther away from the electrode 14 of the semiconductor chip 10 . The second through hole 25 can be formed, for example, by irradiating a laser beam from the electrode 14 side of the semiconductor chip 10 , or by irradiating a laser beam from the side opposite to the electrode 14 . In addition, other forms and formation methods of the second through hole 25 are as described above.
[0110] Figure 6B The semiconductor chip 10 having the above-mentioned second through hole 25 is a schematic diagram ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com