Rotor assembly, permanent magnet motor and compressor
A component and rotor technology, applied in the direction of electric components, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the performance and reliability of motors and compressors, the weakening of the anti-demagnetization ability of rotor permanent magnets, and affecting the service life of products, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
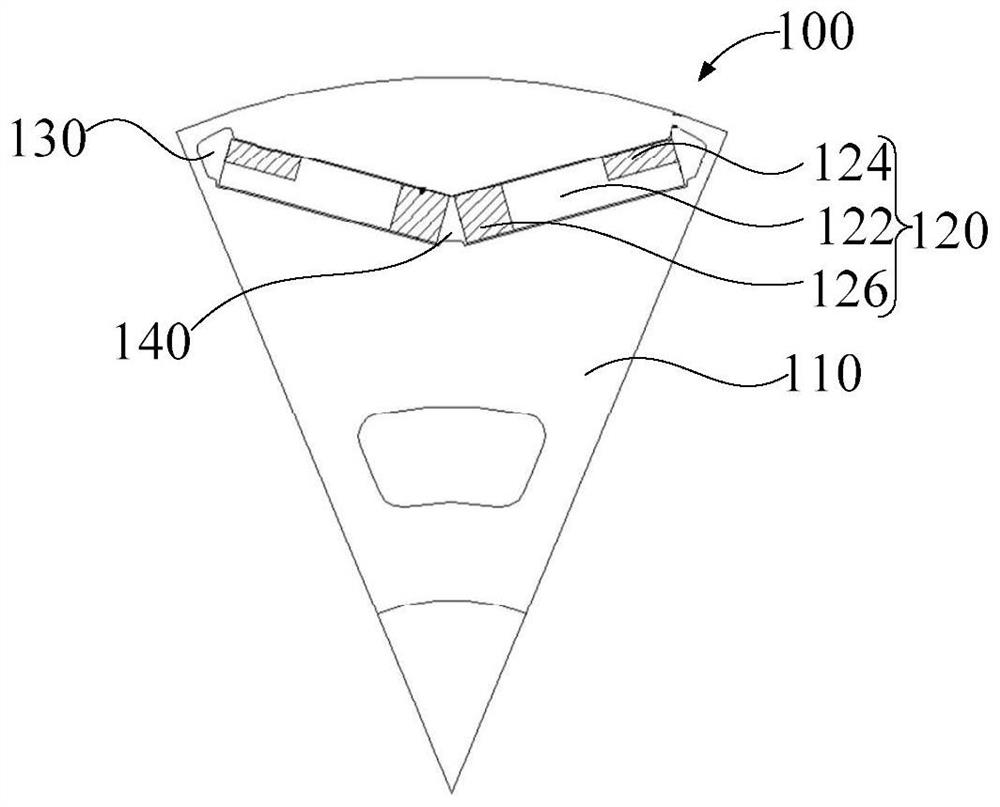
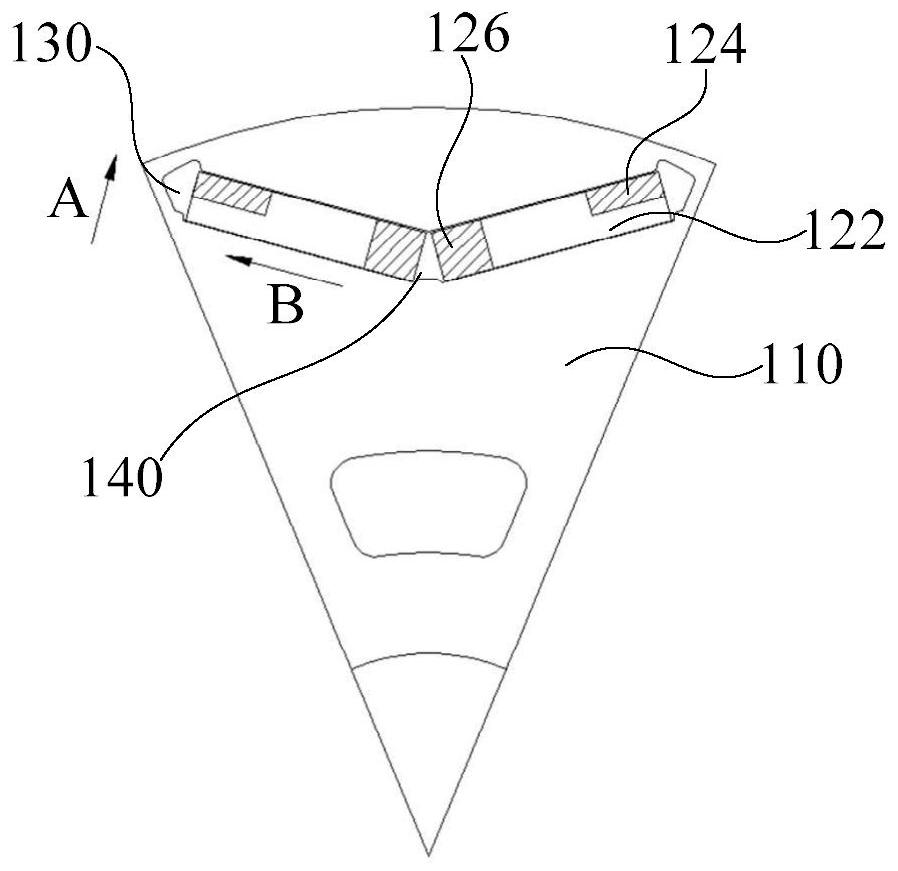
[0060] like figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention provides a rotor assembly 100. The rotor assembly 100 includes:
[0061] The rotor iron core 110 includes a through hole; the permanent magnet 120 is arranged in the through hole, and the permanent magnet 120 is cut through a plane perpendicular to the axis of the rotor iron core 110 to obtain a first cross section. On the first cross section, the permanent magnet 120 is extension direction ( image 3 The included angle between the B direction is the extension direction) and the radial direction of the rotor core 110 is greater than 0° and less than 90°. The permanent magnet 120 includes: a non-diffusion part 122, and in the extension direction, the non-diffusion part 122 includes: The first end and the second end, the first end is adjacent to the peripheral side surface of the rotor core 110, and the second end is adjacent to the axis of the rotor core 110; t...
Embodiment 2
[0070] like figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 As shown, in the embodiment of the second aspect of the present invention, in the radial direction of the rotor iron core 110, the distance between the first magnetic isolation bridge 130 and the circumferential side surface of the rotor iron core 110 is W1; length is L1 where W1 1.3 ×L1=K1, 0.04≤K1≤0.57.
[0071] In this embodiment, the dimensional relationship between the first magnetic isolation bridge 130 and the first diffusion part 124 is defined. Specifically, the distance between the first magnetic isolation bridge 130 and the peripheral side surface of the rotor iron core 110 is W1, that is, in the radial direction, the minimum distance between the first magnetic isolation bridge 130 and the peripheral side surface of the rotor iron core 110 is W1. On the first cross section, the length of the first diffusion part 124 in the extending direction of the permanent magnet 120 is L1. On this basis, W1 and L1 satisfy the f...
Embodiment 3
[0075] like figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 As shown, in the embodiment of the third aspect of the present invention, two permanent magnets 120 are a group, and the rotor assembly 100 includes multiple groups of permanent magnets 120; on the first cross-section, the two permanent magnets 120 of the same group are distributed in a V-shape.
[0076] In this embodiment, the layout of the permanent magnets 120 on the rotor assembly 100 is defined. Specifically, each rotor assembly 100 is provided with a plurality of groups of permanent magnets 120 , and the plurality of groups of permanent magnets 120 are arranged around the axis of the rotor core 110 . Each group of permanent magnets 120 includes two permanent magnets 120, and the two permanent magnets 120 are symmetrically arranged on both sides of the first plane. The axis of the rotor iron core 110 and the diameter of the rotor iron core 110 are both in the first plane. Specifically, the rotor iron core 110 and the perman...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com