Novel method for recycling rare earth from neodymium iron boron recycled material
A technology of neodymium iron boron and recycled materials, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as high requirements for equipment materials, polluting the environment, and difficult disposal, and achieve the effect of simple process, high rare earth leaching rate, and efficient recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
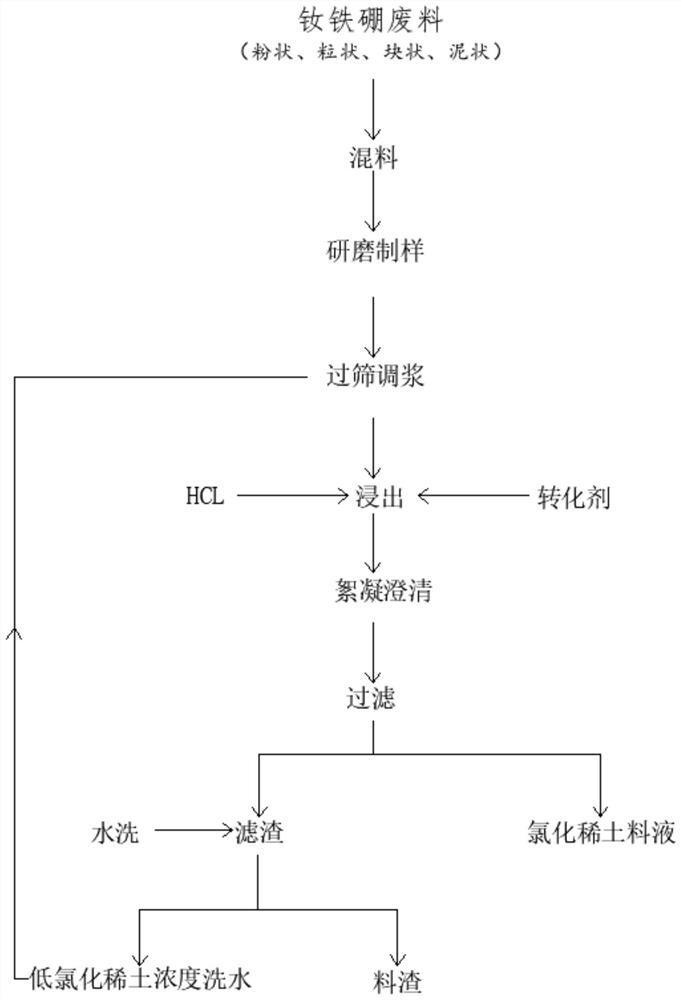
[0040] A new method for recovering rare earth from neodymium iron boron recycled material, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Step 1: Mixing: fully mix the NdFeB wastes in the form of powder, granular, block, mud, etc. to obtain NdFeB wastes that are dry and wet evenly and are convenient for abrasive sample preparation;
[0042] Step 2: Grinding and sample preparation: Weigh 500 g of the NdFeB waste obtained in Step 1 and add it to the sample preparation machine for grinding to obtain NdFeB waste powder;
[0043] Step 3: sieving and slurrying: sieve the NdFeB waste powder obtained in step 2 with a 200-mesh sample to obtain the oversize and undersize, and detect the content of rare earth and iron in the undersize. The rare earth content is 26%, and the iron content is 67%. Put the material on the sieve into the sample making machine to continue grinding, weigh 200g of the material under the sieve, and add 350ml of water to make it into a slurry;
[0044] Step 4: Leaching...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Step 1: Mixing: fully mix the NdFeB wastes in the form of powder, granular, block, mud, etc. to obtain NdFeB wastes that are dry and wet evenly and are convenient for abrasive sample preparation;
[0050] Step 2: Grinding and sample preparation: Weigh 500 g of the NdFeB waste obtained in Step 1 and add it to the sample preparation machine for grinding to obtain NdFeB waste powder;
[0051] Step 3: sieving and slurrying: sieve the NdFeB waste powder obtained in step 2 with a 200-mesh sample to obtain the oversize and undersize, and detect the content of rare earth and iron in the undersize. The rare earth content is 28%, and the iron content is 65%. Put the material on the sieve into the sample making machine to continue grinding, weigh 200g of the material under the sieve, and add 380ml of water to make it into a slurry;
[0052] Step 4: Leaching: slowly add 140 ml of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 30% to the slurry obtained in step 3, and then slowly add 160...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Step 1: Mixing: fully mix the NdFeB wastes in the form of powder, granular, block, mud, etc. to obtain NdFeB wastes that are dry and wet evenly and are convenient for abrasive sample preparation;
[0058] Step 2: Grinding and sample preparation: Weigh 500 g of the NdFeB waste obtained in Step 1 and add it to the sample preparation machine for grinding to obtain NdFeB waste powder;
[0059] Step 3: sieving and slurrying: sieve the NdFeB waste powder obtained in step 2 with a 200-mesh sample to obtain the oversize and undersize, and detect the content of rare earth and iron in the undersize. The rare earth content is 30%, and the iron content is 66%. Put the material on the sieve into the sample making machine to continue grinding, weigh 200g of the material under the sieve, and add 400ml of water to make it into a slurry;
[0060] Step 4: Leaching: slowly add 150 ml of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 30% to the slurry obtained in step 3, and then slowly add 172...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com