Tissue adhesive matrices and uses thereof
A tissue, matrix technology, applied in the field of tissue adhesion matrix and its use, can solve problems such as lack of adhesion strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0329] Preparation of Exemplary Compositions and Controls
[0330] Polymer blend fibers (exemplary compositions of the invention and controls) were prepared as follows:
[0331] The electrospinning process was performed at a temperature of 23±5°C and a relative humidity of 35±10% using a syringe pump, a 22-gauge needle (inner diameter ~0.51 mm) and a high voltage (maximum 30 kV) DC power supply. The solution flow rate was 2.6 ml / hr with a voltage supply of 6±2 kV and a tip-to-collector distance of 5-8 cm. The patches were collected on a rotating aluminum vertical wheel with a diameter of 51 mm and a width of 45 mm at 310 rpm. The patch was prepared with a thickness of 200 ± 30 μm and dried in vacuum at room temperature for 24 hours to remove residual solvent.
[0332] Preparation of PLCL fibers containing activated PEG polymer
[0333] Control 1.1: Electrospinning of blended PLCL to methoxy-PEG-NHS (Mw=20K) at a ratio of 1:0.333 (w / w) [6.67E-06, 1.65E-05 mol, respectively]....
Embodiment 2
[0366] Peel Test Procedure
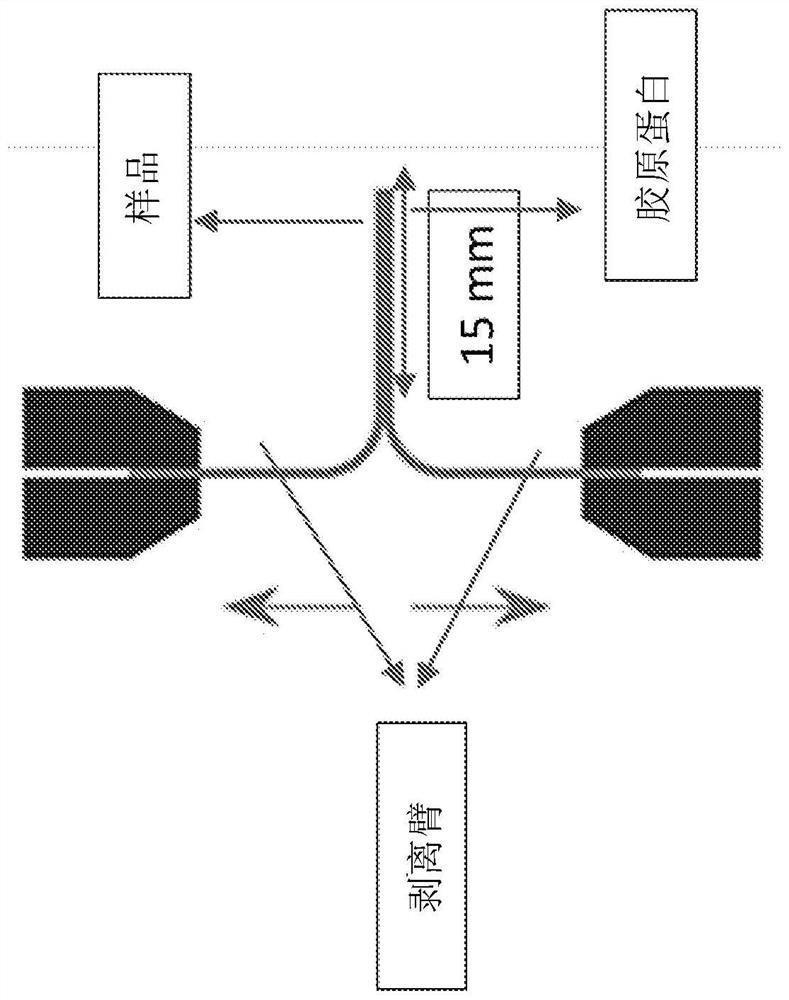
[0367] Samples of each matrix layer of electrospun fibers were cut into 15 mm x 30 mm strips; half of the strips were wetted with saline, while the other half were left dry. Such as figure 1 As shown, each strip was placed in parallel on top of a wet 15 mm x 30 mm collagen strip to yield a minimum binding area of 15 x 15 mm. The wet half of each sample was pressed onto the collagen strip for 2 minutes, and then the other half was left unbound to the collagen to form the peel arm. For better handling, all samples were dried at room temperature. The force required to break the bond between the collagen and the sample was measured using a universal testing machine LLOYD LS1. Pull the peel arm apart at a speed of 10 mm / min and measure the force required to break the bond. Adhesive strength is defined by the average of the peel force and maximum force recorded during the test.
[0368] Shear Test Procedure
[0369] Such as figure 2 Wet collage...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com