Epitaxial wafer, epitaxial wafer preparation method and blue-green light emitting diode
A technology of epitaxial wafers and sub-layers, applied in chemical instruments and methods, post-processing details, crystal growth, etc., can solve the problems of low electron-hole radiation recombination efficiency, reduce electron overflow, improve interface quality, and improve electron density. Effect of hole radiative recombination efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
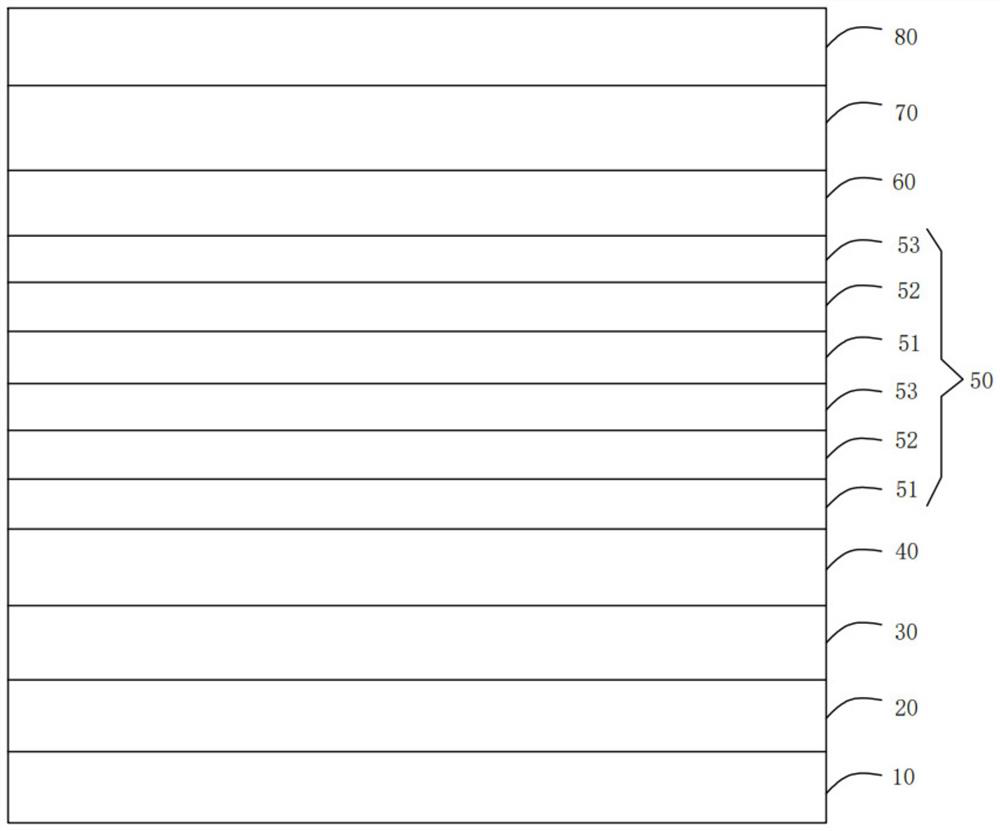
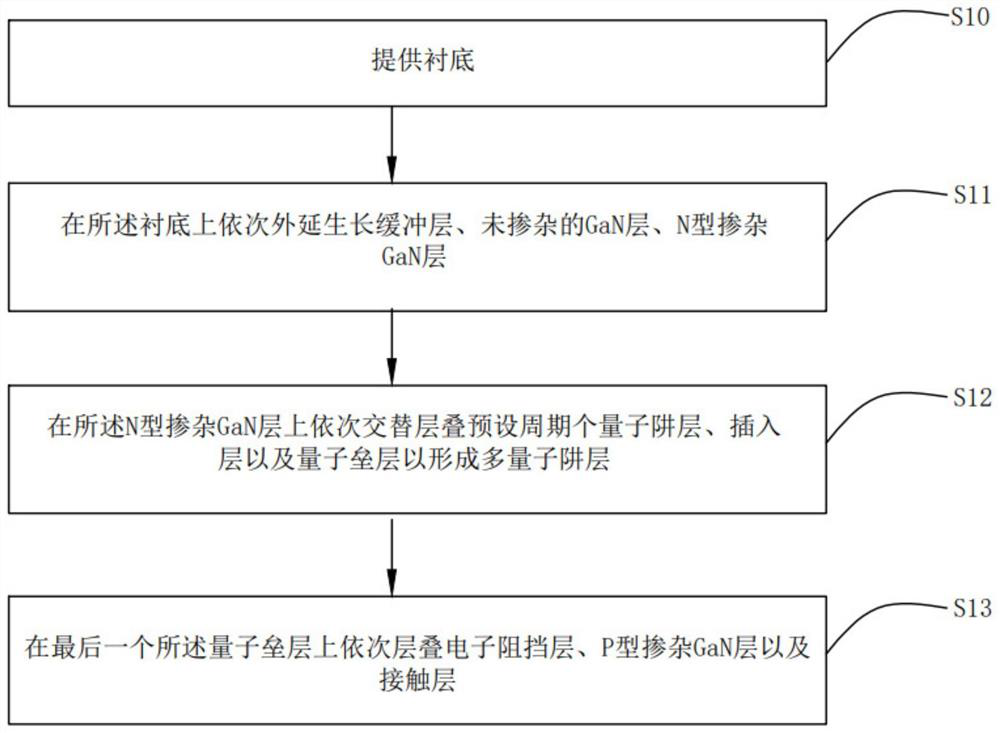
[0065] provide a substrate;
[0066] The AlN layer is grown on the substrate by PVD to form the buffer layer, and then placed in the MOCVD system, and the undoped GaN layer, the N-type AlGaN layer, and the quantum well layer and the insertion layer are sequentially grown epitaxially on the buffer layer. and the quantum barrier layer, after the last quantum barrier layer is grown, the electron blocking layer, the P-type doped layer and the contact layer are grown in sequence.
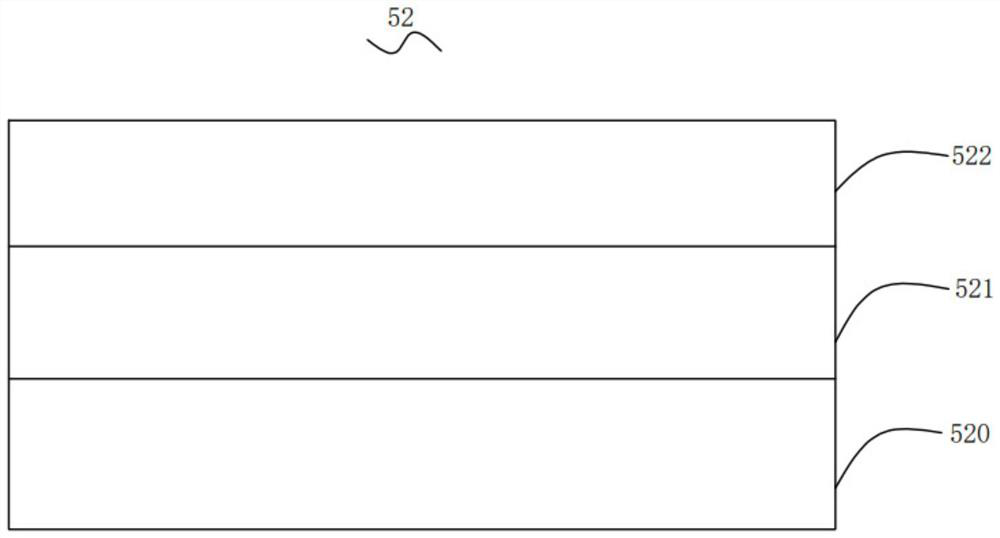
[0067] Wherein, when growing the insertion layer, an AlN layer with a thickness of 1 nm is first grown under the conditions of a growth temperature of 900° C. and a growth pressure of 100 torr to form a first insertion sub-layer, and then a growth temperature of 900° C. and a growth pressure of 100 torr A SiN layer with a thickness of 1 nm is grown to form a second insertion sub-layer under the conditions of Three insertion sublayers.
[0068] Among them, trimethylaluminum (TMAl), trimethylgallium or t...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference between the light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and its preparation method in this embodiment and the light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and its preparation method in Example 1 is:
[0071] The growth thickness of the first insertion sublayer is 0.5 nm, the growth thickness of the second insertion sublayer is 1.0 nm, and the growth thickness of the third insertion sublayer is 2.0 nm.
Embodiment 3
[0073] The difference between the light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and its preparation method in this embodiment and the light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer and its preparation method in Example 1 is:
[0074] The growth thickness of the first insertion sublayer is 0.5 nm, the growth thickness of the second insertion sublayer is 1.0 nm, and the growth thickness of the third insertion sublayer is 2.0 nm; The growth pressure of the inserted sublayers is all 50torr.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com