Brevibacillus laterosporus and application thereof
A technology of Brevibacillus and Laterosporus, applied in Brevibacillus Laterosporus and its application field, to achieve the effects of broad antibacterial spectrum, good safety performance and improved feeding safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1 , strain screening
[0061] 1. Materials and methods
[0062] 1.1 Samples: Tissue materials such as roots, stems, and leaves of the medicinal plant honeysuckle.
[0063] 1.2 Pathogenic bacteria
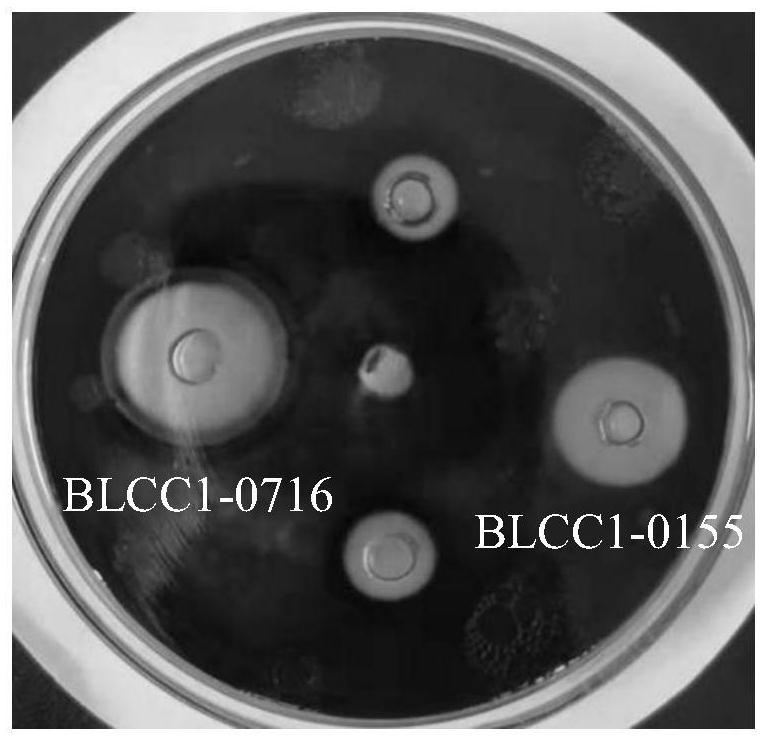
[0064] The strains tested are listed in Table 1.
[0065] Table 1 Pathogen number and source
[0066]
[0067] 1.3 Isolation medium
[0068] Improved MRS medium: peptone 1%, beef extract 1%, yeast extract 0.5%, glucose 2%, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.2%, sodium acetate 0.5%, ammonium citrate 0.2%, magnesium sulfate 0.02%, manganese sulfate 0.05 %, Tween-80 0.1%, pH 6.5; used to isolate lactic acid bacteria.
[0069] LB medium: 0.5% glucose, 1.0% peptone, 0.5% beef extract, 0.5% sodium chloride, adjust pH to 6.5; used to isolate bacteria such as Bacillus.
[0070] PDA medium: 20% potato (boiled juice), 20g glucose, 15g agar, natural pH; used to isolate fungi.
[0071] 1.4 Fermentation medium
[0072] Lactic acid bacteria fermentation medium is MRS liq...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2 , strain identification and safety test
[0098] 1. Materials and methods
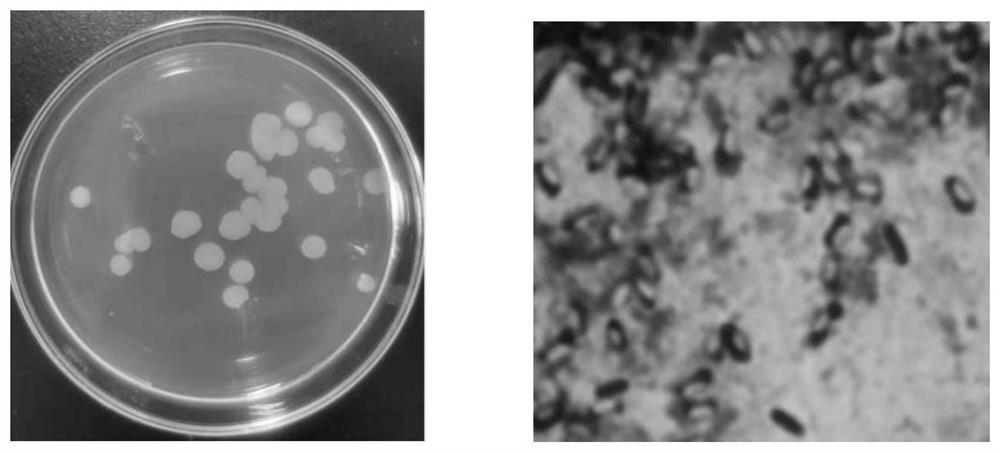
[0099] 1.1 Bacterial species: the bacterial strain BLCC1-0716 screened in Example 1 of the present invention.
[0100] Experimental animals: 40 healthy female Kunming mice (body weight 20±2g) were purchased from Jinan Pengyue Experimental Animal Breeding Co., Ltd.
[0101] 1.2 Routine biochemical identification of bacteria: Unless otherwise specified, the general morphology, physiological and biochemical tests were carried out according to "Bergey's Bacterial Identification Manual" (9th edition) and "Microbiology Experiment Manual".
[0102] 1.3 16S rDNA identification of strains
[0103] 1.3.1 Amplification and sequence analysis of 16S rDNA
[0104]The target strain was inoculated in fresh fermentation medium and cultured for 20 hours. The DNA of the bacteria was extracted with a kit from Tiangen Company, and its 16SrDNA sequence was amplified. The primers used are bacterial 16S...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3 , Determination of strain tolerance
[0128] 1. Materials and methods
[0129] 1.1 Strains: Brevibacillus dissporogenes BLCC1-0716 screened out in Example 1 of the present invention;
[0130] 1.2 culture medium is the same as the LB medium of embodiment 1
[0131] 1.3 Method
[0132] 1.3.1 Determination of bile salt tolerance
[0133] Take 1 mL of Brevibacillus lateralosporus BLCC1-0716 seed solution (about 80% spore rate) cultured on a shaker at 37°C for 24 hours to 50 mL of liquid LB medium, and add different volumes of bile salt mother solution to make the final bile salt concentration 0.1% respectively , 0.3% and 0.5%, cultured at 37°C for 4h, and samples were taken at 0h and 4h for counting viable bacteria.
[0134] 1.3.2 Determination of acid resistance
[0135] Take 0.3 mL of Brevibacillus lateralosporus BLCC1-0716 seed solution (spore rate about 80%) cultured on a shaker at 37 °C to 15 mL of liquid LB medium with different pH values (2.5, 3.5,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com