Method for identifying parameters of non-Gaussian aquifer by fusing underground water level and natural potential data based on convolutional neural network
A convolutional neural network and natural potential technology, applied in the field of groundwater numerical simulation, can solve problems such as limited estimation accuracy and insufficient borehole observation data, and achieve the effects of reducing observation costs, ensuring characterization accuracy, and reducing the number of boreholes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
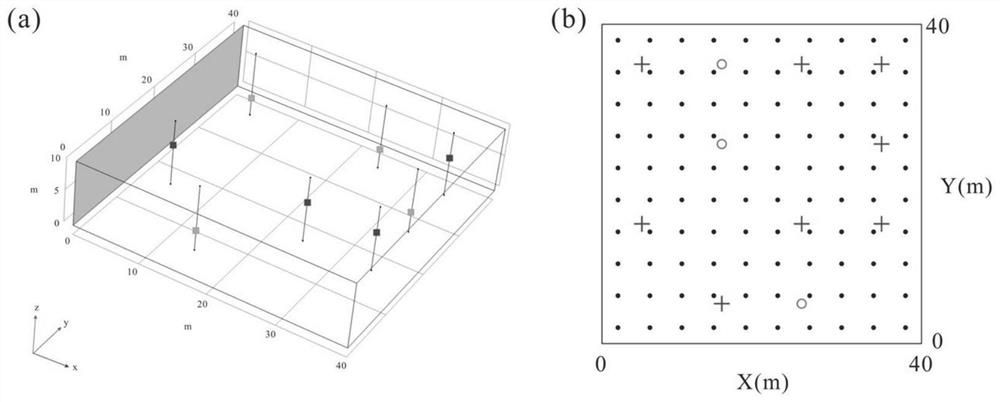
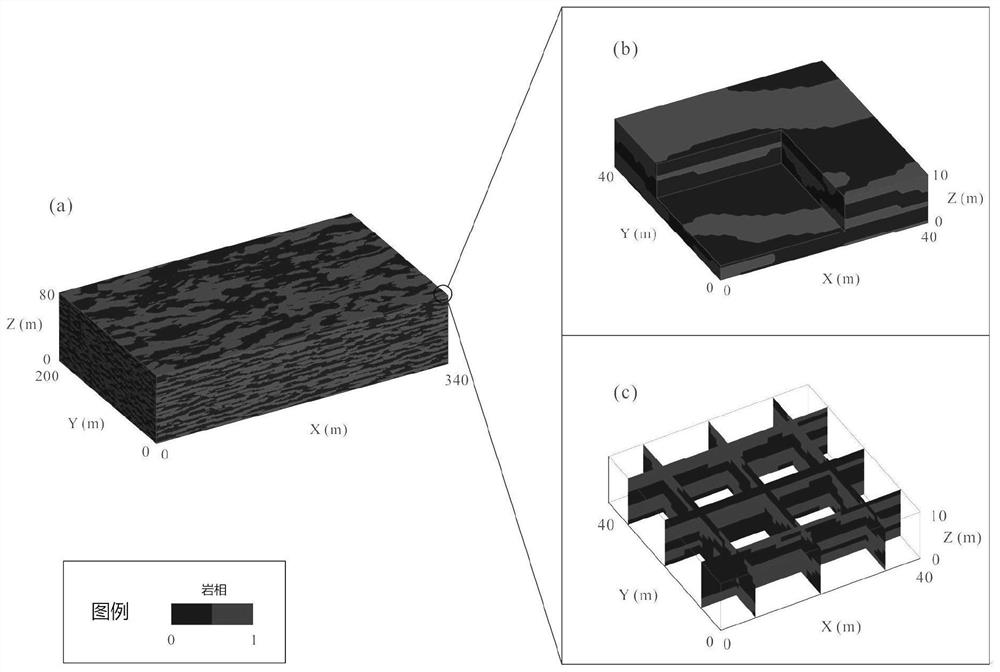
[0042] Such as figure 1As shown, the present invention proposes a set of hydro-geophysical joint inversion framework for non-Gaussian permeability coefficient field coupling hydraulic tomography (Hydraulic Tomography, HT) and spontaneous potential method. In this framework, CVAE in deep learning and ESMDA in data assimilation methods are used to deal with the inversion of non-Gaussian fields, and the estimation of non-Gaussian permeability coefficient fields can be improved by integrating natural potential data and limited hydraulic head data. Effect.
[0043] The self-potential data mentioned above are obtained by the self-potential method (Self-Potential, SP for short), and the self-potential data are used as additional distribution information of the heterogeneity parameter of the underground aquifer. SP is a passive geophysical method that can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com