Accelerator for osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
A bone marrow mesenchymal and osteogenic differentiation technology, applied in the field of stem cells, can solve problems that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
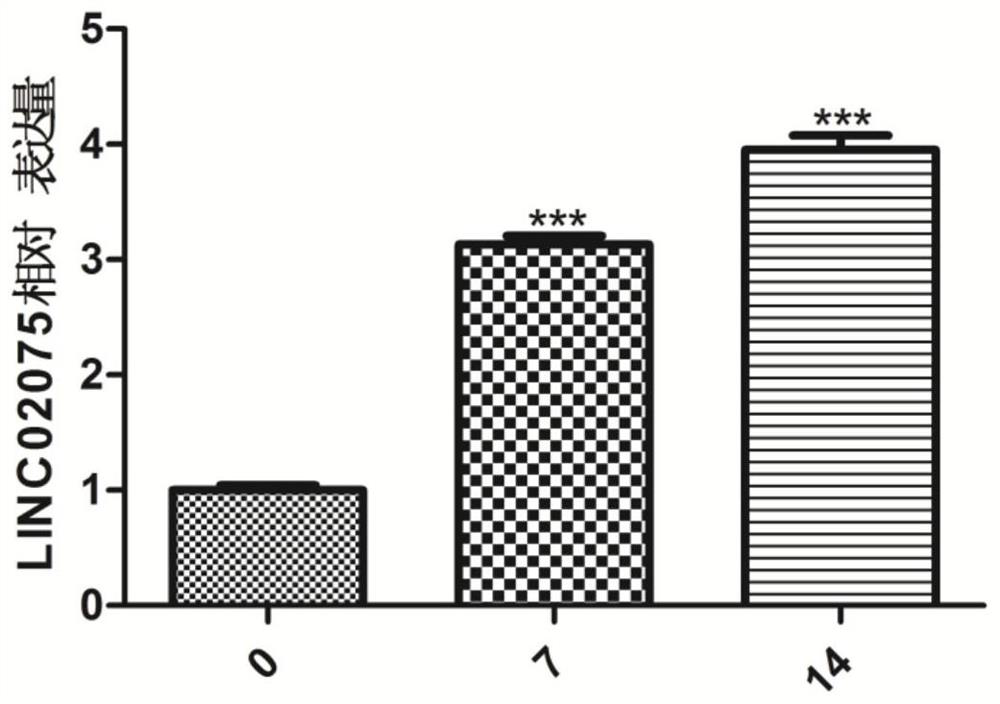
[0035] Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection of LINC02075 expression level during adipogenic induction
[0036] 1. Adipogenic Induction
[0037] (1) The third-generation human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (purchased from Sciencell) in the logarithmic growth phase were selected and inoculated into culture flasks, and cultured by adding complete medium;
[0038] (2) When the cell confluency reached 70%, the medium was replaced with adipogenic induction medium every 3 days, and RNA was extracted after 14 days of adipogenic induction.
[0039] 2. RNA extraction
[0040] RNA was extracted on day 0, day 7 and day 14 respectively, and three controls were set up in each group.
[0041] (1) Remove the medium, add 500 μL Trizol to each well, and repeatedly pipette the cells until a clear and non-viscous liquid is formed;
[0042] (2) Transfer the mixture to a 1.5ml EP tube, add 100μL chloroform, shake vigorously on the shaker for 15 seconds, and let stand at room temperature f...
Embodiment 2
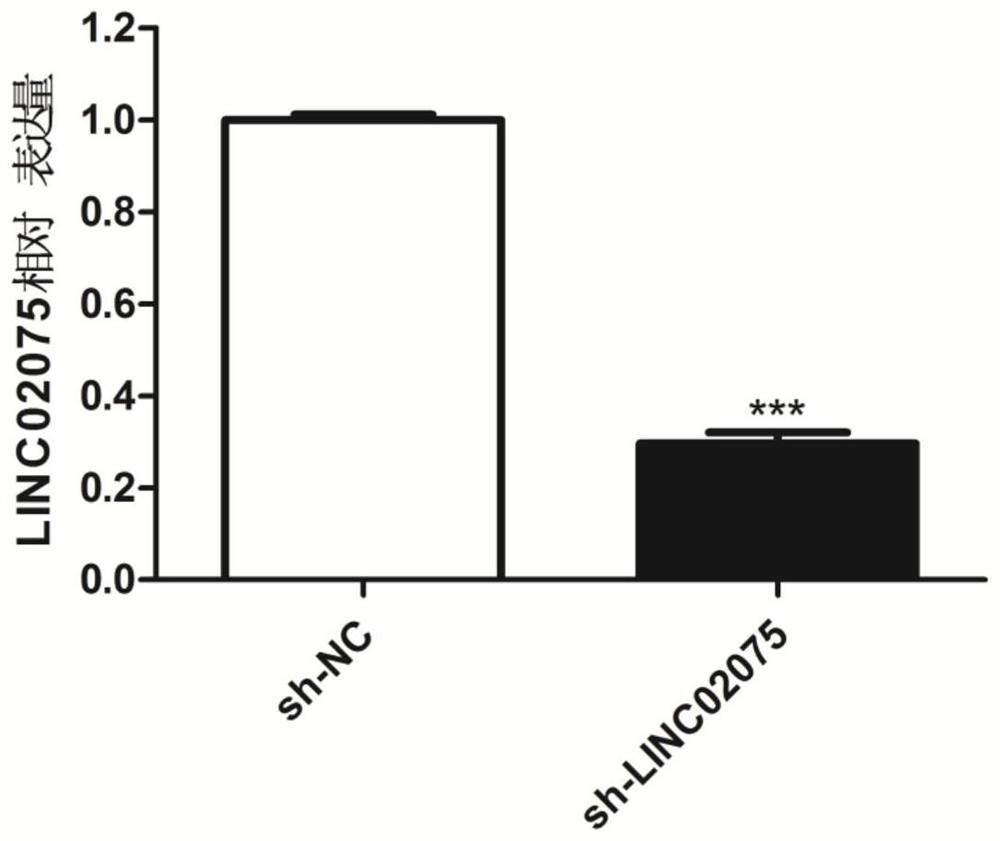
[0061] Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection of the inhibitory effect of sh-LINC02075
[0062](1) The sequence of sh-LINC02075 is as follows:
[0063] Sense strand: 5'-CACCGCTCCTGAAGAAACAGCTTAGCGAACTAAGCTGTTTCTTCAGGAGC-3' (SEQ ID NO.6)
[0064] Antisense strand: 5'-AAAAGCTCCTGAAGAAACAGCTTAGTTCGCTAAGCTGTTTCTTCAGGAGC-3' (SEQ ID NO.7)
[0065] (2) The lentiviral vector was constructed by Jikai Genomics Co., Ltd., and the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were transfected according to the transfection instructions. After 48 hours, the RNA was extracted for quantitative fluorescence detection. The steps were the same as in Example 1.
[0066] Experimental results
[0067] Experimental results such as figure 2 As can be seen from the figure, the inhibition rate of sh-LINC02075 was 70.4%.
Embodiment 3
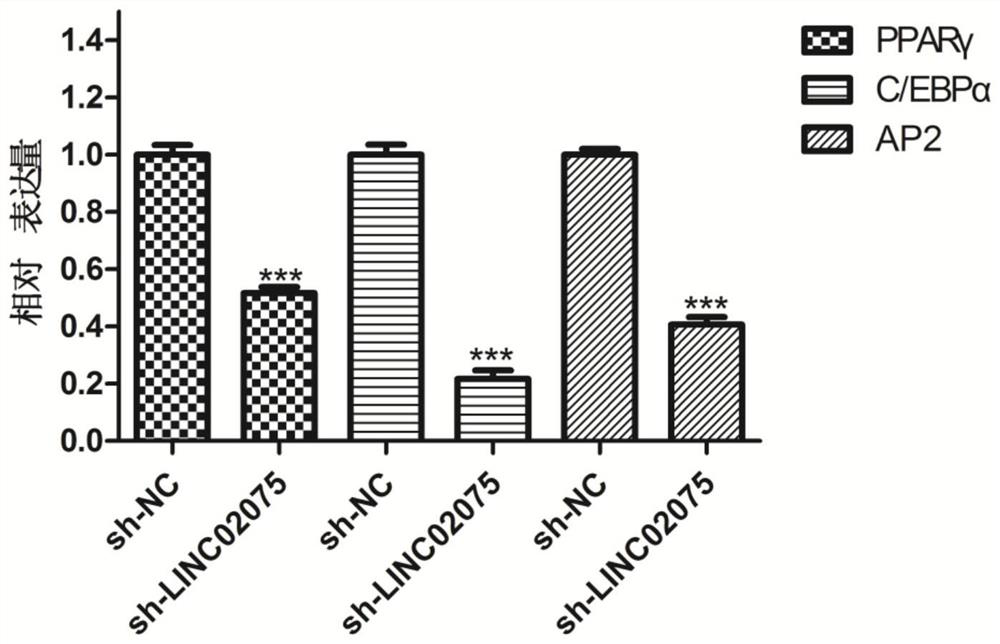
[0069] Effects of LINC02075 inhibition on adipogenic differentiation-related genes PPARγ, C / EBPα and AP2 mRNA levels in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[0070] 1. The primer sequences of PPARγ, C / EBPa and AP2 are as follows:
[0071] gene name Primer sequence PPARγ GCCCAGGTTTGCTGAATGTG (SEQ ID NO. 8) TTGGCAAACAGCTGTGAGGA (SEQ ID NO. 9) C / EBPa AGAACAGCAACGAGTACCGG (SEQ ID NO. 10) GCGGTCATTGTCACTGGTCA (SEQ ID NO. 11) AP2 TGGGCCAGGAATTTGACGAA (SEQ ID NO. 12) CCATCCCATTTCTGCACATGT (SEQ ID NO. 13)
[0072] 2. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected with sh-NC and sh-LINC02075 were inoculated on a culture plate for adipogenic induction. After 14 days of adipogenic induction, RNA was extracted, and fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to detect sh-NC group and sh- Expression differences of PPARγ, C / EBPa and AP2 among LINC02075 groups.
[0073] Experimental results
[0074] Experimental results such as image 3 A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com