Device and method for preparing styrene through ethylbenzene dehydrogenation
A technology for ethylbenzene dehydrogenation to produce styrene, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in reducing the water ratio of the ethylbenzene dehydrogenation unit, and difficulty in increasing the production of styrene. The effect of a good technical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
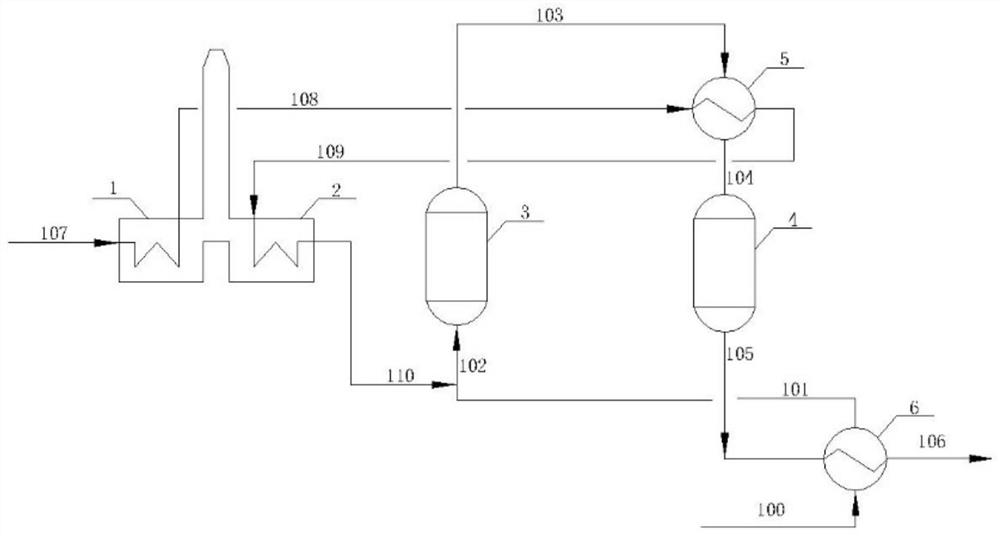
[0053] A 120,000-ton / year ethylbenzene dehydrogenation to styrene plant adopts figure 2 In the process for preparing styrene by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, the raw material flow rate comprising ethylbenzene and water is 31 tons / hour, the temperature is 98° C., and the pressure is 98 kPaA. The raw material is heated to 250°C by the raw material heater, then enters the ethylbenzene superheater to exchange heat to 550°C, mixes with superheated steam from the steam superheater and enters the first dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625°C, pressure 58kPaA), to obtain the second One stream, the first stream is divided into two streams and enters the second dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625 ℃, pressure 44kPaA) after being heated by the intermediate product heater and the intermediate heat exchanger, wherein, the stream entering the intermediate product heater is the same as the first The mass ratio of the stream is 0.3. The steam flow rate entering t...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A 120,000-ton / year ethylbenzene dehydrogenation to styrene plant adopts figure 2 In the process for preparing styrene by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, the raw material flow rate comprising ethylbenzene and water is 31 tons / hour, the temperature is 98° C., and the pressure is 98 kPaA. The raw material is heated to 250°C by the raw material heater, then enters the ethylbenzene superheater to exchange heat to 550°C, mixes with superheated steam from the steam superheater and enters the first dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625°C, pressure 58kPaA), to obtain the second One stream, the first stream is divided into two streams and enters the second dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625 ℃, pressure 44kPaA) after being heated by the intermediate product heater and the intermediate heat exchanger, wherein, the stream entering the intermediate product heater is the same as the first The mass ratio of the stream is 0.1. The steam flow rate entering t...
Embodiment 3
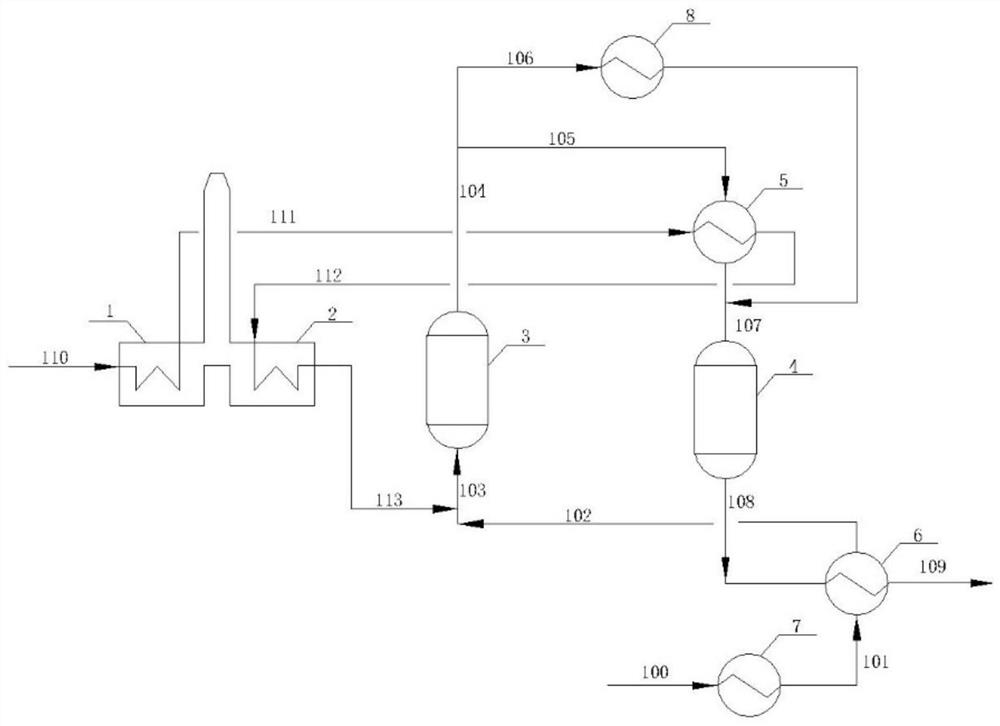
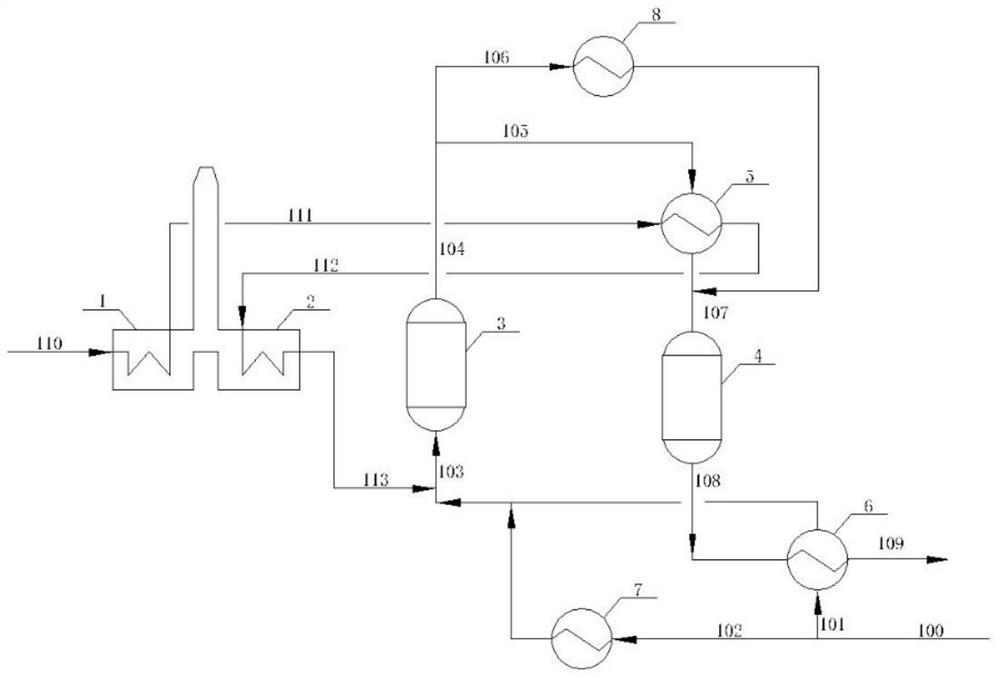
[0059] A 120,000-ton / year ethylbenzene dehydrogenation to styrene plant adopts image 3In the process for preparing styrene by dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, the raw material flow rate comprising ethylbenzene and water is 31 tons / hour, the temperature is 98° C., and the pressure is 98 kPaA. The raw material is divided into two streams, the flow rate of the ethylbenzene superheater is 24.8 tons / hour, and the temperature after heat exchange is 535°C; the flow rate of the raw material heater is 6.2 tons / hour, and the temperature after heating is 540°C. Mix with the superheated steam from the steam superheating furnace and enter the first dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625°C, pressure 58kPaA) to obtain the first stream, which is divided into two streams after being heated by the intermediate product heater and the intermediate heat exchanger. The second dehydrogenation reactor (reaction temperature 625° C., pressure 46 kPaA), wherein the mass ratio of the stream e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com