Six-degree-of-freedom conductor galloping monitoring method, system and device
A technology of wire dancing and degree of freedom, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of large amount of calculation, low precision, and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference in image processing, and achieve the effect of improving monitoring accuracy and broadening the use scene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
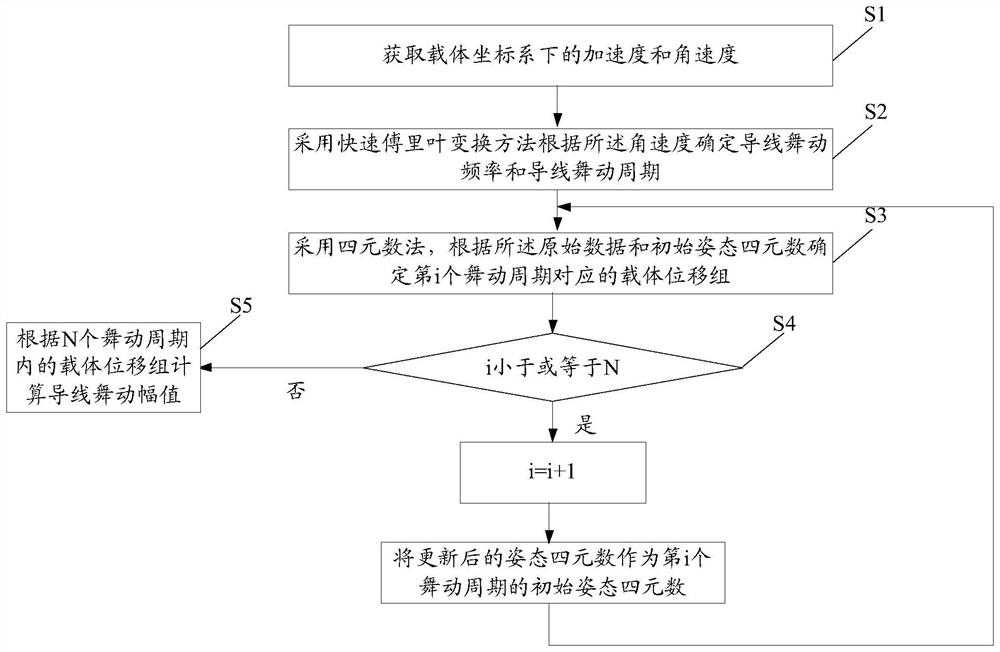
[0067] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom wire galloping monitoring method, the method comprising:
[0068] Step S1: using an inertial sensor to obtain raw data; the raw data is the acceleration and angular velocity in the carrier coordinate system;
[0069] Step S2: using the fast Fourier transform method to determine the wire galloping frequency and the wire galloping period according to the angular velocity;
[0070] Step S3: Using the quaternion method, determine the carrier displacement group corresponding to the i-th dancing cycle according to the original data and the initial attitude quaternion; the carrier displacement group includes n carrier displacements at different times;
[0071] Step S4: Determine whether i is less than or equal to N; if i is less than or equal to N, set i=i+1, use the updated attitude quaternion as the initial attitude quaternion of the i-th dance cycle, and return " Step S3"; if i is greater t...
Embodiment 2
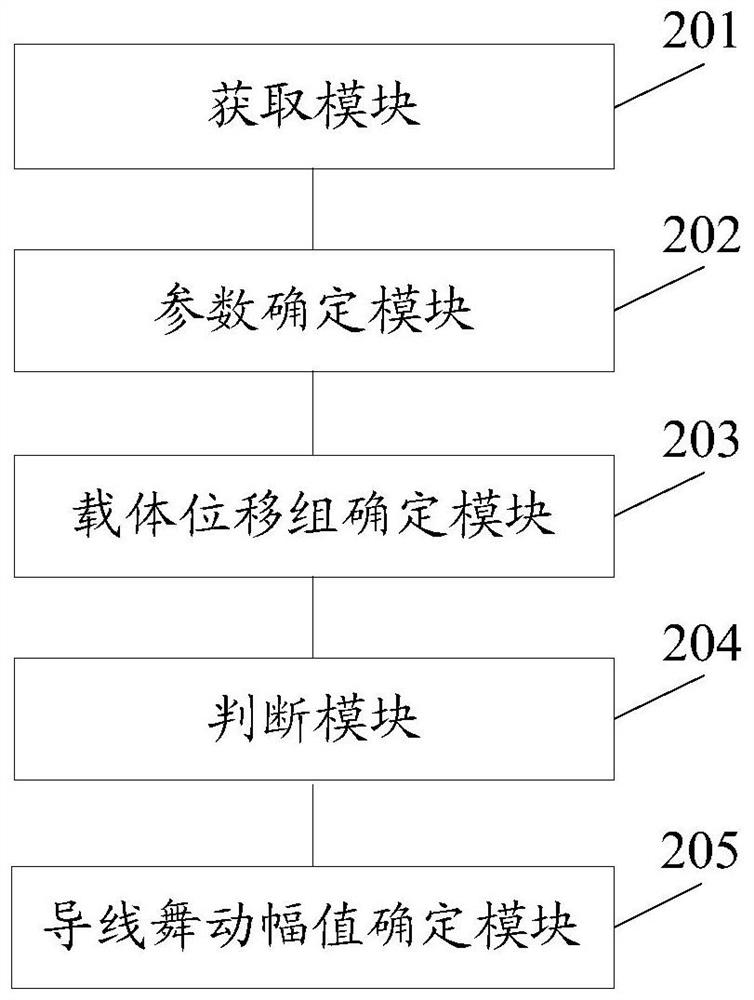
[0117] Such as figure 2 As shown, the present invention also provides a six-degree-of-freedom wire galloping monitoring system, the system comprising:
[0118] The acquiring module 201 is configured to acquire raw data; the raw data is acceleration and angular velocity in the carrier coordinate system.
[0119] The parameter determination module 202 is configured to determine the wire galloping frequency and the wire galloping period according to the angular velocity by using a fast Fourier transform method.
[0120] The carrier displacement group determination module 203 is used to determine the carrier displacement group corresponding to the i-th dancing cycle according to the original data and the initial posture quaternion by using the quaternion method; the carrier displacement group includes n carrier displacements at different times.
[0121] Judgment module 204, is used for judging whether i is less than or equal to N; If i is less than or equal to N, then make i=i+1...
Embodiment 3
[0133] The invention discloses a wire galloping monitoring device with six degrees of freedom. The device includes a microprocessor MCU (Microcontroller Unit), an inertial sensor (IMU) and a housing 2. The microprocessor is connected to the inertial sensor, and the inertial sensor collects The acceleration and angular velocity in the carrier coordinate system are sent to the microprocessor, so that the microprocessor uses the method in Embodiment 1 to calculate the wire galloping frequency and wire galloping amplitude.
[0134] Such as image 3 As shown, Y0 is the cross section of the wire 1, the inertial sensor (not shown in the figure) and the microprocessor 3 are installed inside the housing 2, and the housing 2 is rigidly connected to the wire 1.
[0135] The MCU processes the acceleration and angular velocity collected by the inertial sensor. Because the IMU can only measure the acceleration and angular velocity of the carrier coordinate system, and the final focus is on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com