Method for selectively precipitating magnesium in zinc-magnesium solution
A magnesium solution and selective technology, applied in the field of hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of lack of magnesium, residual extractant, increased production cost of zinc hydrometallurgy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for removing magnesium in a hydrometallurgy process, wherein, comprising the following steps:
[0054] step one:
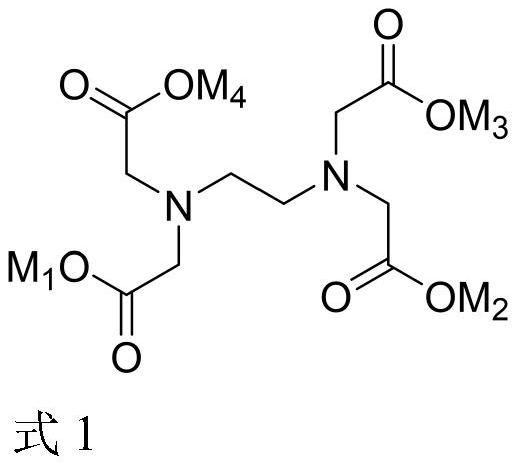
[0055] To the zinc sulfate solution (Zn 2+ : 60g / L, Mg 2+ : 40g / L), add formula 1-A, stir to dissolve; The addition of formula 1-A is 1.09 times of the molar weight of zinc in the solution; Pre-reaction 0.5h;
[0056] step two
[0057] Combined leaching agent solution (sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, wherein, the mol ratio of sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide is 0.5:1; the concentration of sodium carbonate is 0.5M) and the pre-reaction solution of step 1 are pumped respectively with peristaltic pump Send it into a liquid flow (the flow rate of the liquid flow is, for example, 5-10mL / min), mix the two liquid flows, and collect the mixed solution in a container with a stirring structure, adjust the pumping flow rate of the solution, so that the mixing process The pH is maintained at 10-10.5; after the pumping of the pr...
Embodiment 2
[0064] A method for removing magnesium in a hydrometallurgy process, wherein, comprising the following steps:
[0065] step one:
[0066] To the zinc sulfate solution (Zn 2+ : 130g / L, Mg 2+ : 25g / L), add formula 1-A, stir until dissolved; the addition of formula 1-A is 0.8 times of the molar weight of zinc; pre-reaction 0.5h.
[0067] step two
[0068] Use a peristaltic pump to pump the combined leaching agent solution (aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide, the molar ratio of the two is 0.2:1, and the concentration of sodium bicarbonate is 0.2M) and the pre-reaction solution of step 1 into liquid respectively flow (the flow rate of the liquid flow is, for example, 5-10mL / min), the two liquid flows are mixed, and the mixed solution is collected in a container with a stirring structure, and the pumping flow rate of the solution is adjusted so that the pH during the mixing process is maintained at 10.5 ~ 11.0; after the pumping of the pretreatment liqui...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A method for removing magnesium in a hydrometallurgy process, wherein, comprising the following steps:
[0076] step one:
[0077] To the zinc sulfate solution (Zn 2+ : 100g / L, Mg 2+ : 60g / L), add formula 1-A, stir until dissolved; the addition of formula 1-A is 1.2 times the molar weight of zinc; pre-reaction 1h.
[0078] step two
[0079] Combined leaching agent solution (sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, wherein, the mol ratio of sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide is 1:1; the concentration of sodium carbonate is 1M) and the pre-reaction liquid of step 1 are pumped respectively with peristaltic pump into a liquid flow (the flow rate of the liquid flow is, for example, 5-10mL / min), mix the two liquid flows, and collect the mixed solution in a container with a stirring structure, adjust the pumping flow rate of the solution, and make the pH during the mixing process Maintain at 10-10.5; after the pumping of the pretreatment solution is compl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com