Combined microbial agent for fermenting food and application of combined microbial agent
A technology of combining bacterial agents and continuing fermentation, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems that microorganisms cannot adapt to high-salt environments, are easily infected with harmful substances, and are unstable, and achieve the effect of improving actual production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
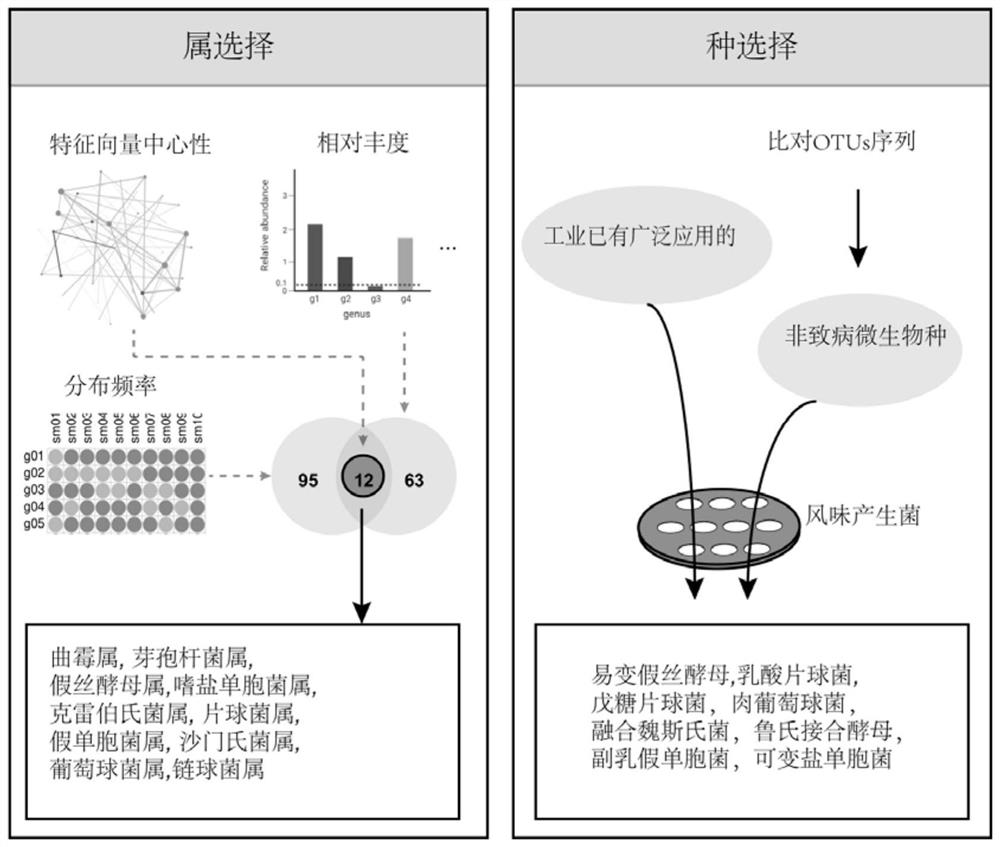
[0025] The microbial screening of embodiment 1 combination microbial agent
[0026] First, the flavor components of the natural fermentation samples were used as evaluation criteria. Select target strains from complex communities using different screening conditions. Then, single-cell fermentations were performed in fully synthetic media to characterize the different strains. And carry out double-strain fermentation according to the function of bacterial strain. Based on the functional performance of single-strain and double-strain fermentations and microbial interactions, microbial communities with three or more microorganisms were established. Solid-state fermentation was carried out to evaluate the actual fermentation effect of the synthetic flora, and finally a combined bacterial agent inoculated with Pediococcus lactis, Staphylococcus carnosus, and Candida vulgaris in equal proportions was constructed. Specific steps include:
[0027] (1) Selection of target microorga...
Embodiment 2
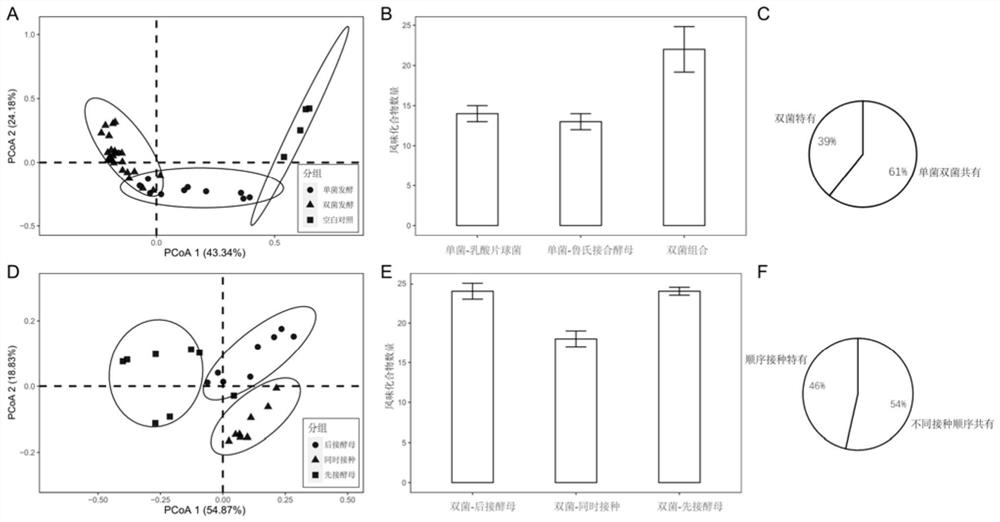
[0052] Embodiment 2 uses three bacterium microorganism combination solid-state fermentation
[0053] In order to construct a synthetic microbiome capable of producing more flavor compounds and closer to the flavor composition of the in situ system, Lactococcus lactis-Staphylococcus carnosus-variable Candida is a three-bacteria combination inoculated in a specific order, and Pediococcus lactis, Staphylococcus carnosus, and Candida vulgaris are cultured to OD 600 =0.7, cultured to OD at a ratio of 2% 600 =0.7 Pediococcus lactis bacteria solution was inoculated into the synthetic medium, cultured for 48 hours and then inoculated and cultivated to OD in a proportion of 2% 600 =0.7 Staphylococcus carnus liquid, cultured for 48 hours and inoculated with 2% to OD 600 =0.7 of the Candida variabilis liquid, co-fermented for 6 days, the test results of volatile substances showed that, with the expansion of the scale of the synthetic microbiome, the number of flavors produced by the mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com