Breeding method of harmonia axyridis
A technology of ten-spotted ladybug and ten-spotted ladybug, which is applied in animal husbandry and other fields, can solve problems such as the lack of breeding methods of ten-spotted ladybug, and achieve rapid response to natural disasters of aphids, simple breeding methods, and mild breeding conditions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
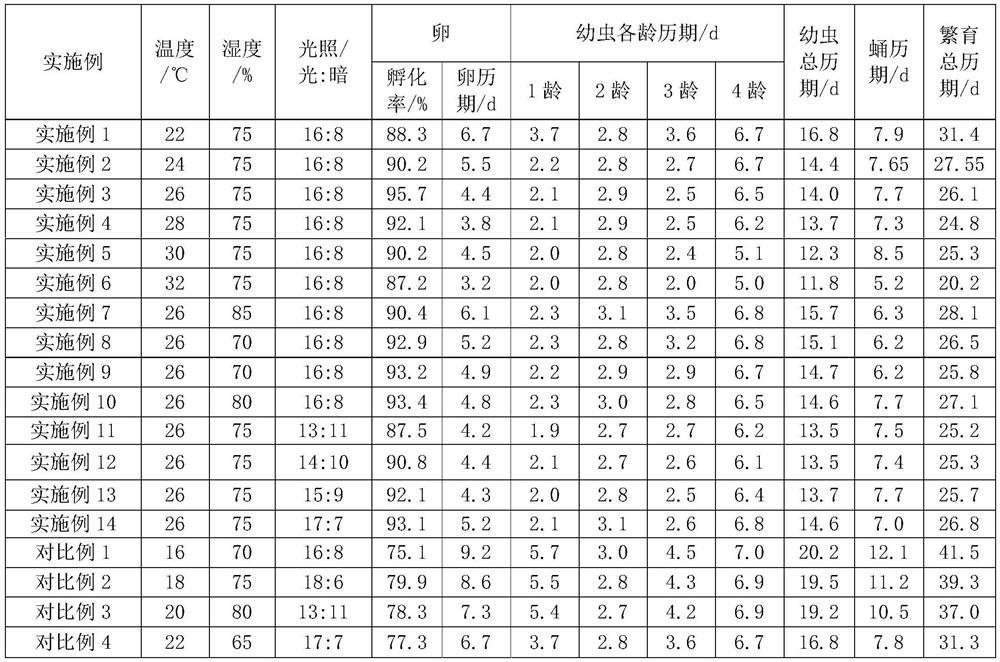
[0033] Examples 1-14, comparative examples 1-4 are shown in Table 1 as shown in Table 1. Take embodiment 1 as example, illustrate the breeding method of ten-spotted ladybug:
[0034] Example 1:
[0035] A kind of raising method of ten-spotted ladybug, comprises the steps:
[0036] S1: Prepare broad bean seedlings: soak broad beans for 12 hours and sow them on trays containing substrates at intervals of 3*5cm, cover substrates after sowing, and water evenly until the substrates are held together by hand; control the temperature at 25°C and cultivate Wait until the seedlings are 5-7cm long;
[0037]S2: Propagation of bean aphid: Inoculate broad bean seedlings with 100 heads / plant of bean aphid, and then place the inoculated broad bean seedlings in a net room for rearing at a temperature of 28°C (the optional range is 25°C to 28° C.), humidity 80% (the optional range is humidity 80% to 85%), and light L:D=14:10; 5 to 7 days after inoculation, the bean aphid is covered with soy...
experiment example 1
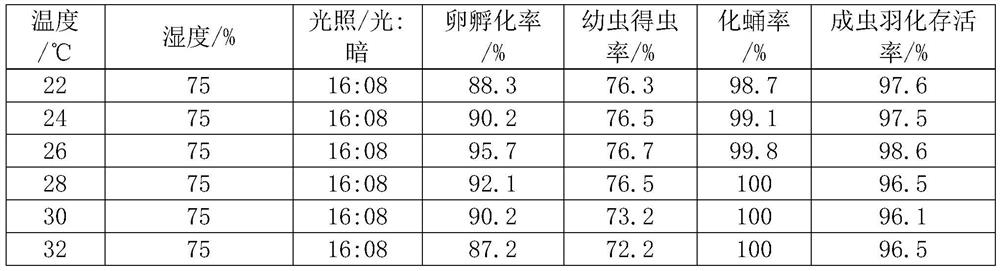
[0046] Experimental Example 1: The survival rate of the ten-spotted ladybug at different temperatures
[0047] Hatch and breed the eggs of the ten-spotted ladybug under different temperature conditions, measure the hatching rate of the ten-spotted ladybug eggs, and the yield of each stage of the ten-spotted ladybug, and treat 100 eggs for each temperature condition, and the results As shown in table 2.
[0048] Table 2 The survival rate of the ten-spotted ladybug at different temperatures
[0049]
[0050] Note: The larvae yield rate is that of the 4th instar larvae.
[0051] Experimental data show that the interspecific suicide phenomenon in the larval stage is relatively serious, mainly manifested in the phenomenon of intraspecific killing and feeding in a small number of larvae just before the eggs hatch and before the larvae disperse and climb, and then the third and fourth instar stages Because of reasonable cage separation and supplementary aphids, the phenomenon of...
experiment example 2
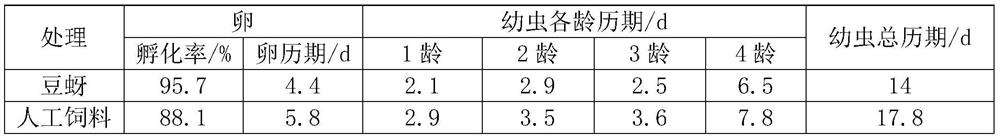
[0052] Experimental Example 2: Multiplication of different aphid species
[0053] Select different aphid species to inoculate on different plants. The inoculation amount of aphids is 100 heads / plant. %~85%), under the condition of light being L:D=14:10, the aphids are propagated, the plant emergence time, the plant inoculation time and the number of aphids after 7 days are measured, each experiment is repeated 10 times, and the average values, and the results are shown in Table 3.
[0054] Table 3 Population expansion of different aphid species
[0055] Inoculate aphids Inoculate plants Emergence time / d Inoculation time / d Number of aphids / head after inoculation 7 days cabbage aphid Piaoerbai 5 26 316 Aphids tobacco 4 34 524 bean aphid Pea sprouts 3.5 7 1160
[0056] The experimental results show that in the process of aphid multiplication, the aphid population can be multiplied under any combination of humidity ranging from ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com